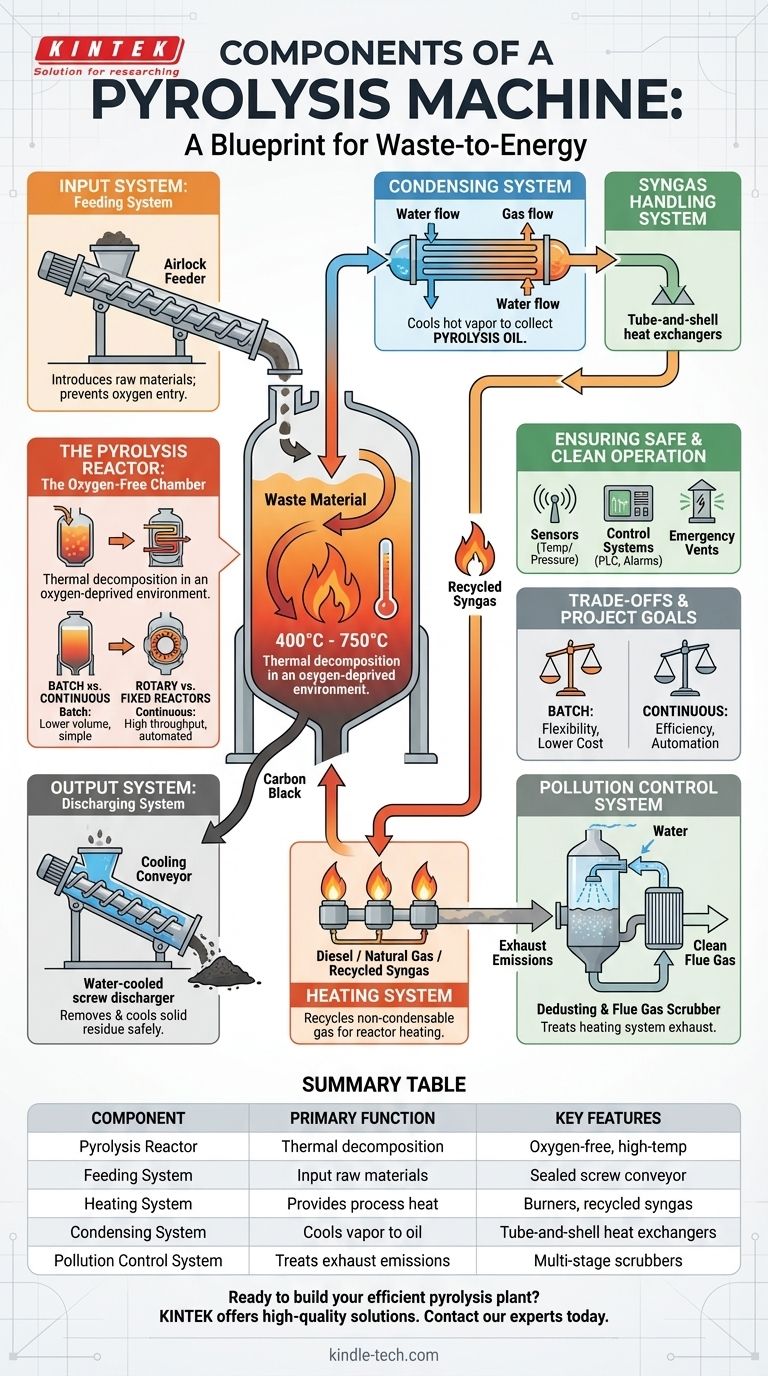
At its core, a pyrolysis machine is an integrated system of five essential components. These are the pyrolysis reactor, the feeding system, the heating system, the condensing system for oil collection, and the pollution control system for safe operation. Together, these parts create a high-temperature, oxygen-free environment to thermally decompose waste materials into valuable outputs like pyrolysis oil, carbon black, and syngas.
A pyrolysis machine is not a single piece of equipment but a complete plant. Understanding it means seeing how each distinct system—from material input to emission control—must work in concert to ensure efficiency, safety, and product quality.

The Core of the Process: The Pyrolysis Reactor
The reactor is the heart of the entire pyrolysis plant. It is the sealed, oxygen-deprived chamber where the raw material is heated and undergoes thermal decomposition.
Function: The Oxygen-Free Chamber
The primary role of the reactor is to heat the feedstock to temperatures typically between 400°C and 750°C without the presence of oxygen. This specific condition prevents combustion (burning) and instead causes the long polymer chains in materials like plastic or rubber to break down into smaller, valuable molecules.
Common Reactor Designs
Reactors primarily come in two operational types: batch and fully continuous. Batch reactors are loaded, run through a cycle, and then unloaded, while continuous systems are fed constantly at one end and discharge products at the other.
Common designs include rotary kilns, which tumble the material for even heat distribution, and fixed reactors, which are simpler but may require agitators to prevent cold spots.
Material and Construction
The reactor must be constructed from boiler-grade steel (like Q245R or Q345R) or stainless steel. This is critical to withstand the extremely high temperatures and corrosive substances produced during the process, ensuring both a long operational life and operator safety.
Managing Material Flow: Input and Output Systems
Efficiently moving material into the reactor and getting the products out is crucial for both performance and safety.
The Feeding System
This system introduces raw materials into the sealed reactor. Simpler batch systems may use manual loading or a basic hydraulic feeder.
Automated continuous systems often use a sealed screw conveyor. An essential feature of any feeding system is an airlock to prevent oxygen from entering the reactor, which would cause the material to burn instead of pyrolyze.
The Discharging System
Once the process is complete, the solid residue (carbon black) must be removed. This system is often a water-cooled screw discharger that cools the carbon black to a safe temperature before it exits the sealed environment. This prevents dust explosions and protects operators.
The Oil Condensing System
The hot vapor (pyrolysis gas) produced in the reactor is channeled to the condensing system. Here, a series of coolers—often tube-and-shell heat exchangers—use water to lower the gas temperature.
This temperature drop causes the heavier hydrocarbon molecules to condense into a liquid, which is the pyrolysis oil.
The Syngas Handling System
Not all of the vapor condenses into oil. The remaining light, non-condensable gas is known as syngas. This gas is rich in fuel value and is typically recycled back to the heating system to power the reactor, significantly reducing external fuel consumption.
Ensuring Safe and Clean Operation
These systems provide the energy for the process and manage all emissions, making them critical for safety and environmental compliance.
The Heating System
This system provides the thermal energy required to heat the reactor to pyrolysis temperatures. The burners can be fueled by diesel, natural gas, or, most efficiently, the recycled syngas produced by the process itself.
The Dedusting / Flue Gas Scrubber System
This is a critical pollution control device. It treats the exhaust smoke generated by the heating system's burner, not the pyrolysis gas itself. Multi-stage systems use water sprays, ceramic ring absorption, and other methods to remove particulate matter and acidic gases like sulfur dioxide before they are released into the atmosphere.
Safety and Control Systems
Modern pyrolysis plants are equipped with a suite of sensors to monitor temperature and pressure inside the reactor. These are linked to a central control cabinet with alarms, emergency vents, and auto-shutdown systems to prevent over-pressurization or overheating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right components involves balancing cost, efficiency, and operational complexity.
Batch vs. Continuous Systems
A batch system has a lower initial capital cost and can be simpler to operate, making it suitable for smaller-scale operations. However, it requires more manual labor for loading and unloading.
A fully continuous system represents a much higher upfront investment but offers superior efficiency, automation, and throughput for large-scale industrial applications.
Reactor Design and Heat Transfer
A rotary reactor design provides excellent, uniform heating by constantly tumbling the material. This leads to a more complete reaction but involves more complex mechanical parts (seals, motors) that require maintenance.
A fixed reactor is mechanically simpler and cheaper but can suffer from uneven heating, potentially leaving some material unreacted unless properly designed.
The Importance of Feedstock Preparation
The efficiency of the entire plant is heavily dependent on the quality of the raw material. While not a machine component, a shredding and drying system is often a necessary prerequisite. Dry, uniformly sized material ensures stable feeding and much more efficient heat transfer within the reactor.
Matching Components to Your Project Goals
The ideal configuration of a pyrolysis machine depends entirely on your operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput and automation: A fully continuous plant with a rotary reactor and automated screw-based feeding and discharging systems is the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse materials on a smaller scale: A batch-type reactor offers greater flexibility for handling non-uniform feedstock and requires a lower initial investment.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and operational safety: Prioritize a robust, multi-stage flue gas scrubbing system and a comprehensive PLC-based control system with redundant safety sensors.
Understanding how these core components interlink transforms a simple parts list into a blueprint for a successful and sustainable waste-to-energy operation.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Reactor | Thermal decomposition chamber | Oxygen-free, high-temp (400-750°C), steel construction |
| Feeding System | Input raw materials | Sealed screw conveyor, airlock to prevent oxygen entry |
| Heating System | Provides process heat | Burners using diesel, gas, or recycled syngas |
| Condensing System | Cools vapor into pyrolysis oil | Series of heat exchangers (tube-and-shell) |
| Pollution Control System | Treats exhaust emissions | Multi-stage scrubbers for dust and gas removal |
Ready to build your efficient and safe pyrolysis plant?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and pyrolysis systems for converting waste into valuable resources. Whether you need a flexible batch reactor or a high-throughput continuous system, our expertise ensures optimal performance, safety, and environmental compliance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can provide the right pyrolysis solution for your laboratory or industrial needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















