At its core, a filter press has two fundamental configurations: recessed chamber and membrane. These configurations are defined by the type of filter plate used within the press, which directly dictates how the system dewaters a slurry and the final dryness of the resulting filter cake.
While a filter press is a complete system built from a frame, manifold, and filter cloths, the choice between a recessed chamber and a membrane configuration is the most critical decision, as it defines the machine's operational capabilities and dewatering efficiency.
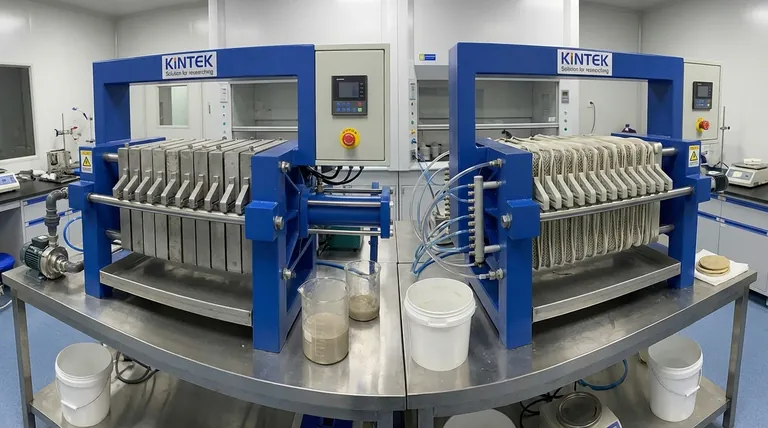

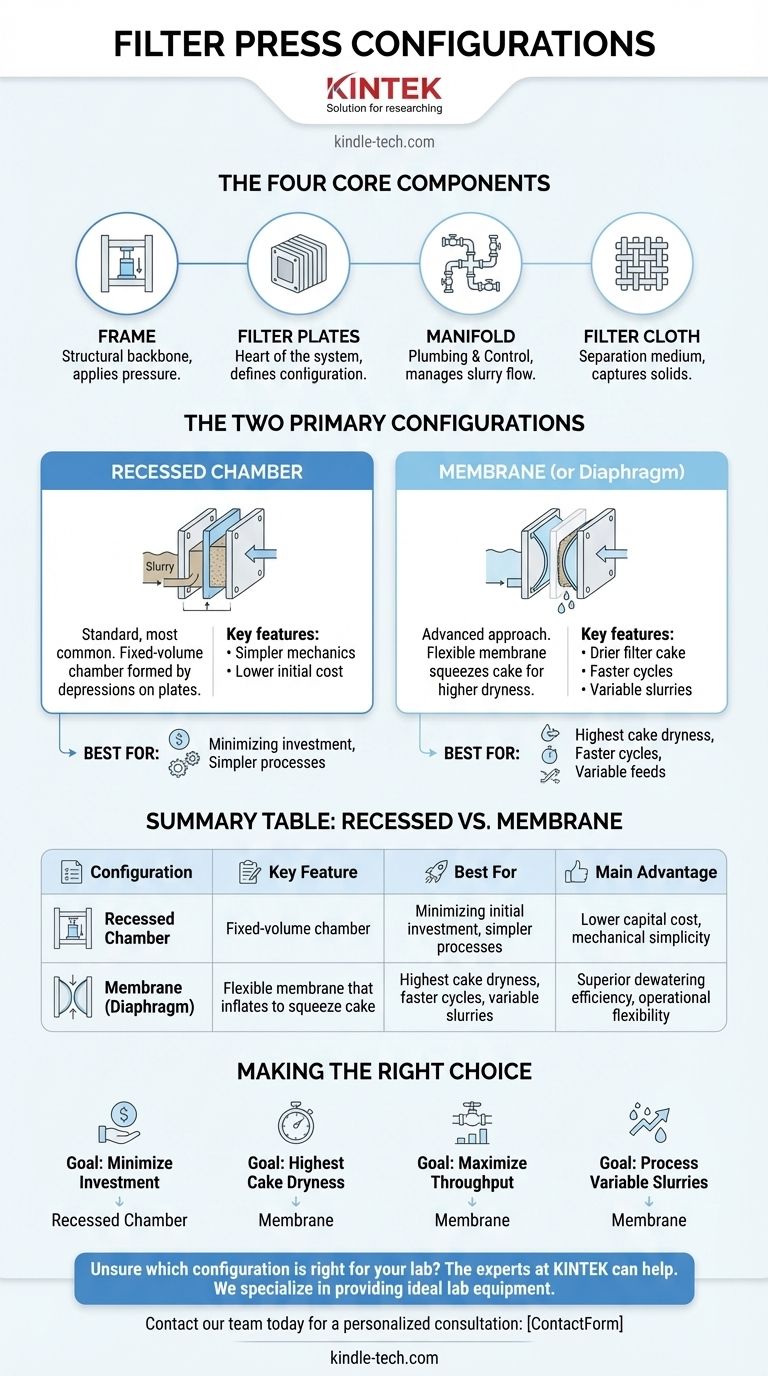
Deconstructing the Filter Press: The Four Core Components
To understand the configurations, you must first understand the machine. Every filter press, regardless of configuration, is built from four essential components working in unison.
The Frame: The Structural Backbone
The frame is the main structure that holds all other components together under immense pressure. It typically consists of a head stand, a tail stand, and sidebars or overhead beams that connect them.
This framework houses the hydraulic system responsible for clamping the filter plates together, creating a tight seal for the filtration process.
Filter Plates: The Heart of the System
This is the most critical component and defines the press's configuration. A series of plates are lined up inside the frame, each covered with a filter cloth.
When clamped together, the void between two plates forms a chamber where the slurry is pumped. The liquid passes through the cloth, and the solids are captured, forming a filter cake.
Manifold: The Plumbing and Control
The manifold consists of the integrated piping and valves that control the flow of slurry into the press and the filtrate (the separated liquid) out of the press.
This system ensures that each chamber between the plates is filled uniformly and efficiently to optimize the filtration cycle.
Filter Cloth: The Critical Separation Medium
The filter cloth is a specialized woven fabric tailored to cover the filter plates. Its specific weave and material are selected based on the slurry's chemical properties and particle size.
This cloth is the true medium of separation; it must allow liquid to pass through freely while reliably capturing the solid particles.
The Two Primary Configurations Explained
The choice between a recessed chamber and a membrane plate dictates how the filter press operates and the results it can achieve.
Configuration 1: Recessed Chamber
This is the standard, most common configuration. Recessed chamber plates have a depression on each side, and when two plates are pushed together, they form a single, fixed-volume chamber.
Slurry is pumped into these chambers until the solids fill the entire void. The process stops once the chamber is full and the pump pressure reaches a set limit.
Configuration 2: Membrane (or Diaphragm)
Membrane plates offer a more advanced approach. One or both sides of the plate have a flexible, impermeable face (the membrane) over a drainage surface.
After the initial filtration cycle fills the chamber with solids, a fluid (typically water or air) is pumped behind the flexible membrane. This inflates the membrane, squeezing the filter cake and forcing out additional liquid.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a configuration is a matter of balancing initial cost against operational performance and desired results.
Simplicity and Lower Capital Cost
The recessed chamber configuration is mechanically simpler, with no moving parts within the plates themselves. This results in a lower initial purchase price and potentially less complex maintenance.
Higher Performance and Efficiency
The membrane configuration delivers a significantly drier filter cake due to the final "squeeze" phase. This can reduce disposal costs (less water weight) and can shorten overall cycle times.
Operational Flexibility
Membrane presses are more forgiving if the slurry feed characteristics change or if chambers are not completely full. The squeeze function can still effectively dewater a partially formed cake, whereas a recessed chamber press relies on a full chamber for optimal performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific operational goal is the most important factor in selecting the right filter press configuration.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment: The robust and straightforward recessed chamber configuration is the most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible cake dryness: The membrane configuration's ability to mechanically squeeze the cake is essential and will deliver the best results.
- If your primary focus is reducing cycle time and maximizing throughput: A membrane press can often shorten cycle times by expelling liquid faster than relying on high pump pressure alone.
- If you process variable slurries or have inconsistent feed: The membrane configuration offers greater operational flexibility and more consistent performance under changing conditions.
Ultimately, understanding these core components and configurations empowers you to select the precise filter press system that aligns with your specific dewatering goals.
Summary Table:
| Configuration | Key Feature | Best For | Main Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recessed Chamber | Fixed-volume chamber formed by depressed plates | Minimizing initial investment, simpler processes | Lower capital cost, mechanical simplicity |
| Membrane (Diaphragm) | Flexible membrane that inflates to squeeze cake | Highest cake dryness, faster cycles, variable slurries | Superior dewatering efficiency, operational flexibility |
Unsure which filter press configuration is right for your lab's dewatering process? The experts at KINTEK can help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment, including filter presses, to meet your specific requirements for efficiency, cost, and performance. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right configuration can optimize your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















