At its core, powder metallurgy (PM) is a manufacturing process that creates solid metal objects from powder instead of molten metal. The primary considerations revolve around the characteristics of the initial powder, the methods used to compact and fuse it, and the inherent properties of the final part, such as its density and strength. Success depends on carefully controlling each stage to produce precise, highly accurate components.
Powder metallurgy offers a powerful way to create complex, net-shape parts with minimal material waste. However, its effectiveness hinges on managing the critical relationship between the initial powder properties and the final part's porosity, which directly impacts its mechanical strength.
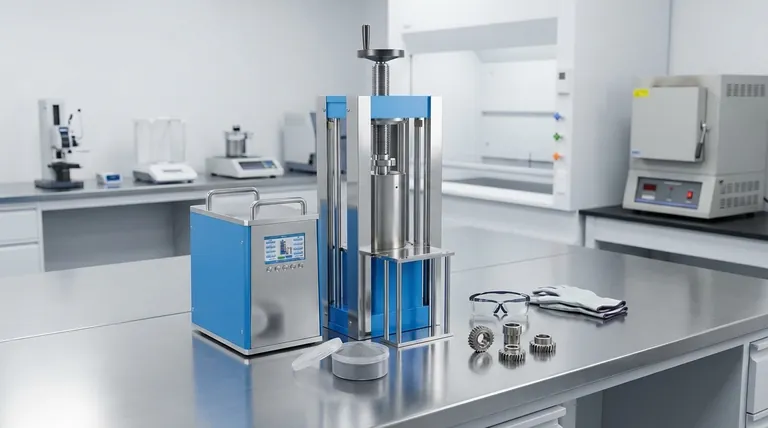

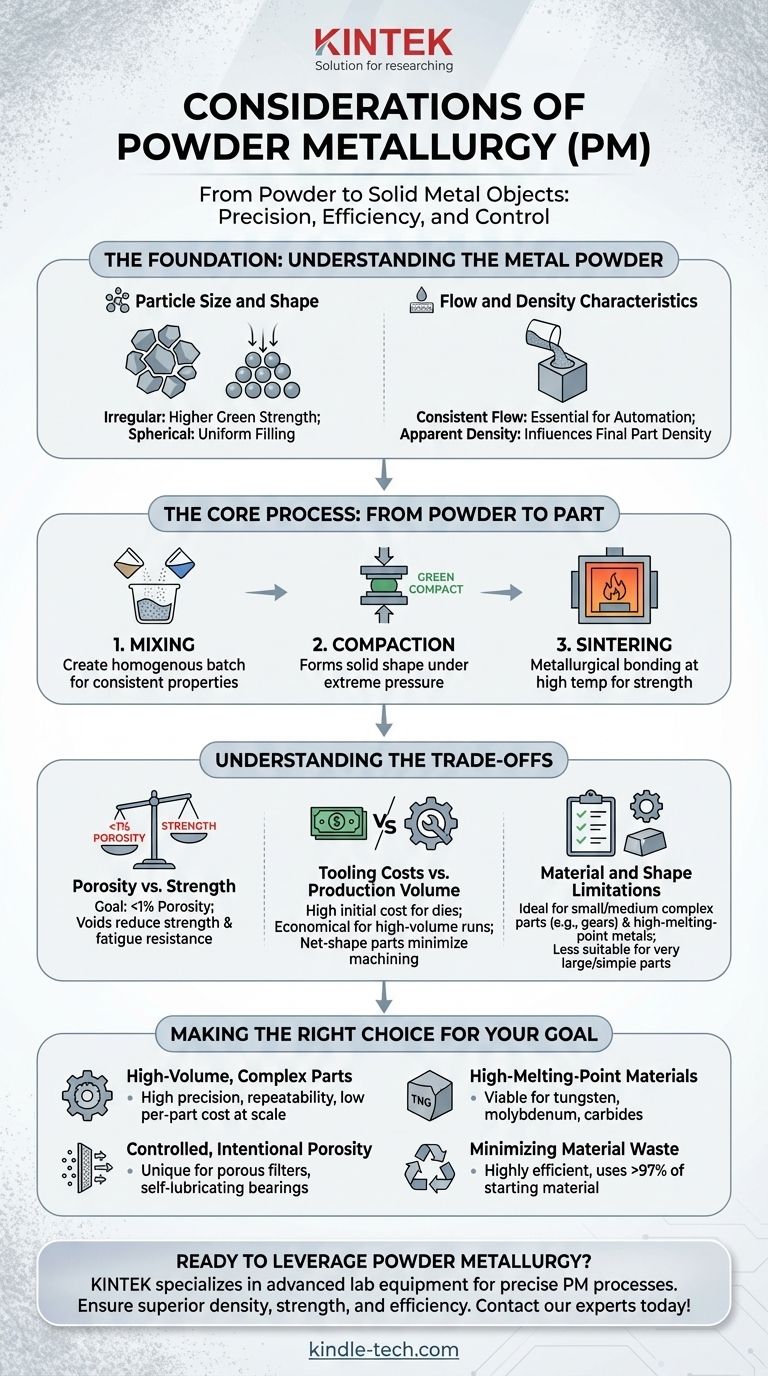
The Foundation: Understanding the Metal Powder
The starting material is the single most important factor in the powder metallurgy process. Its physical properties dictate how it will behave during manufacturing and determine the final characteristics of the component.
Particle Size and Shape
The size and shape of the individual metal powder particles are critical. Irregular or angular particles tend to interlock better during compaction, leading to higher strength in the pre-sintered state. Spherical powders, on the other hand, flow more easily, which can be crucial for filling complex die cavities uniformly.
Flow and Density Characteristics
A powder's ability to flow consistently is essential for high-volume automated production. Poor flow can lead to uneven filling of the die, resulting in density variations and defects in the final part. The apparent density of the powder (how it packs under gravity) influences the final part's density and the required compaction pressure.
The Core Process: From Powder to Part
Powder metallurgy is a multi-step process. Each stage must be precisely controlled to achieve the desired outcome. The conventional method involves three key steps: mixing, compacting, and sintering.
Step 1: Mixing
Different metal powders can be blended to create alloys, or lubricants can be added to improve the compaction process. The goal of mixing is to create a perfectly homogenous batch to ensure every part produced has consistent chemical and mechanical properties.
Step 2: Compaction
The powder mixture is fed into a rigid die and subjected to extreme pressure. This compaction process forms the powder into a solid shape known as a "green compact." This part is strong enough to be handled but has not yet developed its final metallurgical bonds or strength.
Step 3: Sintering
Sintering is the critical heat treatment that transforms the green compact into a durable metal part. The part is heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below the primary material's melting point. At this temperature, the particles metallurgically bond and weld together, significantly increasing the part's strength and integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, powder metallurgy is not a universal solution. Understanding its inherent limitations and trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Porosity vs. Strength
The ultimate goal of most PM processes is to create a fully dense part with less than 1% porosity. Any remaining voids can act as stress concentration points, reducing the overall strength and fatigue resistance of the component. Achieving high density often requires more advanced and costly techniques.
Tooling Costs vs. Production Volume
Creating the hardened steel or carbide dies used for compaction is expensive. This high initial tooling cost means PM is generally not economical for small production runs. However, for high-volume production, the cost per part becomes very low, as the process is fast, highly repeatable, and produces net-shape parts that require little to no machining.
Material and Shape Limitations
Powder metallurgy is ideal for producing small-to-medium-sized but complex parts like gears, bushings, and structural components. It is also the go-to process for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten carbide, which are very difficult to process via casting. However, it is less suitable for very large or simple parts where casting or forging may be more cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting powder metallurgy should be a strategic decision based on your specific application requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, complex parts: PM is an excellent choice due to its high precision, repeatability, and low per-part cost at scale.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials: PM is often the only viable method for fabricating parts from materials like tungsten, molybdenum, or their carbides.
- If your primary focus is creating controlled, intentional porosity: PM is unique in its ability to produce components like porous filters and self-lubricating, oil-impregnated bearings.
- If your primary focus is minimizing material waste: PM is a highly efficient process, using over 97% of the starting material in the final part, unlike subtractive machining.
By carefully weighing these considerations, you can strategically leverage powder metallurgy to achieve manufacturing outcomes that other processes cannot deliver.
Summary Table:
| Consideration | Key Factor | Impact on Final Part |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Properties | Particle size, shape, flow, density | Determines compactability, uniformity, and final strength |
| Process Steps | Mixing, Compaction, Sintering | Affects part integrity, dimensional accuracy, and metallurgical bonds |
| Trade-offs | Porosity vs. Strength, Tooling Cost vs. Volume | Influences mechanical performance, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for high-volume runs |
| Material & Shape | Suitability for complex geometries, high-melting-point metals | Defines application scope, ideal for gears, bushings, and tungsten carbide parts |
Ready to leverage powder metallurgy for your high-volume or complex part needs? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored for precise powder metallurgy processes. Whether you're developing materials with high melting points or need efficient, net-shape production, our solutions ensure superior density, strength, and minimal waste. Contact our experts today to optimize your manufacturing outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the cold isostatic pressing method? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Parts
- What's the difference between cold press and regular press? Choosing Between Quality and Efficiency
- What is the process of CIP and HIP? Forming vs. Densifying for Superior Materials
- What are the applications of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- What is cold isostatic pressing examples? Achieve Uniform Density in Powder Compaction



















