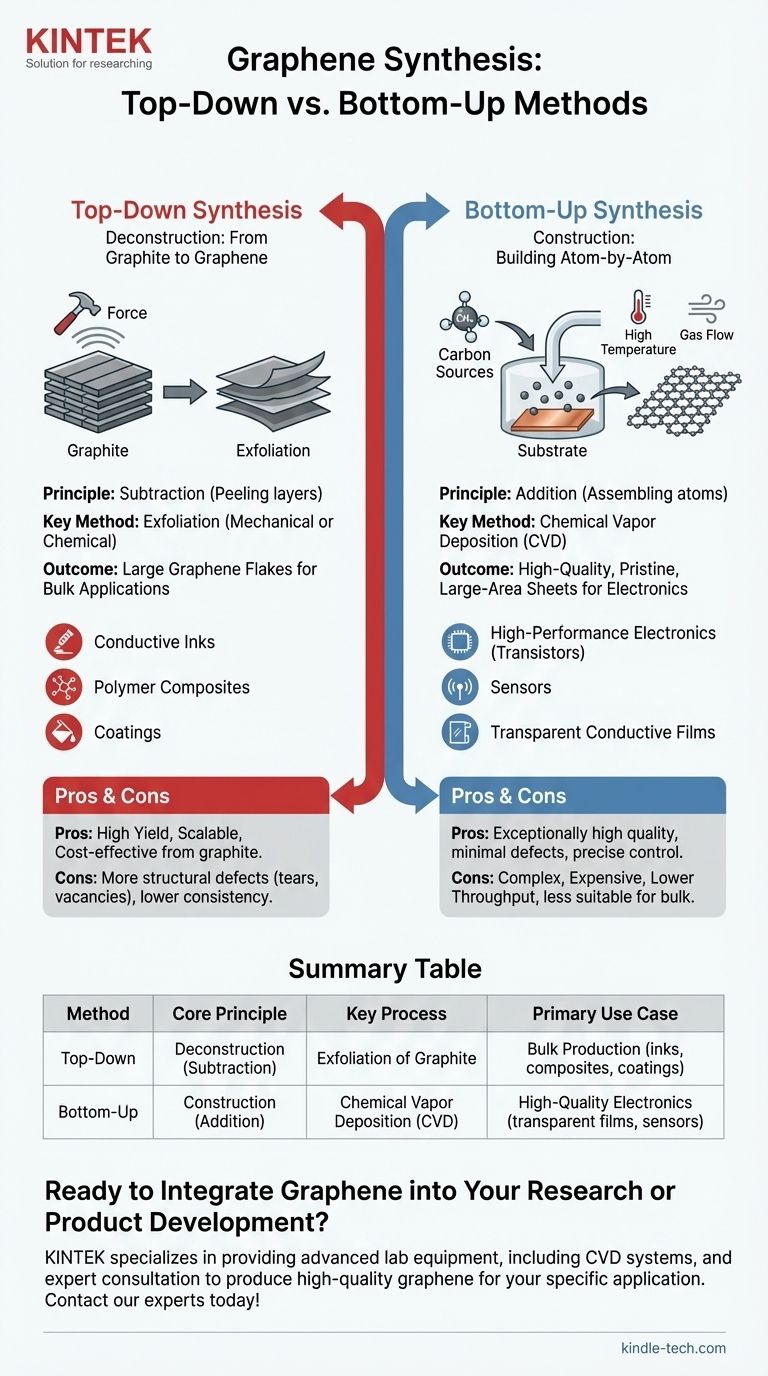
At its core, graphene synthesis is divided into two fundamentally different approaches. The first is a "top-down" strategy that starts with graphite and breaks it down, while the second is a "bottom-up" strategy that builds graphene atom-by-atom from carbon sources.
The central decision in graphene synthesis is a trade-off between scalability and structural perfection. Top-down methods produce large quantities of graphene flakes suitable for bulk applications, while bottom-up methods create high-quality, pristine sheets required for advanced electronics.
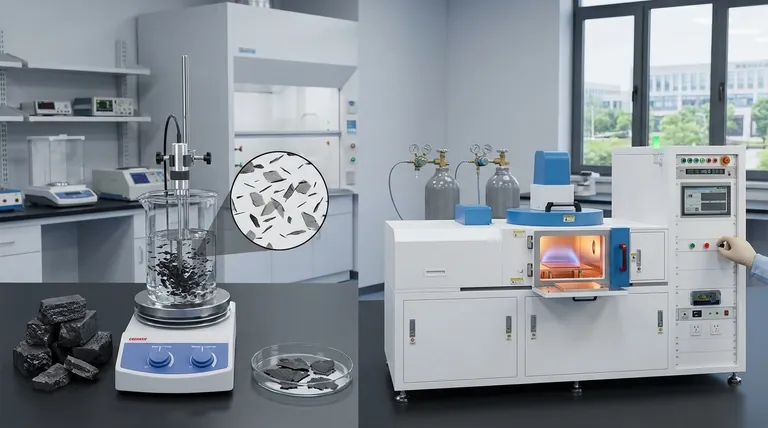

Top-Down Synthesis: Deriving Graphene from Graphite
The Core Principle: Subtraction
Top-down methods are fundamentally processes of deconstruction. They begin with bulk graphite—essentially a stack of countless graphene layers—and apply force to separate these layers.
Key Method: Exfoliation
The most common approach is exfoliation, which can be done mechanically or chemically. This involves overcoming the weak forces holding the graphene layers together to peel them apart into individual or few-layer sheets.
Primary Use Case: Bulk Production
Because these methods are derived from an inexpensive starting material (graphite), they are highly effective for producing large volumes of graphene flakes. This makes top-down graphene ideal for applications like conductive inks, polymer composites, and coatings where quantity is more critical than a perfect atomic structure.
Bottom-Up Synthesis: Building Graphene Atom-by-Atom
The Core Principle: Addition
In direct contrast to top-down methods, bottom-up synthesis is a process of construction. It involves assembling graphene from individual carbon atoms or molecules onto a suitable surface, offering precise control over the final structure.
The Premier Method: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the leading bottom-up technique. It allows for the growth of large, continuous, single-layer graphene sheets, which is impossible with top-down methods.
How CVD Works
In a typical CVD process, a carbon-containing gas like methane is introduced into a high-temperature chamber containing a metal substrate, often a copper foil. The gas decomposes, and the carbon atoms arrange themselves into the hexagonal lattice of graphene on the metal surface. The resulting graphene sheet can then be transferred to another substrate for use.
Primary Use Case: High-Quality Electronics
The pristine, large-area films produced by CVD are essential for high-performance applications. This includes transparent conductive films, transistors, sensors, and other next-generation electronic devices where atomic-level perfection is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Scalability
Top-Down: High Yield, More Defects
The aggressive forces used in exfoliation can introduce structural defects, such as tears or vacancies, into the graphene sheets. While this method excels at producing material in bulk, the quality is generally lower and less consistent.
Bottom-Up: High Quality, Lower Throughput
CVD produces exceptionally high-quality graphene with minimal defects. However, the process is more complex, expensive, and less suited for producing the large powder quantities needed for composite materials.
The Role of the Carbon Source
For CVD, methane gas is the most popular and reliable carbon source. While less common and more difficult to work with, less expensive options like petroleum asphalt can also be used.
Optimizing for Perfection
Researchers fine-tune CVD by studying the growth process in stages, stopping it before a full film forms. These "partial growth studies" provide crucial insights into how parameters like temperature and gas flow affect crystal quality, helping to minimize defects and optimize the synthesis of perfect graphene films.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
Selecting a synthesis method depends entirely on the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial composites, batteries, or conductive inks: Top-down exfoliation methods provide the most cost-effective path to producing the necessary volume of material.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics, sensors, or fundamental research: Bottom-up CVD is the industry standard for creating the pristine, large-area graphene sheets you require.
Ultimately, your application's tolerance for defects versus its need for scalability will determine the ideal synthesis strategy.
Summary Table:
| Method | Core Principle | Key Process | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-Down | Deconstruction (Subtraction) | Exfoliation of Graphite | Bulk Production (inks, composites, coatings) |
| Bottom-Up | Construction (Addition) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | High-Quality Electronics (transparent films, sensors) |
Ready to Integrate Graphene into Your Research or Product Development?
Choosing the right synthesis method is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment, including Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) systems, and expert consultation needed to produce high-quality graphene for your specific application—whether for groundbreaking electronics or scalable industrial materials.
Let's discuss your project requirements and find the perfect solution. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is sputtering deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- What is a thin film in physics? Unlocking Scale-Dependent Properties for Advanced Applications
- Is diamond coating same as ceramic coating? Uncover the Truth About Premium Paint Protection
- What are the categories of carbon nanotubes? Understand SWCNT vs. MWCNT for Your Application
- What are the growth processes of thin films? Master the 3 Modes for Precise Material Engineering
- What is the target sputtering deposition? A Guide to Precision Thin-Film Coating
- What is the reactive sputtering technique? Synthesize Advanced Thin Films with Precision
- What is the effect of temperature on graphene oxide? Master Thermal Reduction for Precise Material Properties



















