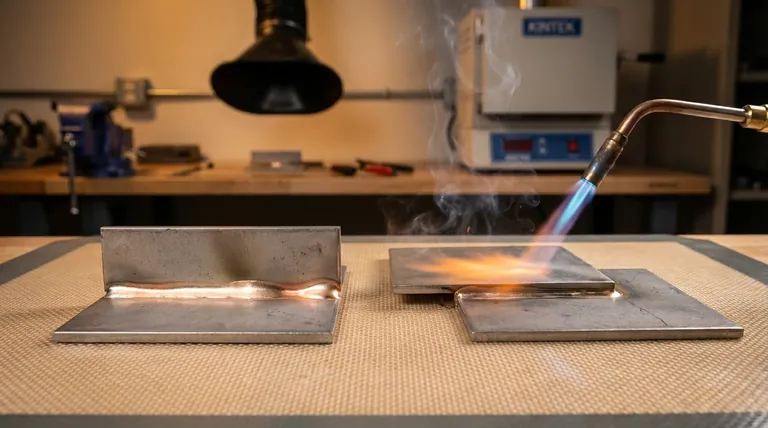
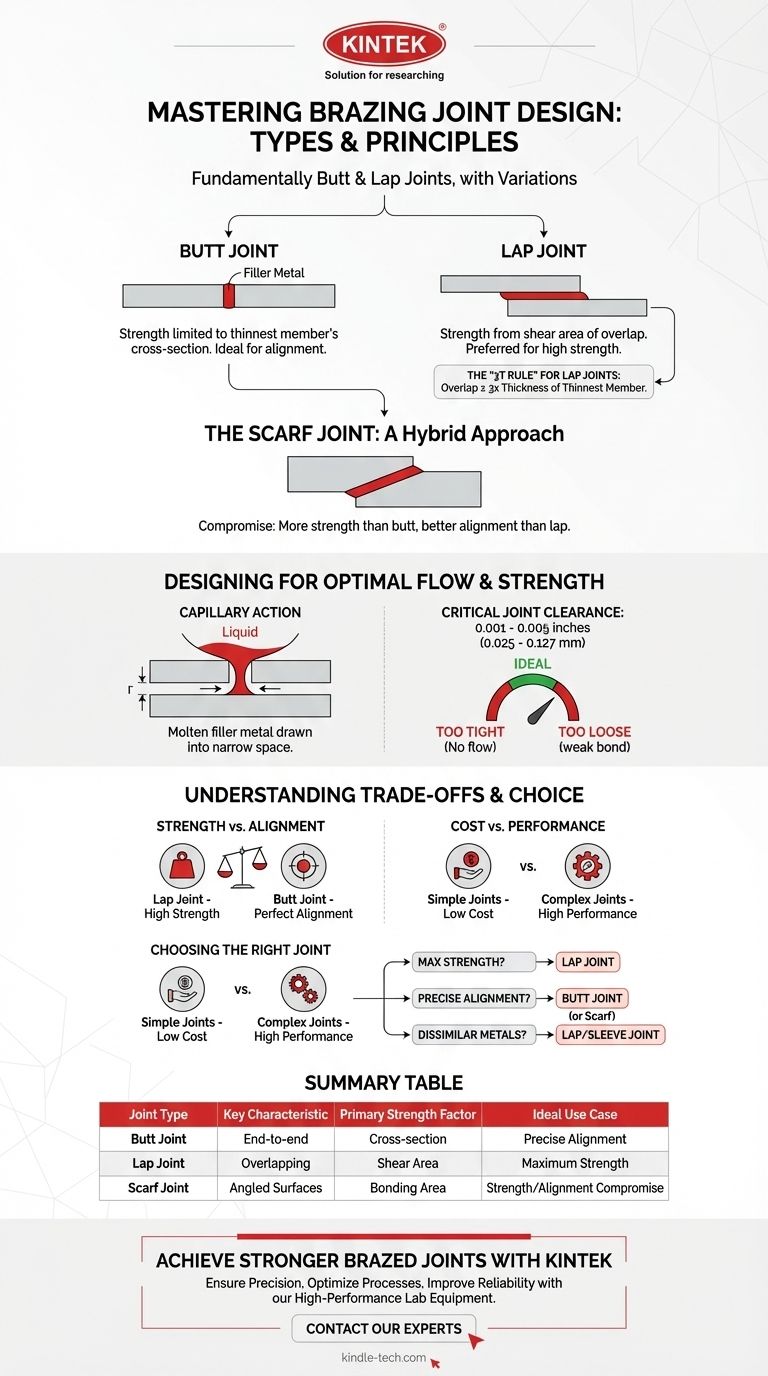
At its core, there are two fundamental types of brazing joints: the butt joint and the lap joint. While other designs exist, they are almost always variations or combinations of these two primary configurations. The choice between them is the most critical decision in designing a robust, reliable brazed assembly.
The goal of brazing is to create a joint that is as strong, or even stronger, than the base metals being joined. This strength is derived almost entirely from the shear area of the filler metal, which is why the lap joint, with its overlapping surfaces, is the cornerstone of high-strength brazing design.

The Core Joint Designs: Butt vs. Lap
Understanding the fundamental strengths and weaknesses of butt and lap joints is the first step toward designing for manufacturability and reliability.
The Butt Joint
A butt joint is formed when the two members are joined end-to-end. The edges of the parts are placed flush against each other with a small, uniform gap for the filler metal.
The primary weakness of a butt joint is that its strength is limited to the cross-sectional area of the thinnest member. The joint is placed in tension or compression, which is not the ideal loading condition for a brazed filler metal.
The Lap Joint
A lap joint is created by overlapping the two members. The filler metal flows between these overlapping surfaces.
This is the preferred design for most brazing applications. The strength of a lap joint is determined by its shear area (the area of overlap), not the cross-sectional area of the parts. By simply increasing the overlap, you can create a joint that is significantly stronger than the base metals themselves.
The Scarf Joint: A Hybrid Approach
A scarf joint is essentially an angled butt joint. By cutting the mating ends at an angle instead of straight across, you increase the surface area available for bonding.
This design offers a compromise. It provides more strength than a standard butt joint while maintaining better alignment and a smoother profile than a lap joint. However, it requires more complex preparation of the parts.
Designing for Optimal Filler Flow and Strength
The type of joint is only part of the equation. A successful brazed connection depends on designing for the physics of the brazing process itself.
The Principle of Capillary Action
Brazing works because of capillary action. This is the phenomenon where a liquid (the molten filler metal) is automatically drawn into a narrow space between solid surfaces (the base metals).
A properly designed joint creates the ideal conditions for capillary action to pull filler metal completely through the entire joint interface, ensuring a void-free bond.
The Critical Role of Joint Clearance
Joint clearance is the gap between the two mating surfaces. It is perhaps the single most important factor in joint design.
If the clearance is too tight, the filler metal cannot flow into the joint. If it is too loose, capillary action will be weak, and the resulting bond will be thin and prone to voids and porosity, drastically reducing its strength.
For most common filler metals, the ideal clearance is between 0.001 and 0.005 inches (0.025 to 0.127 mm).
The "3T Rule" for Lap Joints
A widely accepted rule of thumb for designing strong lap joints is the "3T Rule."
This states that the length of the overlap should be at least three times the thickness of the thinnest member being joined. Following this rule typically ensures the brazed joint will be stronger than the base metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Joint Design
Every design choice involves balancing competing factors. Choosing a joint type is no different and requires you to weigh performance against manufacturability.
Strength vs. Alignment
A lap joint offers superior strength but can introduce an offset in the assembly, which may be unacceptable. A butt joint maintains perfect alignment but at the cost of significantly lower strength.
Cost vs. Performance
Simple butt and lap joints are the easiest and cheapest to prepare. More complex designs like scarf joints or custom interlocking joints (e.g., sleeve joints for tubes) offer better performance but require more precise machining, increasing costs.
The Impact of Dissimilar Metals
Brazing excels at joining dissimilar metals, like copper to steel. However, these materials often have different rates of thermal expansion. A lap joint is generally more forgiving in these situations, as it can better accommodate the stresses that build up during heating and cooling. A butt joint between two materials with vastly different expansion rates is more likely to fail.
Choosing the Right Joint for Your Application
Your design choice should be driven by the primary requirement of the finished part.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and reliability: Use a lap joint. Ensure the overlap follows the "3T Rule" and that joint clearance is tightly controlled for proper capillary action.
- If your primary focus is maintaining precise dimensions and alignment: Start with a butt joint. If more strength is needed, consider a scarf joint as a stronger alternative that avoids the offset of a lap joint.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or tubes: Favor a lap or sleeve-style joint. This design provides superior strength and better accommodates the stresses from different thermal expansion rates.
Ultimately, thoughtful joint design is how you transform brazing from a simple joining method into a powerful engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Joint Type | Key Characteristic | Primary Strength Factor | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Butt Joint | Parts joined end-to-end | Cross-sectional area of thinnest member | Applications requiring precise alignment |
| Lap Joint | Parts are overlapped | Shear area (area of overlap) | Maximum strength and reliability |
| Scarf Joint | Angled mating surfaces | Increased bonding surface area | A compromise between strength and alignment |
Ready to achieve stronger, more reliable brazed joints in your lab or production line?
The right joint design is critical, but so is having the right equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific brazing and thermal processing needs.
We help you:
- Ensure Precision: Achieve the critical joint clearances (0.001-0.005 inches) necessary for perfect capillary action.
- Optimize Processes: Utilize furnaces and heating systems designed for uniform thermal cycles, essential when joining dissimilar metals.
- Improve Reliability: Get consistent, high-strength results batch after batch.
Let's discuss how our solutions can enhance your brazing applications. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using high-precision vibrating sieving systems? Master Filler Quality in Wood-Plastic Composites
- What is the principle of vibratory sieve shaker? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What are the principles of a sieve shaker? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation




