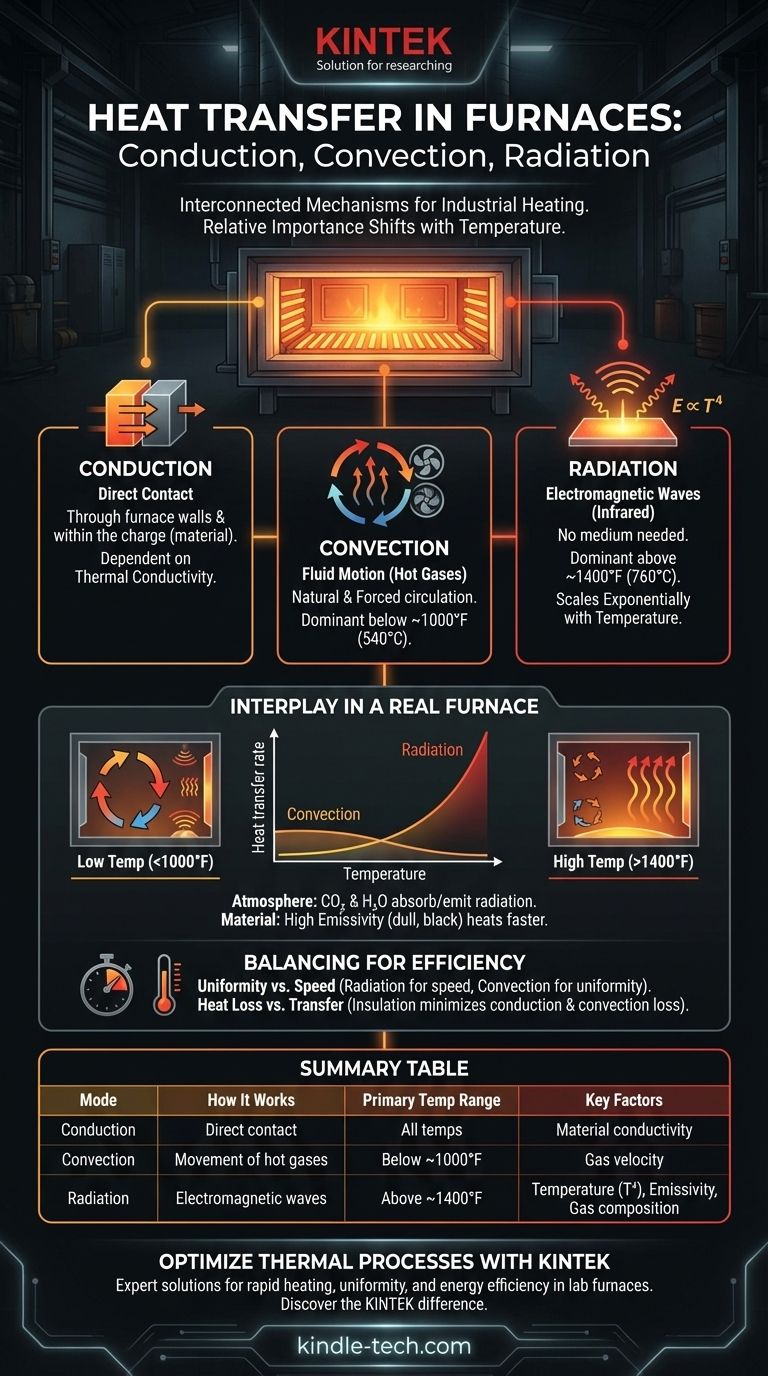
In any industrial furnace, heat is transferred through three distinct yet interconnected mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. While all three are always present, their relative importance shifts dramatically based on the furnace's temperature, design, and the material being heated. Understanding how they work together is the foundation of controlling any thermal process.
The core principle to grasp is that while conduction and convection are dominant at lower temperatures, thermal radiation becomes the primary mode of heat transfer in most high-temperature furnace operations, scaling exponentially with temperature.

The Three Pillars of Heat Transfer in Furnaces
To understand a furnace, you must first understand the fundamental ways energy moves within it. We can visualize these modes using the analogy of a campfire: feeling the heat on your face is radiation, the rising hot air is convection, and the heat traveling up a metal poker placed in the fire is conduction.
Conduction: Heat Through Direct Contact
Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy between objects in direct physical contact. At the atomic level, more energetic particles vibrate and collide with their neighbors, passing energy along.
In a furnace, this occurs in two primary areas:
- Through the furnace structure: Heat conducts through the dense refractory walls, through the steel shell, and is ultimately lost to the surrounding environment. Good insulation is simply a material with low thermal conductivity.
- Within the material being heated (the "charge"): As the surface of the charge heats up, that energy must conduct toward its core. The material's thermal conductivity determines how quickly the entire piece reaches a uniform temperature.
Convection: Heat Through Fluid Motion
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (in this case, hot gases). As fuel burns, it creates hot products of combustion that circulate within the furnace chamber.
This moving gas transfers heat when it makes contact with the furnace walls and the surface of the charge.
- Natural convection occurs as hot, less-dense gas rises and cooler, denser gas sinks, creating a natural circulation loop.
- Forced convection, which uses fans to aggressively circulate the hot gases, is far more effective and is used to achieve rapid and uniform heating, especially in lower-temperature applications like tempering.
Radiation: Heat Through Electromagnetic Waves
Radiation is the transfer of heat via electromagnetic waves (specifically infrared radiation). Unlike conduction or convection, it requires no medium to travel through. Any object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation.
This is the most critical mode in high-temperature furnaces. The rate of heat transfer is governed by the Stefan-Boltzmann law, which states that energy emission is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature (T⁴). This means doubling the temperature of a radiating source increases its energy output by a factor of sixteen.
Key sources of radiation in a furnace include:
- The luminous flame itself
- Hot combustion gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water vapor (H₂O)
- The incandescent surfaces of the hot refractory walls
How These Modes Interact in a Real Furnace
No single mode acts in isolation. The efficiency and effectiveness of a furnace depend entirely on the interplay between conduction, convection, and radiation.
The Decisive Role of Temperature
The dominant heat transfer mechanism is a direct function of operating temperature.
- Below 1000°F (~540°C): Convection is typically the most significant mode. This is why annealing and tempering furnaces often rely on high-velocity fans to ensure uniform heating.
- Above 1400°F (~760°C): Radiation rapidly takes over as the primary mechanism due to the T⁴ relationship. In forging and melting furnaces, burner placement and refractory design are optimized for maximum radiant heat exposure.
The Influence of Furnace Atmosphere
The composition of the furnace atmosphere has a major impact on radiant heat transfer. Diatomic gases like nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen (O₂) are essentially transparent to radiation.
However, gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water vapor (H₂O)—both products of combustion—are excellent absorbers and emitters of radiant energy. A higher concentration of these gases can significantly increase the rate of heat transfer to the charge.
The Impact of the Charge Itself
The material being heated is not a passive recipient. Its properties dictate how effectively it absorbs energy. The most important property for radiation is emissivity—a measure of a surface's ability to absorb and emit radiant energy. A dull, black surface (high emissivity) will heat up much faster under radiation than a shiny, reflective one (low emissivity).
Understanding the Trade-offs for Efficiency
Designing a furnace involves balancing competing priorities, and heat transfer is at the center of these trade-offs.
The Challenge of Uniformity vs. Speed
Relying heavily on direct radiation from a flame can create hot spots on the charge, leading to non-uniform heating and thermal stress. Conversely, relying solely on convection might provide better uniformity but at a much slower heating rate, reducing throughput. This is why many designs use radiation to heat refractory walls, which then re-radiate heat more uniformly toward the charge.
Heat Transfer vs. Heat Loss
The same physical principles that heat the product also cause heat to be lost from the system.
- Conduction drives heat through the refractory walls and insulation.
- Convection carries heat away from the furnace's outer shell.
- Radiation emits heat from any hot external surface, like peep sights or doors.
Improving efficiency always involves minimizing these unwanted paths of heat transfer through better insulation, sealing leaks, and reducing external surface temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles allows you to evaluate and optimize a furnace based on its intended purpose.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature heating: Prioritize maximizing radiant heat transfer by optimizing burner placement for direct line-of-sight and using high-emissivity refractories.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature uniformity: Utilize forced convection with high-velocity fans or employ indirect heating methods where the charge is shielded from direct flame radiation.
- If your primary focus is improving energy efficiency: Focus on minimizing heat loss by upgrading insulation (to reduce conduction) and implementing a system to recover waste heat from the flue gases (to recapture convective and radiant energy).
Mastering the interplay of conduction, convection, and radiation is the key to achieving complete control over any industrial heating process.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mode | How It Works | Primary Temperature Range | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct contact between materials | All temperatures | Material's thermal conductivity |
| Convection | Movement of hot gases (fluids) | Dominant below ~1000°F (540°C) | Gas velocity (natural/forced) |
| Radiation | Electromagnetic waves (no medium needed) | Dominant above ~1400°F (760°C) | Temperature (T⁴), surface emissivity, gas composition |
Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Understanding heat transfer is the first step to achieving precise, efficient, and uniform results in your laboratory. Whether you need rapid high-temperature heating, exceptional temperature uniformity, or improved energy efficiency, the right furnace design is critical.
KINTEK specializes in supplying high-performance lab furnaces and equipment tailored to your specific research and production goals. Our experts can help you select the ideal system that leverages conduction, convection, and radiation to perfection.
Let us help you:
- Increase throughput with faster, more efficient heating.
- Improve product quality with superior temperature control and uniformity.
- Reduce operating costs by maximizing energy efficiency.
Ready to enhance your thermal processing? Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in laboratory equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the precautions of muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace in food analysis? A Guide to Precise Mineral Content Measurement
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What is the theory of muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Controlled High-Temperature Processing
- How to use a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Operation



















