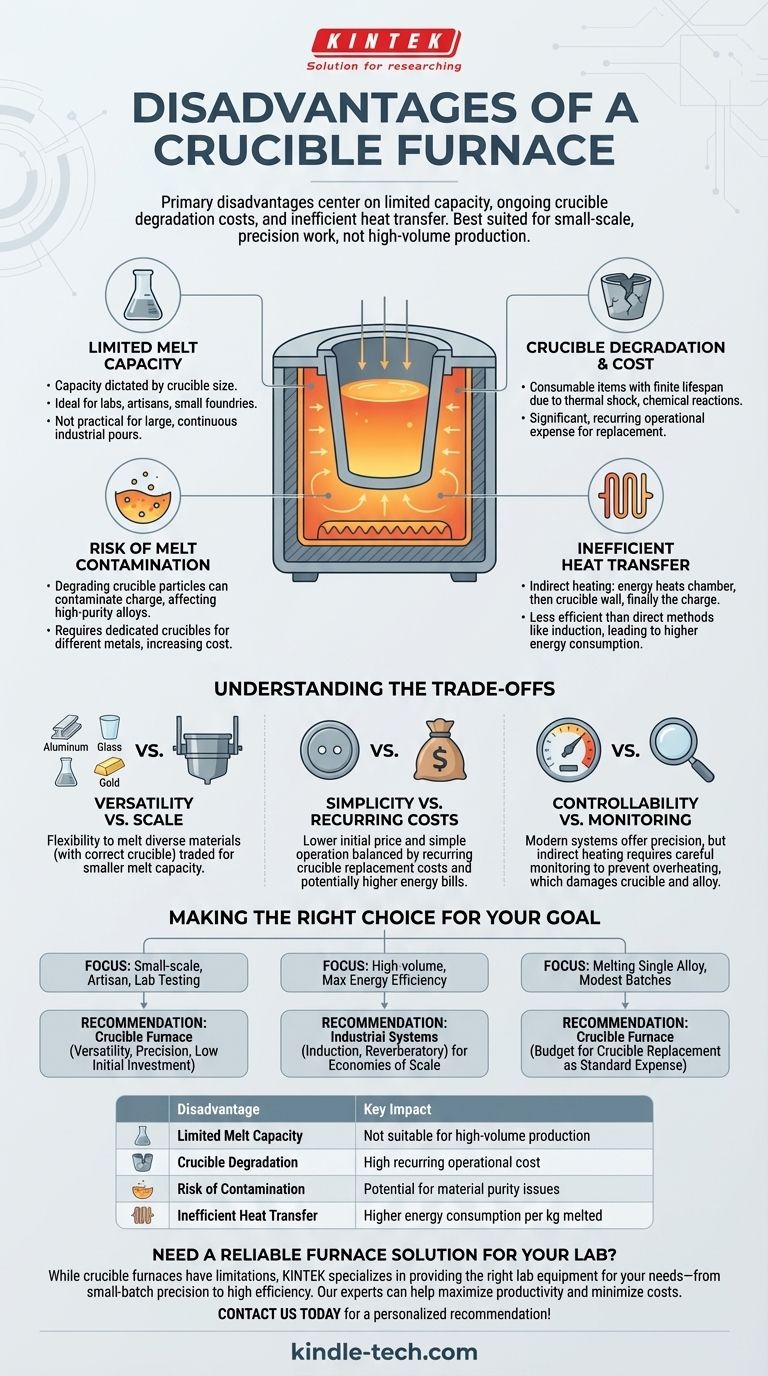
The primary disadvantages of a crucible furnace center on their limited capacity, the ongoing operational cost from crucible degradation, and inherent inefficiencies in heat transfer. While exceptionally useful, these factors make them best suited for small-scale, precision-oriented work rather than high-volume industrial production.
While highly versatile for small-batch applications, a crucible furnace's core limitations are its scale and the consumable nature of the crucible itself. This introduces a recurring operational expense and a critical point of potential failure that is less prevalent in larger, industrial furnaces.
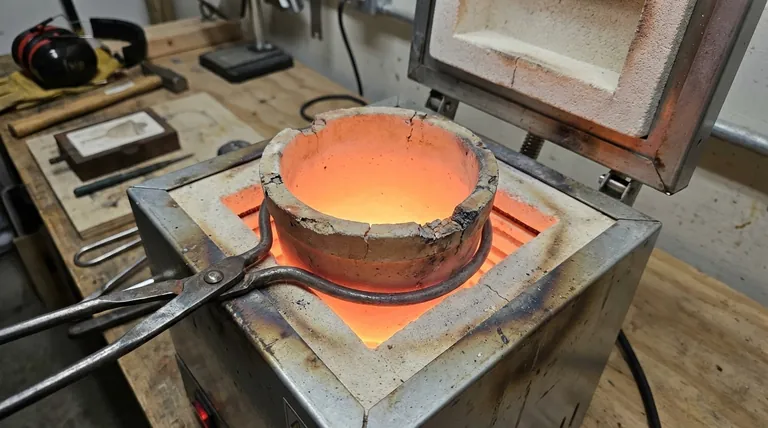

How a Crucible Furnace Works
To understand its limitations, it's essential to understand its simple design. A crucible furnace has two core components that define its function and its drawbacks.
The Heating System
The furnace cavity contains a heating element, typically powered by electricity or gas. Its sole job is to generate intense heat within the insulated chamber.
The Crucible
The crucible is a cup-shaped container made from a material that can withstand extreme temperatures, such as graphite or silicon carbide. It sits inside the furnace and holds the metal or other material (the "charge") to be melted. The heat from the elements transfers through the walls of the crucible to melt the charge inside.
Key Disadvantages of Crucible Furnaces
The design simplicity that makes these furnaces accessible also creates specific operational challenges and limitations.
Limited Melt Capacity
The amount of material you can melt is strictly dictated by the size of the crucible. This makes them ideal for laboratories, artisans, jewelers, and small-scale foundries.
However, they are not practical for applications requiring large, continuous pours of molten metal, as seen in major industrial foundries.
Crucible Degradation and Cost
Crucibles are consumable items with a finite lifespan. They are subjected to immense thermal stress (thermal shock) from repeated heating and cooling cycles.
This constant stress, along with chemical reactions with molten metal and oxygen, causes the crucible to degrade, crack, or fail over time. Replacing crucibles becomes a significant and recurring operational cost.
Risk of Melt Contamination
As a crucible wears down, particles from its walls can flake off and contaminate the molten material. This is a critical issue in applications requiring high-purity alloys.
To avoid cross-contamination between different metals, a separate, dedicated crucible is often required for each type of alloy, further increasing operational complexity and cost.
Inefficient Heat Transfer
A crucible furnace relies on indirect heating. The energy must first heat the furnace chamber, then conduct through the thick wall of the crucible, and finally transfer into the charge.
This multi-step process is inherently less energy-efficient than direct heating methods, such as an induction furnace, where the magnetic field heats the metal itself. This can lead to higher energy consumption per kilogram of metal melted.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of a crucible furnace are best understood as trade-offs for its distinct advantages.
Versatility vs. Scale
A single crucible furnace can melt a vast range of materials—from aluminum and brass to glass and precious metals—simply by using the correct crucible. This flexibility is traded for a smaller melt capacity.
Simplicity vs. Recurring Costs
Crucible furnaces generally have a lower initial purchase price and are simpler to operate than more complex industrial systems. This accessibility is balanced by the recurring cost of replacing crucibles and potentially higher energy bills.
Controllability vs. Monitoring
While modern crucible furnaces offer precise temperature control systems, achieving that precision requires careful monitoring. The indirect heating method means there can be a lag between the element temperature and the actual melt temperature, requiring diligence to prevent overheating, which can damage the crucible and the alloy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your furnace based on a clear understanding of these trade-offs.
- If your primary focus is small-scale prototyping, artisan work, or laboratory testing: A crucible furnace offers an unmatched combination of versatility, precision control, and low initial investment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and maximum energy efficiency: You should investigate industrial systems like induction or reverberatory furnaces that provide better economies of scale.
- If your primary focus is melting a single alloy in modest batches: A crucible furnace is a strong candidate, but you must budget for crucible replacement as a standard operational expense.
Ultimately, understanding these limitations is key to leveraging the crucible furnace's distinct advantages for the right applications.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Limited Melt Capacity | Not suitable for high-volume production |
| Crucible Degradation | High recurring operational cost |
| Risk of Contamination | Potential for material purity issues |
| Inefficient Heat Transfer | Higher energy consumption per kg melted |
Need a reliable furnace solution for your lab? While crucible furnaces have limitations, KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment for your specific needs—whether it's a crucible furnace for small-batch precision work or an alternative for higher efficiency. Our experts can help you select the ideal equipment to maximize your productivity and minimize operational costs. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- How does vacuum arc melting equipment facilitate Ti-Cr-Al-Nb alloy prep? Precision High-Temp Melting Explained
- What is the primary function of a vacuum arc melting furnace in RHEA preparation? Achieving Extreme Thermal Fusion
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API



















