While a powerful technique for creating high-quality thin films, the disadvantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are significant and center on high operational costs, complex process control, and substantial safety risks. The method frequently requires expensive equipment, high temperatures, and the use of toxic or flammable precursor materials, which create considerable engineering and safety overhead.
The core takeaway is that the disadvantages of CVD are not isolated technical issues, but systemic challenges. Choosing CVD commits you to a high-cost, high-complexity manufacturing environment that demands stringent safety protocols and expert process control.

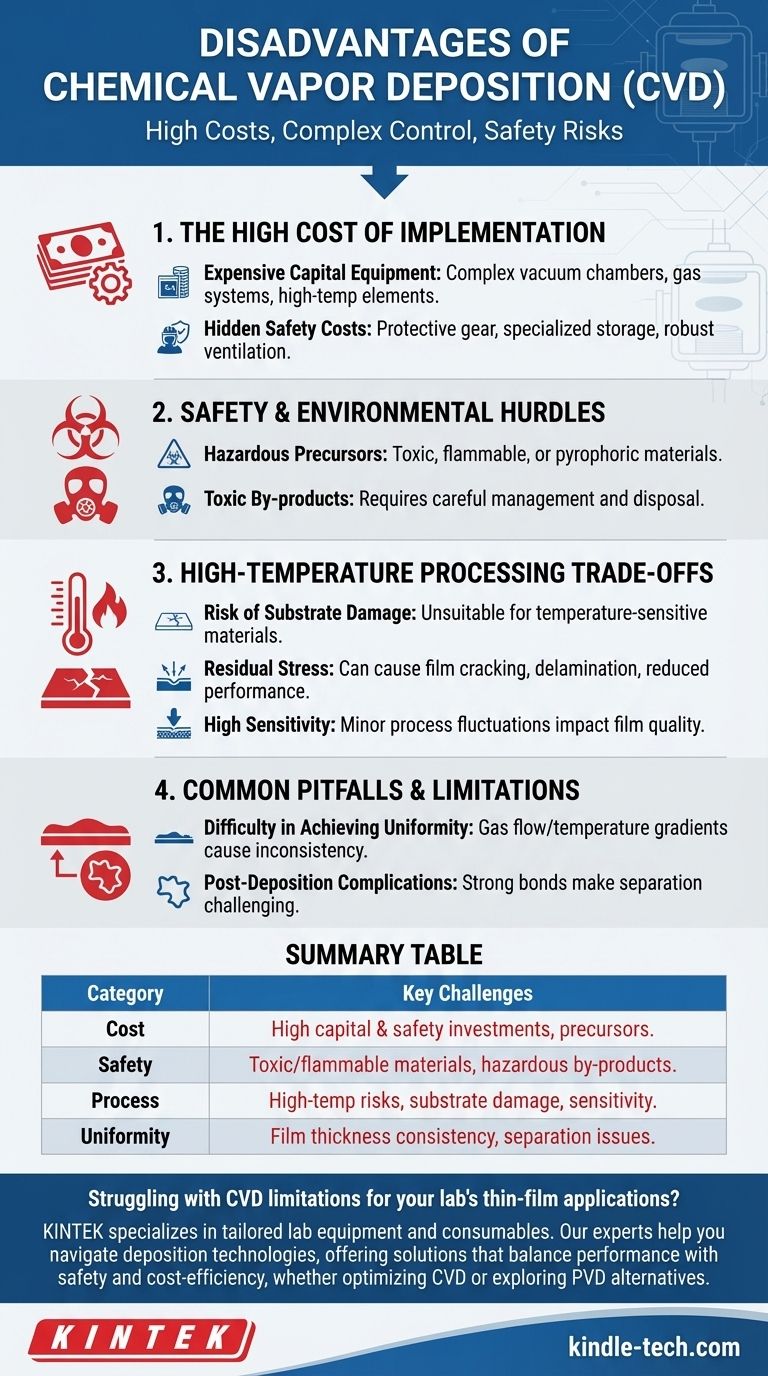
The High Cost of Implementation
The financial barrier to entry and operation is one of the most significant drawbacks of CVD. These costs extend beyond the initial purchase of the deposition chamber itself.
Expensive Capital Equipment
CVD systems are inherently complex, often requiring sophisticated vacuum chambers, precise gas delivery systems, and high-temperature heating elements. This specialized equipment represents a major capital investment.
The Hidden Costs of Safety
The use of chemically active and often hazardous materials necessitates a significant secondary investment. This includes the cost of protective gear, specialized storage for precursors, and robust safety and ventilation systems to handle toxic by-products.
Navigating Safety and Environmental Hurdles
CVD's reliance on chemical reactions introduces safety and environmental concerns that are less prevalent in alternative methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Managing Hazardous Precursors
Many CVD processes rely on source materials—known as precursors—that are toxic, flammable, or pyrophoric (igniting spontaneously in air). This requires meticulous design of the process system and strict handling protocols to prevent accidents.
Dealing with Toxic By-products
The chemical reactions that deposit the desired film also create by-products. These substances are often toxic and require careful management and disposal, adding complexity and cost to waste management and environmental compliance.
Understanding the Trade-offs of High-Temperature Processing
Many, though not all, CVD processes require high temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions. This fundamental requirement creates several critical trade-offs.
Risk of Substrate Damage
The high process temperatures can damage or alter the properties of the substrate being coated. This makes CVD unsuitable for temperature-sensitive materials, such as many polymers or pre-fabricated electronic components.
The Problem of Residual Stress
High temperatures can induce residual stress in the deposited film and the underlying substrate due to differences in thermal expansion. This stress can lead to film cracking, delamination, or reduced performance, requiring careful adjustment of deposition parameters to mitigate.
High Sensitivity to Process Parameters
CVD is extremely sensitive to minor fluctuations in process conditions. Small changes in temperature, pressure, or gas flow rates can dramatically impact the quality, uniformity, and properties of the final film, demanding precise and consistent control.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
Beyond the core challenges of cost and temperature, CVD presents practical limitations that can impact the final product and overall manufacturing workflow.
Difficulty in Achieving Uniformity
While CVD is known for coating intricate shapes, achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness can be challenging, especially for specific advanced materials. Factors like gas flow dynamics and temperature gradients within the reactor can lead to inconsistencies.
Post-Deposition Complications
In some applications, the strong chemical bond between the deposited film and the substrate can be a disadvantage. For example, separating a CVD-grown graphene layer from its metallic catalyst substrate without introducing defects is a well-known engineering challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Evaluating the disadvantages of CVD is about weighing its superior coating capabilities against its significant operational demands.
- If your primary focus is ultimate film quality and purity: CVD is often the superior or only choice, but you must be prepared to invest heavily in the necessary equipment, safety infrastructure, and process expertise.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency or temperature-sensitive substrates: You should strongly consider alternatives like PVD, which typically operate at lower temperatures and avoid the chemical hazards inherent to CVD.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries: CVD's non-line-of-sight nature is a powerful advantage that may justify the higher cost and complexity, as it can produce uniform coatings where other methods cannot.
Understanding these drawbacks is the first step toward making an informed decision that aligns with your technical goals and operational realities.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Cost | High capital investment, expensive safety systems, and precursor materials |
| Safety & Environment | Handling toxic/flammable precursors and managing hazardous by-products |
| Process Limitations | High-temperature requirements, substrate damage risks, and sensitivity to parameters |
| Uniformity & Post-Processing | Challenges in film thickness consistency and substrate separation issues |
Struggling with CVD limitations for your lab's thin-film applications? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions that balance performance with safety and cost-efficiency. Our experts can help you navigate the complexities of deposition technologies to find the right fit for your specific needs—whether it's optimizing your CVD process or exploring alternatives like PVD. Contact us today to enhance your lab's capabilities and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















