While often marketed as a revolutionary leap in surface protection, true graphene coatings come with significant practical disadvantages. Their high cost, demanding and unforgiving application process, and the prevalence of misleading marketing often outweigh their marginal performance benefits over high-quality ceramic coatings.
The core issue with graphene coatings lies not in the graphene material itself, but in its current implementation. Consumers face a market saturated with products that offer questionable benefits for a premium price, coupled with a difficult application that can easily lead to subpar results.
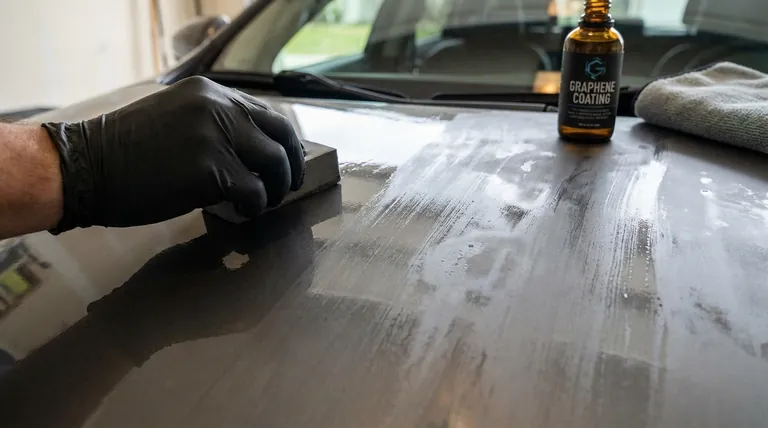

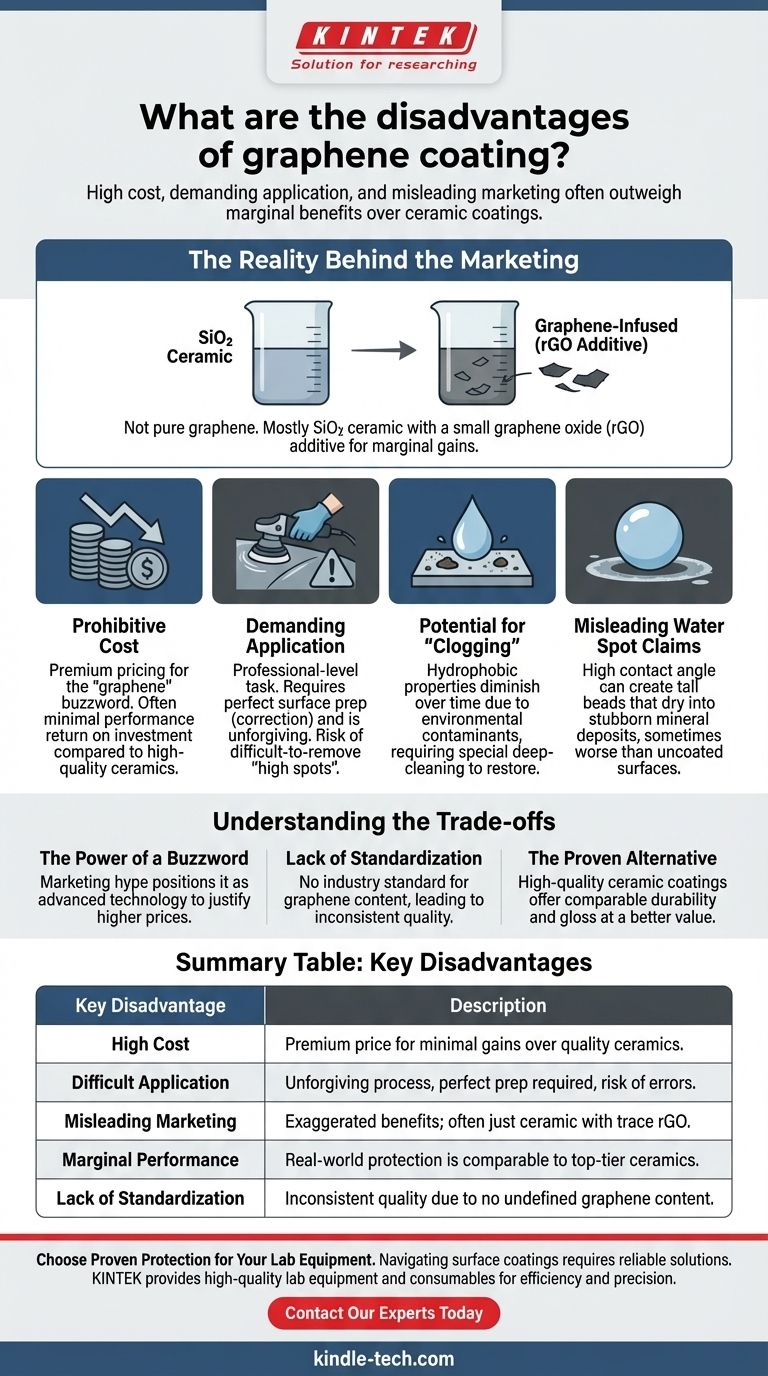
The Reality Behind the Marketing
To understand the disadvantages, it is crucial to first understand what these products actually are. The term "graphene coating" can be highly misleading.
They Are Not Pure Graphene
Consumer-grade coatings are not a pure, one-atom-thick layer of graphene. That technology is not yet commercially viable for applications like car paint.
Instead, these products are fundamentally SiO2 (silicon dioxide) ceramic coatings. They are simply infused with a very small amount of graphene oxide (rGO).
An Additive, Not a Revolution
The rGO is added to the ceramic formula with the goal of improving certain characteristics. Marketers claim it enhances durability, increases slickness, and reduces the potential for water spotting by lowering surface heat.
Marginal Performance Gains
In practice, the real-world difference between a top-tier ceramic coating and a graphene-infused one is often minimal. While some tests show a slight reduction in water spotting, the fundamental protective qualities and longevity are frequently comparable to their high-end ceramic counterparts.
Key Disadvantages in Practice
When you move from marketing claims to real-world application and ownership, the drawbacks become clear.
Prohibitive Cost
Graphene coatings are consistently priced at a premium. You are paying extra for the "graphene" buzzword and the small amount of rGO additive, which may not deliver a justifiable return on investment in terms of performance.
Demanding and Unforgiving Application
Applying a graphene coating is a professional-level task. The surface must be perfectly prepared through washing, chemical decontamination, claying, and paint correction (polishing).
The coating itself can be difficult to work with. It may have a short "flashing" time, and if you miss a spot during wipe-off, the resulting high spot (a dark, hazy mark) is extremely difficult to remove once cured, often requiring machine polishing.
Potential for "Clogging"
Like all coatings, the hydrophobic surface can become "clogged" with environmental contaminants over time. When this happens, its water-beading and self-cleaning properties diminish significantly, requiring a special deep-cleaning wash to restore.
Misleading Water Spot Claims
While marketed as reducing water spots, the high water-contact angle can create very tall, round beads. If this water contains minerals and is left to dry on the surface, it can leave behind concentrated mineral deposits that are just as stubborn, if not more so, than those on an uncoated car.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use a graphene coating is often a battle between material science and clever marketing.
The Power of a Buzzword
"Graphene" is a powerful marketing term associated with strength and advanced technology. This allows brands to position their products as the next generation of protection and justify a higher price tag, even if the underlying technology is an incremental evolution of existing ceramic formulas.
Lack of Standardization
There is no industry standard for what constitutes a "graphene coating." A product could contain a trivial, ineffective amount of rGO and still be marketed as such. This leads to a marketplace with massive variance in quality and performance, making it difficult for consumers to make an informed choice.
The Proven Alternative
For most users, a high-quality, professionally installed ceramic coating offers nearly all the same benefits—long-term durability, chemical resistance, and enhanced gloss—at a more reasonable cost and with a more predictable outcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, you must weigh the purported benefits against the real-world costs and risks.
- If your primary focus is proven, cost-effective protection: Stick with a reputable, high-quality SiO2 ceramic coating from an established brand.
- If you are an enthusiast who wants the latest product: A graphene coating can be a viable option, but go in with realistic expectations about its performance jump over top-tier ceramics.
- If your goal is to simplify maintenance: No coating is a replacement for proper washing and drying techniques; both ceramic and graphene coatings require upkeep to perform their best.
Choose your protection based on proven results and realistic needs, not just marketing hype.
Summary Table:
| Key Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Cost | Premium price for minimal performance gains over high-quality ceramic coatings. |
| Difficult Application | Requires perfect surface prep; unforgiving with short flash time and risk of high spots. |
| Misleading Marketing | Often just a ceramic coating with minimal graphene oxide; benefits are exaggerated. |
| Marginal Performance | Real-world protection and longevity are comparable to top-tier ceramic alternatives. |
| Lack of Standardization | No industry standard for graphene content, leading to inconsistent product quality. |
Choose Proven Protection for Your Lab Equipment
Navigating the complexities of surface coatings requires reliable solutions and expert advice. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your laboratory operates with efficiency and precision.
- Benefit from Our Expertise: Avoid the hype and invest in proven, durable materials that meet the rigorous demands of your research.
- Tailored Solutions: We understand laboratory needs and can recommend the best products for your specific applications.
Enhance your lab's performance with trusted equipment from KINTEK. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools










