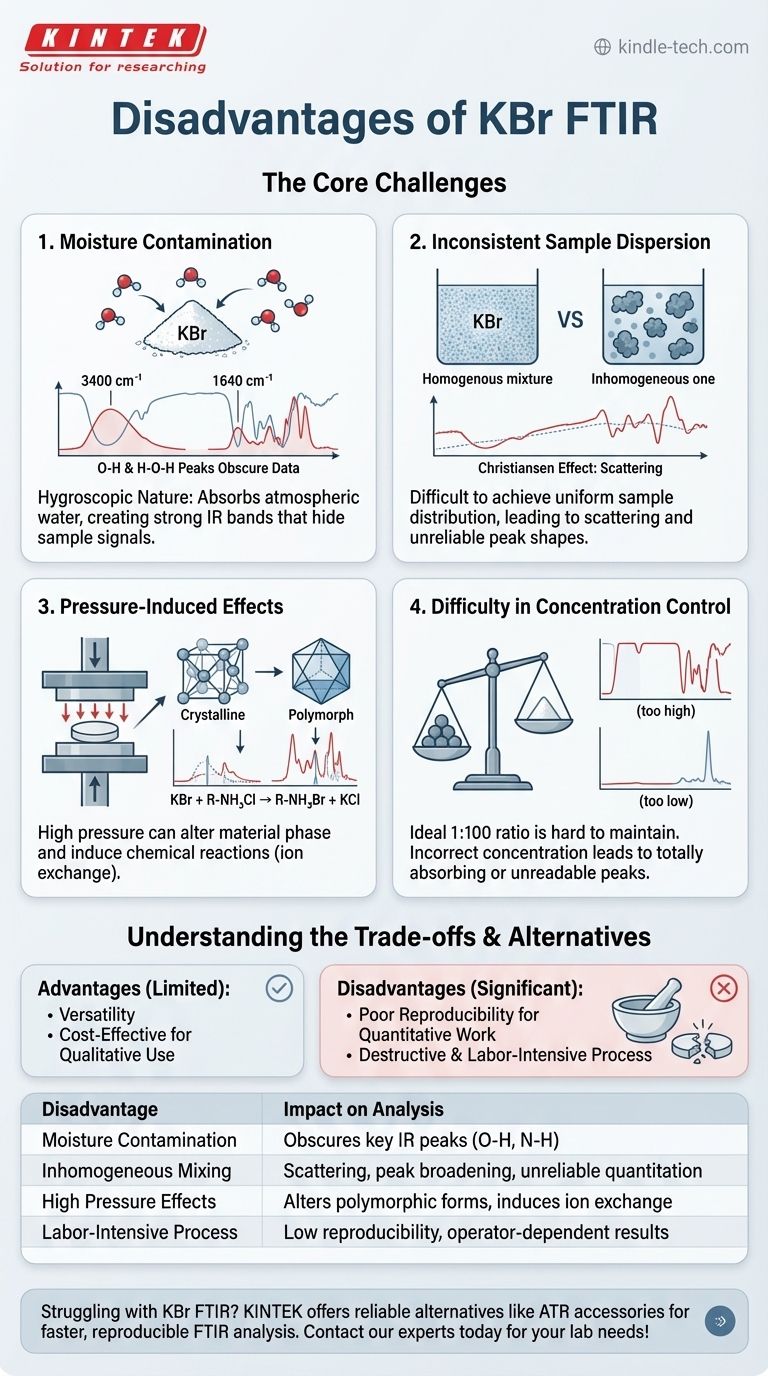
While a foundational technique in infrared spectroscopy, the potassium bromide (KBr) pellet method is fraught with potential disadvantages that can compromise data quality. The most significant drawbacks are its extreme sensitivity to atmospheric moisture, the difficulty of achieving a truly homogenous sample mixture, the potential for pressure-induced changes or chemical reactions with the sample, and the overall labor-intensive and operator-dependent nature of the preparation process.
The primary challenge of the KBr pellet method is not the technique itself, but its sensitivity to environmental and preparation variables. Moisture contamination and improper sample grinding are the most common sources of error, capable of obscuring true sample signals and leading to incorrect interpretations.

The Core Challenges of the KBr Pellet Method
To understand whether the KBr method is right for your analysis, you must be aware of its specific technical limitations. Each step of the preparation process introduces a potential source of error.
The Problem of Water Contamination
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the atmosphere. This is the single most common failure point of the technique.
Water has very strong infrared absorption bands, notably a broad peak around 3400 cm⁻¹ (O-H stretching) and a sharp peak near 1640 cm⁻¹ (H-O-H bending).
These water peaks can easily overlap with and obscure important functional group signals from your sample, such as N-H or O-H stretches, making the resulting spectrum difficult or impossible to interpret accurately.
Inconsistent Sample Dispersion and Scattering
The theory behind the KBr pellet relies on the sample being diluted and uniformly dispersed in an IR-transparent matrix. Achieving this is harder than it sounds.
If the sample is not ground into particles smaller than the wavelength of the IR light, scattering can occur. This phenomenon, known as the Christiansen effect, results in a distorted, sloping baseline that complicates analysis.
Inhomogeneous mixing creates "islands" of concentrated sample within the pellet, leading to peak broadening and making any form of quantitative analysis unreliable.
Pressure-Induced Effects and Sample Reactivity
The high pressure required to form a transparent pellet (typically 8-10 tons) is not always benign.
For polymorphic materials—substances that can exist in multiple crystalline forms—this pressure can induce a phase transition, meaning you are analyzing a different form of the material than you started with.
Furthermore, KBr is an alkali halide and can undergo ion exchange with certain samples, particularly amine salts (e.g., hydrochlorides). This chemical reaction creates spectral artifacts that do not belong to the original sample.
Difficulty in Controlling Concentration
The ideal sample-to-KBr ratio is approximately 1:100. Deviating from this can ruin the measurement.
If the sample concentration is too high, the strongest absorption bands will be "totally absorbing," resulting in flat-topped peaks that lack meaningful information.
If the concentration is too low, the signal may be too weak to distinguish from the background noise, especially for less abundant functional groups.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The persistence of the KBr method despite these flaws is due to a specific set of advantages and historical context. Acknowledging the trade-offs is key to using it wisely.
Advantage: Versatility and Cost-Effectiveness
For stable, non-hygroscopic, solid organic and inorganic compounds, the KBr pellet method works well for qualitative identification. The materials (spectroscopy-grade KBr and a press) are relatively inexpensive.
Disadvantage: Poor Reproducibility for Quantitative Work
Because of the high variability in pellet thickness, sample concentration, and homogeneity, the KBr method is not recommended for quantitative analysis. The path length is not precisely known, violating a key principle of the Beer-Lambert law.
Disadvantage: Destructive and Labor-Intensive
The sample is intimately mixed with KBr and typically cannot be recovered. The process of grinding, mixing, and pressing is also time-consuming and requires significant operator skill to perform reproducibly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
The decision to use KBr pellets should be based on your analytical goals and the nature of your sample. Modern alternatives, especially Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), have surpassed the KBr method for many applications.
- If your primary focus is rapid qualitative identification of a stable solid: The KBr method can be a reliable workhorse, provided you take rigorous precautions to control moisture.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Avoid the KBr method. Solution-based transmission cells or, more commonly, ATR-FTIR offer far superior reproducibility.
- If your primary focus is analyzing sensitive, unknown, or polymorphic materials: The KBr method is a high-risk choice. Non-destructive techniques like ATR-FTIR are strongly preferred as they require no sample preparation and do not use high pressure.
Understanding these limitations is the first step toward generating reliable and meaningful spectroscopic data.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact on Analysis |
|---|---|
| Moisture Contamination | Obscures key IR peaks (e.g., O-H, N-H stretches) |
| Inhomogeneous Mixing | Causes scattering, peak broadening, unreliable quantitation |
| High Pressure Effects | May alter polymorphic forms or induce ion exchange |
| Labor-Intensive Process | Low reproducibility, operator-dependent results |
Struggling with KBr FTIR inconsistencies? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering reliable alternatives like ATR accessories for faster, more reproducible FTIR analysis. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















