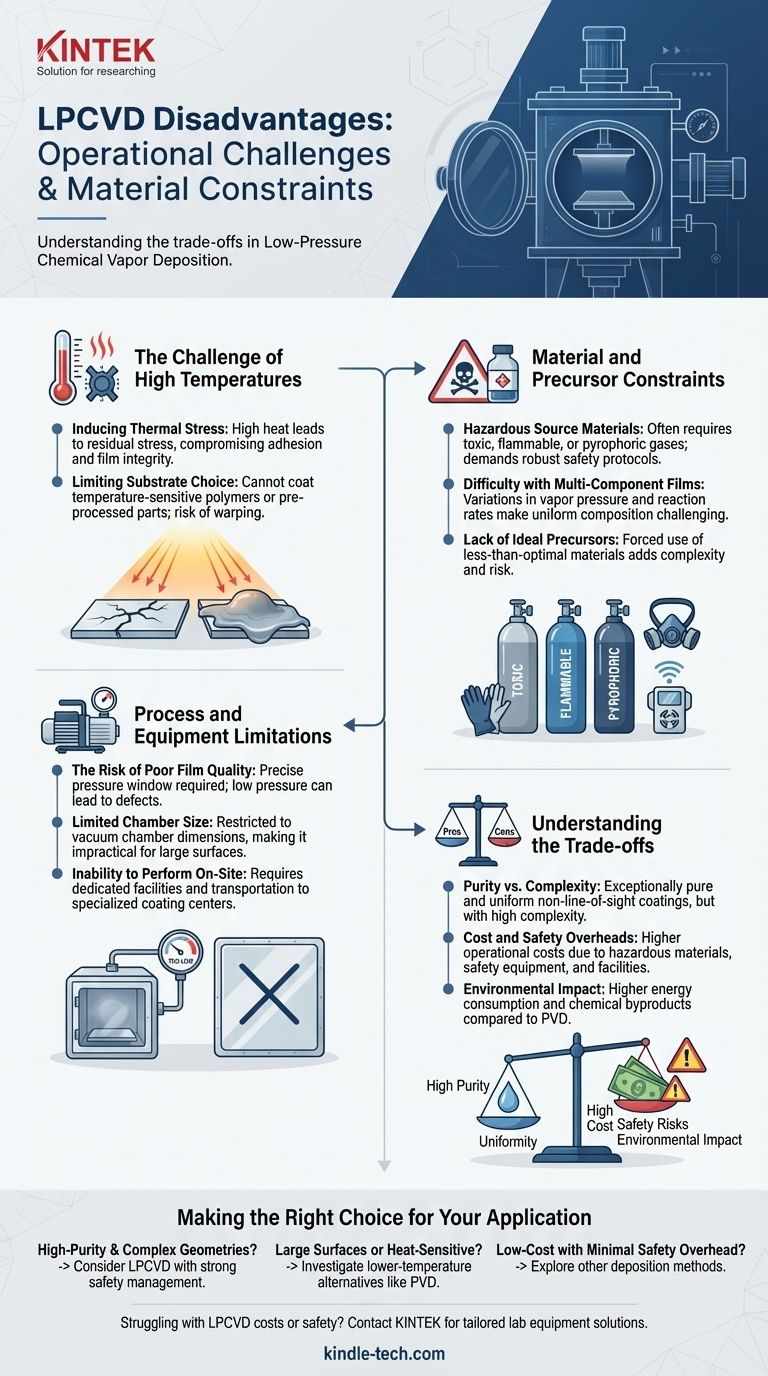
The primary disadvantages of Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) center on its operational complexity and material constraints. The process demands high temperatures that can damage sensitive substrates, relies on precursor gases that are often toxic or flammable, and presents challenges in creating uniform multi-component films. Furthermore, if process parameters like pressure are not meticulously controlled, it can lead to poor film quality and defects.
While LPCVD is valued for producing highly pure and uniform films, its main drawbacks are the high temperatures that introduce thermal stress and limit substrate choice, and the inherent safety and cost burdens associated with its reactive precursor gases.
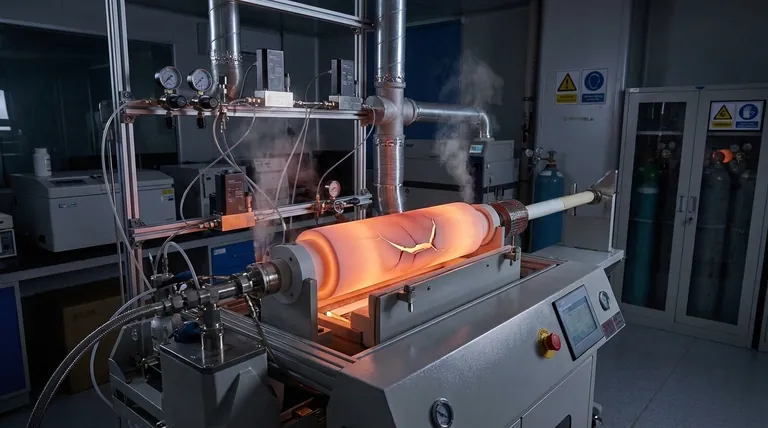

The Challenge of High Temperatures
One of the most significant operational hurdles in any CVD process, including LPCVD, is the requirement for high heat. This creates several downstream problems that must be managed.
Inducing Thermal Stress
The high temperatures required for the chemical reactions can lead to significant residual stress in both the deposited film and the underlying substrate. This mismatch in thermal expansion can compromise the coating's adhesion and mechanical integrity.
Limiting Substrate Choice
Many materials, particularly certain polymers or pre-processed components, cannot withstand the high temperatures of the CVD chamber. This heat can cause warping, melting, or other forms of thermal damage, severely restricting the types of substrates that can be coated.
Material and Precursor Constraints
The quality and composition of the final film are entirely dependent on the source materials, known as precursors. These materials introduce their own set of challenges.
Hazardous Source Materials
LPCVD precursors are often highly toxic, flammable, or pyrophoric gases. This necessitates careful handling and robust safety protocols, including specialized gas cabinets, detectors, and exhaust treatment systems.
Difficulty with Multi-Component Films
Synthesizing films with multiple components is difficult due to variations in the vapor pressure and reaction rates of different precursors. This can result in a heterogeneous film composition, where the desired elemental ratio is not uniform throughout the material.
Lack of Ideal Precursors
For some applications, an ideal precursor—one that is highly volatile, non-toxic, and stable—simply doesn't exist. This forces engineers to work with less-than-optimal materials, adding complexity and risk to the process.
Process and Equipment Limitations
The physical nature of the LPCVD process imposes several practical constraints on its use and scalability.
The Risk of Poor Film Quality
While the process is called "low pressure," there is a precise window for operation. If the pressure is too low, it can negatively affect the film's deposition mechanism, leading to a decrease in density and the formation of needle-like defects.
Limited Chamber Size
The process must take place inside a vacuum chamber, which has a finite size. This makes it difficult and often impractical to coat very large surfaces, limiting the application to smaller, individual components.
Inability to Perform On-Site
LPCVD is a complex industrial process that requires a dedicated facility. It cannot be performed on-site, meaning all parts must be transported to a specialized coating center for treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition technology requires balancing its benefits against its inherent drawbacks. LPCVD is no exception.
Purity vs. Complexity
The reason to accept LPCVD's disadvantages is its ability to produce exceptionally pure, dense, and uniform films. Because it is a non-line-of-sight process, it can evenly coat components with highly complex shapes, an area where other methods fail.
Cost and Safety Overheads
The use of chemically active and hazardous materials directly translates to higher operational costs. Significant investment is required for the protective and safety equipment needed to manage these risks effectively.
Environmental Impact
Compared to alternative technologies like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), the chemical byproducts and high energy consumption of LPCVD can make it a less environmentally friendly option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if LPCVD is suitable, you must weigh its limitations against your primary technical and business goals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, uniform coatings on complex geometries: LPCVD is a strong contender, but you must be prepared to manage the high thermal loads and strict safety protocols.
- If your primary focus is coating large surfaces or temperature-sensitive substrates: The high heat and chamber size limitations of LPCVD make it a poor fit; you should investigate lower-temperature alternatives like PVD.
- If your primary focus is low-cost production with minimal safety overhead: The complexity and hazardous materials inherent to LPCVD suggest you should explore other deposition methods.
Ultimately, understanding these disadvantages is the key to determining if LPCVD's exceptional film quality justifies its significant operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| High Temperatures | Thermal stress on substrates, limited material compatibility |
| Material & Precursors | Toxic/flammable gases, difficulty with multi-component films |
| Process & Equipment | Precise pressure control needed, limited chamber size, high operational costs |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy use and chemical byproducts vs. alternatives like PVD |
Struggling with LPCVD's high costs or safety concerns? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for your deposition challenges. Our experts can help you select safer, more efficient alternatives or optimize your current setup. Contact us today to enhance your lab's safety and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Why is Argon flow rate control critical in Tantalum Carbide CVD? Optimize Transport and Stoichiometry
- What are the applications of chemical Vapour deposition method? Achieve High-Performance Thin Films
- How does chemical Vapour deposition work? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Growth
- What is electrical chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the main challenge in the large scale production of graphene? Overcoming the Quality vs. Cost Trade-Off
- What is high temperature chemical vapor deposition process? Grow Superior Thin Films Atom by Atom
- How are ion beam based deposition techniques different from sputtering? Decoupling Plasma for Superior Film Control
- For which types of materials is RF sputtering used? Master Thin-Film Deposition of Dielectrics and Beyond



















