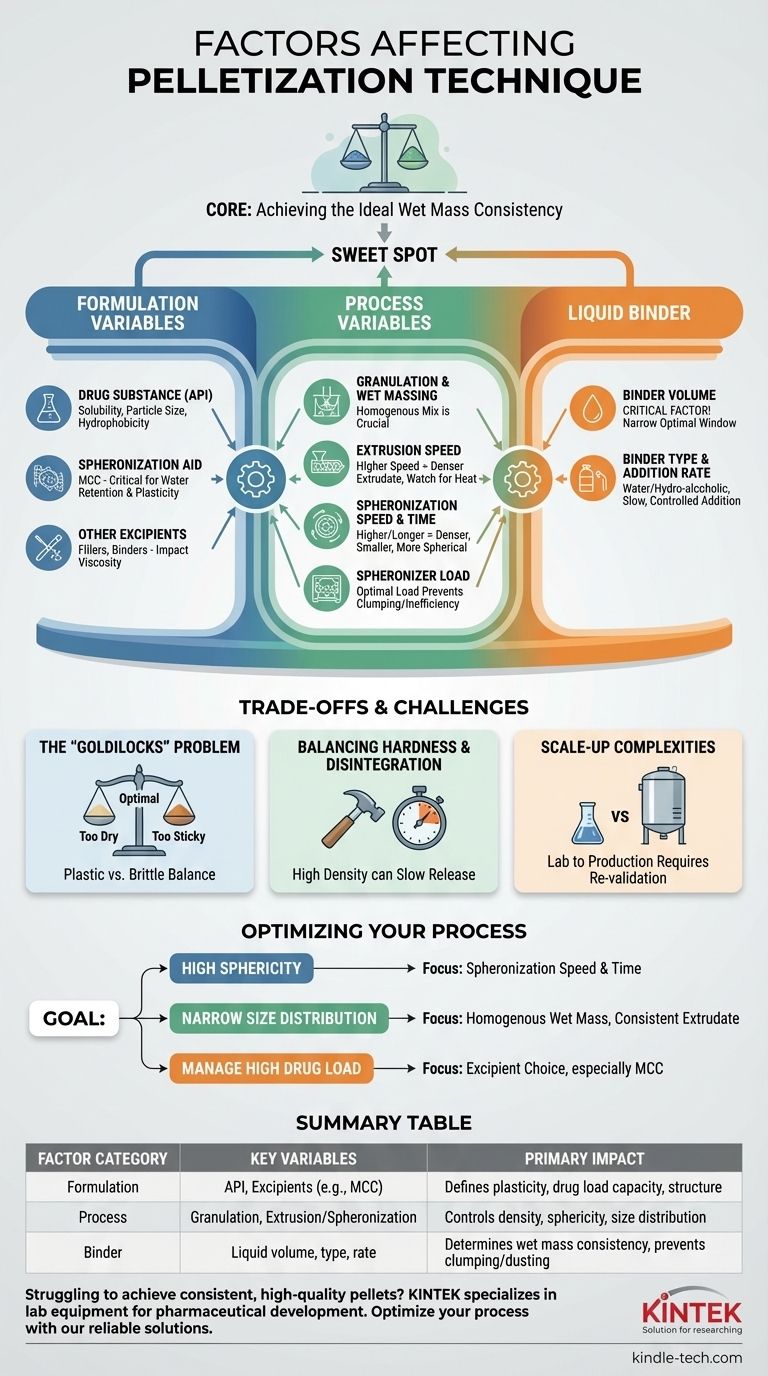
The success of any pelletization technique is governed by a precise interplay between the materials you use, the settings on your equipment, and the liquid that binds everything together. The most significant factors are the properties of the active drug and excipients (formulation variables), the speed and duration of the process steps (process variables), and the amount and type of liquid binder used.
At its core, successful pelletization is not about optimizing a single variable, but about achieving the ideal consistency in the wet mass. This "sweet spot" ensures the material can be shaped and densified without becoming either too fragile or an unworkable, sticky clump.
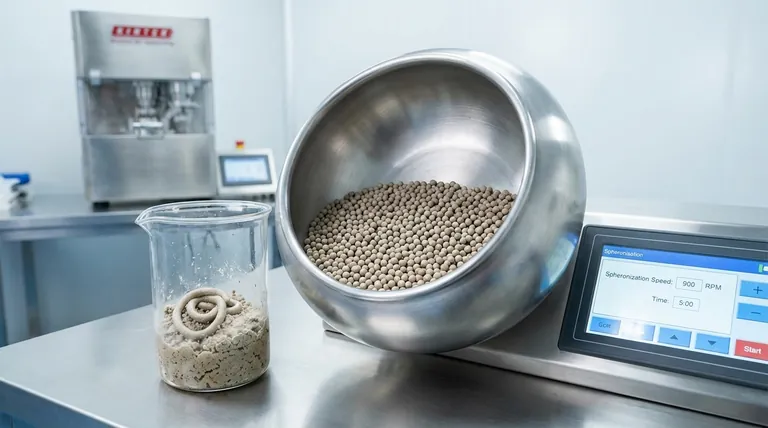

Formulation Variables: The Building Blocks of Your Pellets
The characteristics of your starting materials fundamentally define the boundaries of your process. Poorly chosen ingredients cannot be overcome by process adjustments alone.
The Drug Substance (API)
The properties of the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) are a primary consideration. Its solubility, particle size, and hydrophobicity dictate how it will interact with the binding liquid and other excipients. A very high drug load, for instance, can make it difficult to form a plastic mass suitable for extrusion.
The Spheronization Aid
For the common technique of extrusion-spheronization, an excipient like Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) is almost always required. MCC is critical because of its ability to absorb and retain large quantities of water, creating a cohesive, plastic wet mass without becoming overly sticky. This property is essential for the material to be shaped into spheres.
Other Excipients
Additional components like fillers, binders, or disintegrants also play a role. A water-soluble filler, for example, will dissolve in the granulation liquid, changing its viscosity and impacting the consistency of the final wet mass.
Process Variables: Controlling the Transformation
These are the parameters you control on the equipment. They determine the amount of energy put into the system to transform the wet mass into finished pellets.
Granulation and Wet Massing
The initial step of mixing your dry powders with the liquid binder is crucial. The goal is to create a homogenous wet mass. An uneven distribution of liquid will lead to inconsistent extrudate and, ultimately, a wide and unacceptable pellet size distribution.
Extrusion Speed
The speed of the extruder screw forces the wet mass through a screen or die. A higher speed increases the work put into the material, typically resulting in a denser and more uniform extrudate. However, excessive speed can generate heat, which may be detrimental to sensitive drugs.
Spheronization Speed and Time
This is where the extruded rods are broken and rounded. Higher spheronizer plate speeds and longer processing times generally produce denser, smaller, and more spherical pellets. There is, however, a point of diminishing returns where excessive energy input can cause pellet attrition or fusion.
Spheronizer Load
The amount of extrudate added to the spheronizer chamber impacts performance. An under-filled chamber can lead to inefficient rounding and a broad size distribution, while an over-filled chamber can impede pellet movement, causing clumping and preventing uniform spheronization.
The Critical Role of the Liquid Binder
The interaction between the solid particles and the liquid binder is arguably the most sensitive part of the entire process.
Binder Volume
The quantity of liquid added is the single most critical factor. Too little liquid results in a dry, friable extrudate that generates excessive dust and forms weak pellets. Too much liquid leads to an overly plastic, sticky mass that agglomerates into large, unusable clumps instead of discrete spheres. The optimal window is often very narrow.
Binder Type and Addition Rate
While water is the most common binder, hydro-alcoholic systems are sometimes used. The choice affects drying times and API solubility. Furthermore, the rate at which the liquid is added to the dry powder blend influences the uniformity of the wet mass. A slow, controlled addition is key to avoiding localized overwetting.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Achieving the desired pellet characteristics involves balancing competing factors and navigating common pitfalls.
The "Goldilocks" Problem of Wet Mass
The ideal wet mass is plastic enough to be extruded without excessive force, but brittle enough to break into short segments in the spheronizer. This narrow processing window is the central challenge of process development.
Balancing Hardness and Disintegration
Creating very hard, dense pellets is often desirable for withstanding downstream processes like coating. However, this increased density can significantly slow down the pellet's ability to disintegrate and release the drug once administered.
Scale-Up Complexities
Parameters that work perfectly on a small, lab-scale machine often do not translate directly to larger production equipment. Geometric differences and energy inputs change with scale, requiring careful process re-validation.
Optimizing Your Pelletization Process
Your specific goal will determine which factors require the most attention during development and control.
- If your primary focus is achieving high sphericity: Prioritize optimizing the spheronization speed and time while ensuring your wet mass has the correct plastic consistency.
- If your primary focus is a narrow particle size distribution: Concentrate on achieving a completely homogenous wet mass and maintaining a consistent, dense extrudate.
- If your primary focus is managing a high drug load: Your choice of excipients, particularly the type and grade of MCC, will be the most critical factor.
Mastering these interconnected factors transforms pelletization from a complex challenge into a precise and repeatable manufacturing science.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Variables | Primary Impact on Pellets |
|---|---|---|
| Formulation | API properties, Excipients (e.g., MCC) | Defines plasticity, drug load capacity, and final structure |
| Process | Granulation, Extrusion/Spheronization speed & time | Controls density, sphericity, and size distribution |
| Binder | Liquid volume, type, and addition rate | Determines wet mass consistency and prevents clumping/dusting |
Struggling to achieve consistent, high-quality pellets? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pharmaceutical development. Our expertise can help you optimize your pelletization process, from selecting the right excipients to fine-tuning your spheronization parameters. Let us provide the reliable equipment and support you need to scale your formulation successfully. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- How fast is the rotary tablet press? Unlock Peak Production Speeds for Your Tablets
- What is die compression ratio? Master Your Pelleting Process for Optimal Quality & Efficiency
- What are pill presses called? The Correct Term is Tablet Press for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- What are the different pill presses? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production Scale
- What are the disadvantages of press working? High Costs and Design Limits for Mass Production



















