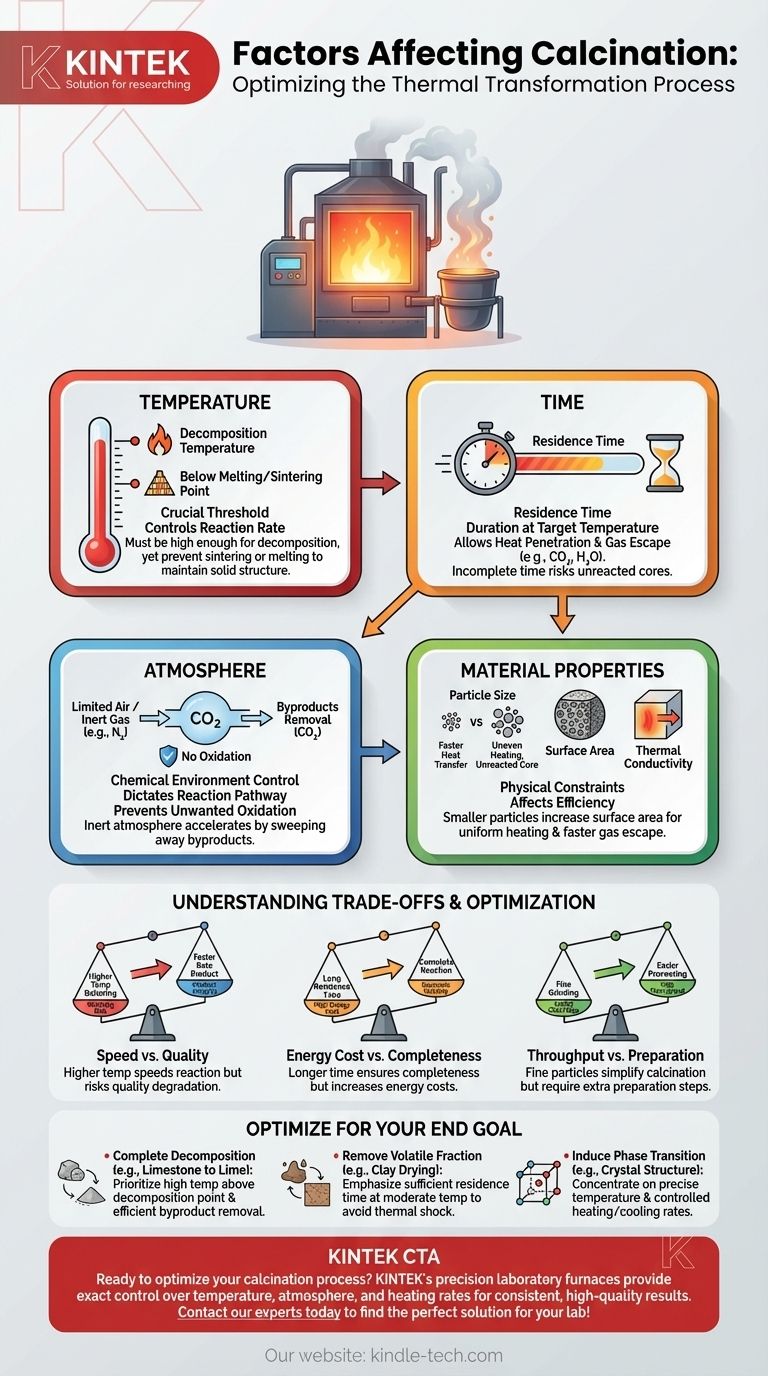
The success of any calcination process depends on the precise control of four primary factors: temperature, time, the surrounding atmosphere, and the physical properties of the material itself. Calcination is a thermal treatment designed to induce a chemical or physical change in a solid, such as thermal decomposition or the removal of volatile components, by heating it to a high temperature but below its melting point.
Calcination is not simply about heating a material. It is a controlled balancing act between temperature, time, and atmosphere to achieve a specific transformation in a material's chemical composition or physical structure without destroying it.

The Core Levers: Temperature and Time
The most fundamental parameters you can control in calcination are how hot you make the material and how long you keep it there. These two factors are inextricably linked.
Achieving the Threshold Temperature
Every calcination reaction, whether it's driving off water or breaking down a carbonate, has a specific decomposition temperature. Below this temperature, the reaction will not proceed at a meaningful rate.
The goal is to operate significantly above this minimum threshold to ensure a practical reaction rate, but always stay safely below the material's melting or sintering point to maintain its solid structure.
The Importance of Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the material is held at the target calcination temperature. A short residence time may result in an incomplete reaction, leaving an uncalcined core within the particles.
Sufficient time must be allowed for heat to penetrate the entire volume of the material and for any gaseous byproducts (like CO₂ or H₂O) to escape.
The Impact of Heating Rate
The speed at which the material is brought up to the target temperature can also influence the final product. A rapid heating rate can cause thermal shock and fracture in some materials or lead to undesirable phase transitions.
The Chemical Environment: Atmosphere Control
The definition of calcination specifies "in the absence or a limited supply of air" for a critical reason. The gas surrounding the material dictates the chemical possibilities.
Defining the Reaction Pathway
The composition of the furnace atmosphere directly impacts the chemical equilibrium. For example, the calcination of limestone (CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂) is driven forward by continuously removing the CO₂ gas produced.
If the atmosphere has a high concentration of CO₂, it can slow or even reverse the reaction. Conversely, using an inert atmosphere like nitrogen can help sweep away byproducts and accelerate the process.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
The "limited supply of air" is crucial when working with materials that can oxidize. By controlling the amount of oxygen, you can prevent unwanted side reactions that would change the chemical nature of the final product.
The Physical Constraints: Material Properties
The inherent characteristics of the solid being processed place fundamental limits on the operation and determine how it will respond to heat.
Particle Size and Surface Area
Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio. This allows for faster and more uniform heat transfer into the particle and easier escape for volatile gases.
Large particles heat unevenly, often resulting in a fully calcined outer shell but an unreacted core. This is one of the most common causes of process failure.
Intrinsic Thermal Properties
A material's thermal conductivity dictates how quickly heat can travel from the surface to the core. Materials with low thermal conductivity are much harder to calcine completely, especially in larger particle sizes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a calcination process always involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to efficient and effective operation.
Speed vs. Quality
Increasing the temperature will speed up the reaction, but it also increases the risk of sintering (particles fusing together) or localized melting. This can degrade the quality of the final product and damage equipment.
Energy Cost vs. Completeness
Holding a material at a high temperature for a very long residence time can guarantee a complete reaction. However, this comes at a significant energy cost, directly impacting the economic viability of the process.
Throughput vs. Preparation
Using very fine particles makes calcination much easier and faster. However, the process of grinding the material to that size adds a significant cost and an extra step (and potential bottleneck) to the overall operation.
Optimizing Calcination for Your Goal
The ideal settings depend entirely on your desired outcome. Use your end goal to determine which factors to prioritize.
- If your primary focus is complete thermal decomposition (e.g., limestone to lime): Prioritize achieving a temperature well above the decomposition point while ensuring the process effectively removes gaseous byproducts.
- If your primary focus is removing a volatile fraction (e.g., water from clay): Emphasize a sufficient residence time at a moderate temperature to drive off the volatile without causing thermal shock or unwanted phase changes.
- If your primary focus is inducing a phase transition (e.g., creating a specific crystal structure): Concentrate on precise temperature control and a well-defined heating and cooling rate, as this will dictate the final crystalline form.
Mastering calcination means understanding it as a system where each of these factors influences the others to deliver a specific material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Must exceed decomposition temperature but stay below melting point. | Controls reaction rate and completeness. |
| Time | Residence time must allow for heat penetration and gas escape. | Determines reaction uniformity and thoroughness. |
| Atmosphere | Limited air supply or inert gas to control chemical pathways. | Prevents unwanted oxidation and removes byproducts. |
| Material Properties | Particle size, surface area, and thermal conductivity. | Affects heat transfer efficiency and reaction speed. |
Ready to optimize your calcination process? KINTEK's precision laboratory furnaces provide the exact control over temperature, atmosphere, and heating rates you need to achieve consistent, high-quality results. Whether you're decomposing carbonates, removing volatiles, or inducing phase transitions, our equipment is designed for reliability and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the speed of kiln for cement? Mastering the Slow Rotation for Optimal Clinker Quality
- What is microwave pyrolysis of polypropylene? An Advanced Chemical Recycling Method
- How is calcination process performed? Master Thermal Decomposition for Industrial Applications
- What fuel is used in rotary kilns? Optimize Your Kiln's Efficiency and Cost
- How do you rejuvenate activated carbon? Restoring Adsorption Power with Thermal Reactivation
- What is the temperature of a rotating kiln? It Depends on Your Material and Process Goal
- What is a rotary kiln? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the disadvantages of rotary kiln? High Costs, Maintenance, and Inefficiency Explained



















