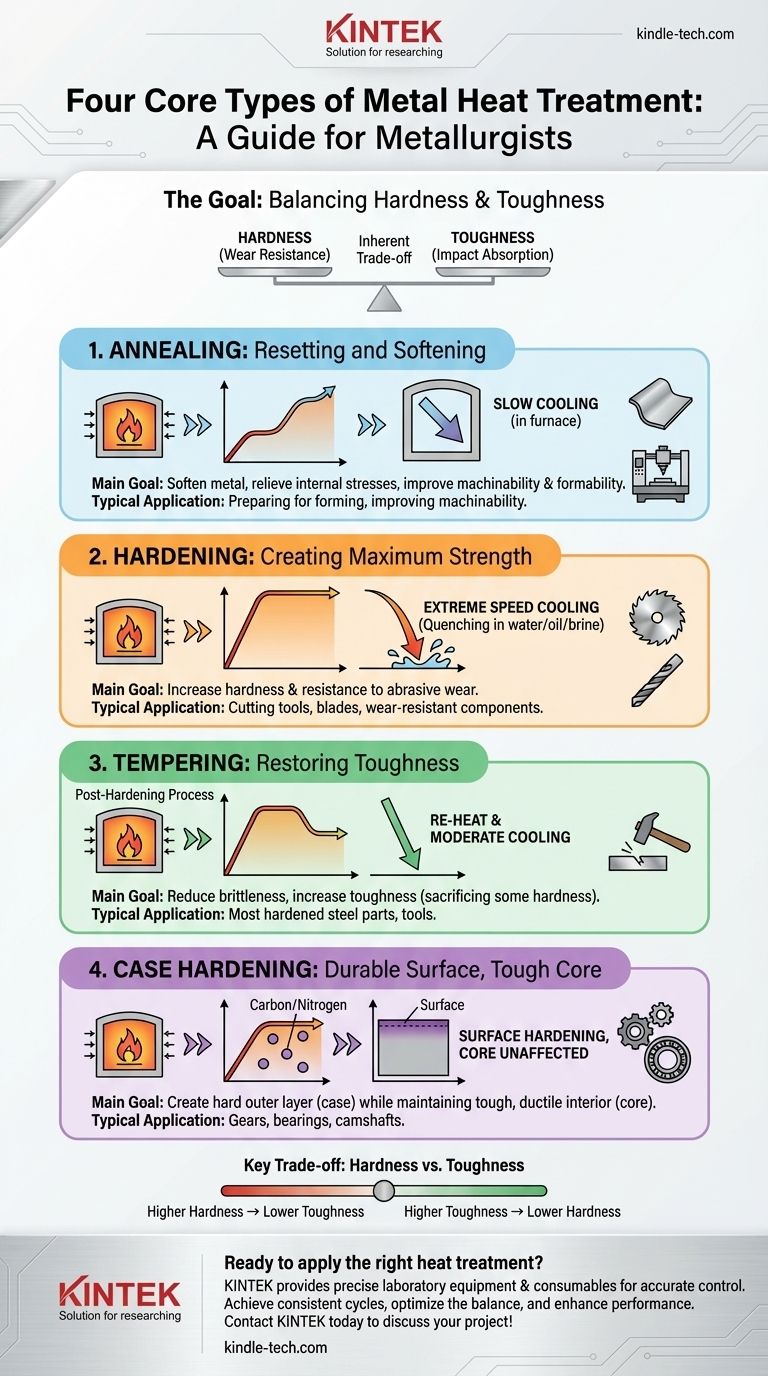
At its core, heat treatment is the controlled process of heating and cooling a metal to fundamentally change its internal structure and, therefore, its physical properties. The four primary types of heat treatment that form the foundation of metallurgy are Annealing, Hardening, Tempering, and Case Hardening. Each process uses a precise thermal cycle to achieve a specific outcome, such as making a metal softer and easier to work with or making it incredibly hard and wear-resistant.
Heat treatment is not a single action but a family of sophisticated processes. The central challenge they solve is managing the inherent trade-off between a metal's hardness (its resistance to wear) and its toughness (its ability to absorb impact without fracturing).

The Foundation: How Heat Treatment Works
Before diving into the specific types, it's crucial to understand the principle at work. Heat treatment physically rearranges the crystalline structure, or "grains," within a metal.
Altering the Crystal Structure
Heating a metal above a critical temperature causes its atoms to rearrange into a different, often more uniform, crystal structure. This phase change effectively "erases" many of the metal's previous properties, like internal stresses from manufacturing.
The Critical Role of Cooling
The most important step is the cooling phase. The rate at which the metal is cooled—whether slowly in the air, rapidly by quenching in oil or water, or at some intermediate speed—locks in a specific grain structure, determining the final properties of the part.
The Four Core Heat Treatment Processes
While many specialized variations exist, they are nearly all based on these four fundamental concepts.
1. Annealing: Resetting and Softening
Annealing is a process designed to make a metal as soft and ductile (formable) as possible. It is often used to relieve internal stresses, improve machinability, and prepare a material for further shaping or forming.
The process involves heating the metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it very slowly, often by leaving it inside the turned-off furnace. This slow cooling allows the internal crystals to grow large and uniform, resulting in maximum softness and ductility.
2. Hardening: Creating Maximum Strength
Hardening, also known as quench hardening, is used to make a metal significantly harder and more resistant to wear. This process is essential for tools, blades, and components that must withstand abrasion.
It involves heating the metal to a temperature where its internal structure changes, then cooling it with extreme speed. This rapid cooling, called quenching, is typically done by plunging the hot metal into water, oil, or brine. This "freezes" the atoms in a very stressed, hard, and brittle crystalline state.
3. Tempering: Restoring Toughness
A metal that has been hardened is often too brittle for practical use; a sharp impact could cause it to shatter. Tempering is a secondary process performed after hardening to reduce that brittleness and increase toughness.
The hardened part is re-heated to a much lower temperature than the hardening temperature and held there for a specific time. This allows some of the internal stresses to relax, sacrificing a small amount of hardness to gain a significant amount of toughness. Virtually all hardened steel parts are subsequently tempered.
4. Case Hardening: A Durable Surface, A Tough Core
Case hardening, or surface hardening, is a technique used to create a part that has a hard, wear-resistant outer layer (the "case") while maintaining a softer, tougher, and more ductile interior (the "core"). This is ideal for components like gears, bearings, and camshafts.
This is achieved by introducing elements like carbon or nitrogen into the surface of a low-carbon steel part, a process known as carburizing or nitriding. The part is then heat-treated in a way that hardens only the high-carbon surface layer, leaving the low-carbon core unaffected and tough.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Hardness vs. Toughness
The choice of heat treatment almost always comes down to balancing hardness and toughness. These two properties are inversely related.
What is Hardness?
Hardness is a metal's ability to resist indentation, scratching, and abrasive wear. A hard material is essential for cutting edges and surfaces that experience friction.
What is Toughness?
Toughness is a metal's ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. A tough material can withstand sudden impacts and shock loads. A glass plate is very hard but has almost zero toughness.
The Inherent Conflict
The crystalline structures that make a metal hard are typically rigid and stressed, making them prone to fracture (brittle). The structures that make a metal tough are more ductile and able to move, making them softer. The goal of a metallurgist is to use heat treatment to find the optimal balance for a specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right process depends entirely on the component's intended function.
- If your primary focus is machinability or formability: Annealing is your process, as it softens the material and relieves internal stresses to prevent cracking during manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and strength: Hardening followed by Tempering provides the necessary hardness for a cutting tool or bearing while managing its inherent brittleness.
- If you need a wear-resistant surface but a shock-absorbent core: Case Hardening is the ideal solution for parts like gears that must endure surface friction while absorbing operational impacts.
By understanding these core processes, you can specify or select materials engineered to perform their function with optimal reliability and longevity.
Summary Table:
| Process | Main Goal | Key Mechanism | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften metal, relieve stress | Heat & slow cool in furnace | Improving machinability, preparing for forming |
| Hardening | Increase hardness & wear resistance | Heat & rapid quench (oil/water) | Cutting tools, blades, wear-resistant parts |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness, increase toughness | Re-heat hardened metal to lower temperature | Post-hardening treatment for tools and components |
| Case Hardening | Hard surface, tough core | Infuse carbon/nitrogen into surface layer | Gears, bearings, camshafts needing surface durability |
Ready to apply the right heat treatment for your metal components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise laboratory equipment and consumables needed for advanced material processing. Whether you're working on annealing, hardening, tempering, or case hardening, our solutions ensure accurate temperature control and reliable results.
We help you:
- Achieve consistent and repeatable heat treatment cycles
- Optimize the hardness vs. toughness balance for your specific application
- Enhance the durability and performance of your metal parts
Let our experts guide you to the ideal equipment for your laboratory's needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how we can support your material science goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of laboratory muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How do you clean a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Safety and Longevity
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- What is the main function of the muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Heating Without Contamination
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace in a lab? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Heat for Your Materials



















