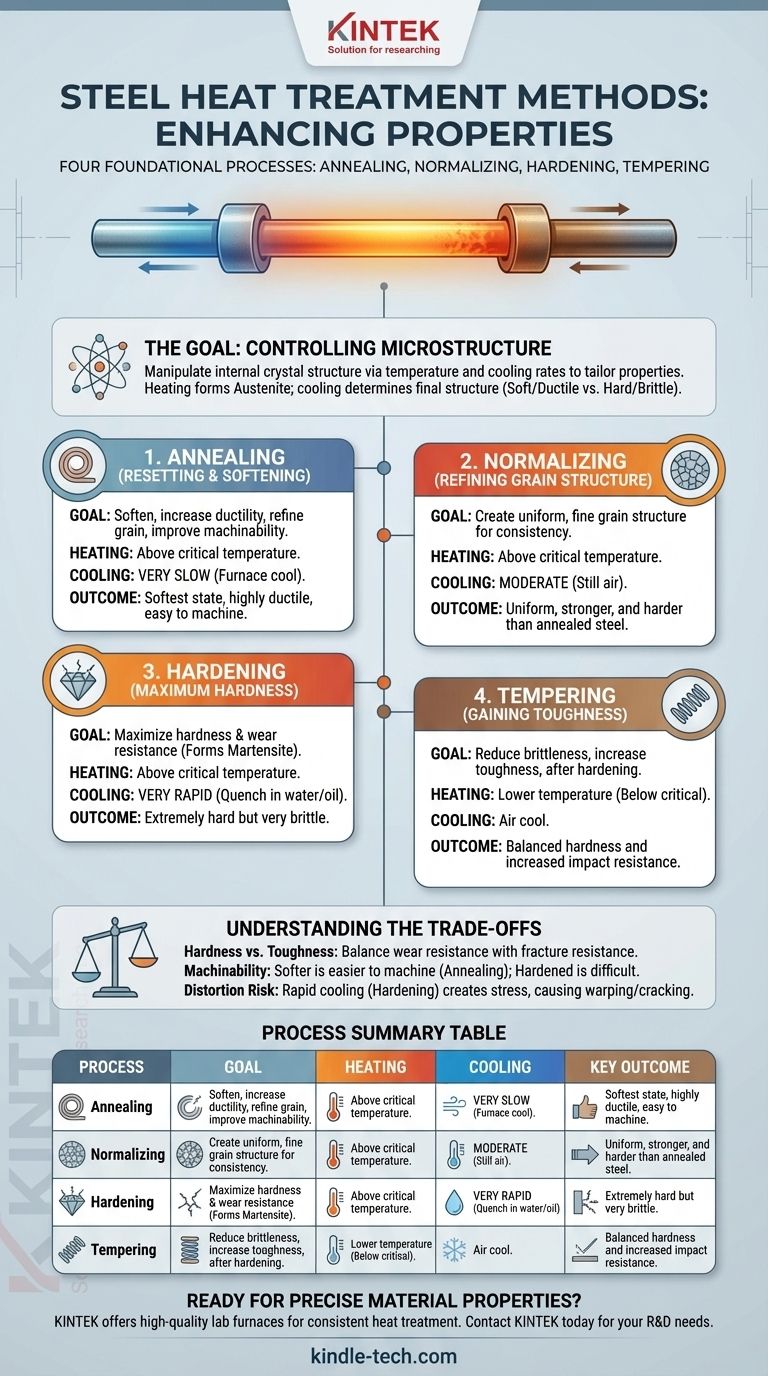
At its core, steel heat treatment involves four foundational processes: annealing, normalizing, hardening, and tempering. Each process modifies the internal structure of the steel by using a specific cycle of heating and cooling to achieve distinct properties. Annealing produces the softest state, hardening produces the hardest, and normalizing and tempering achieve a balance of properties between those two extremes.
Heat treatment is the controlled manipulation of steel's internal crystal structure. By carefully managing temperature and cooling rates, you can precisely tailor the material's properties—trading hardness for toughness or ductility for strength—to meet the demands of a specific engineering application.
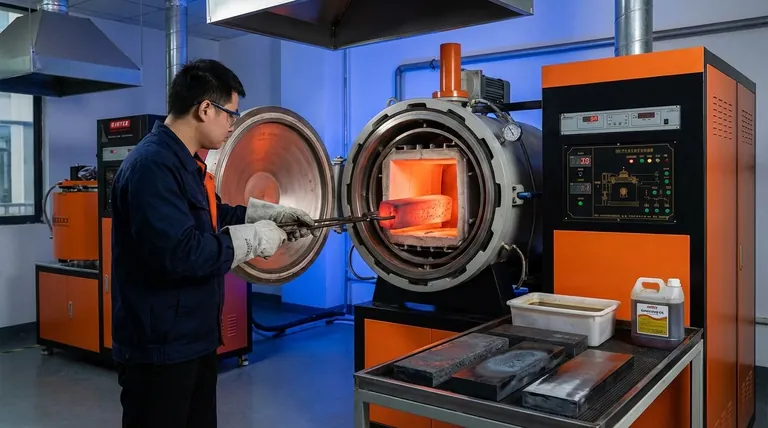

The Goal of Heat Treatment: Controlling the Microstructure
To understand heat treatment, you must first understand that steel is not a static material. Its properties are a direct result of its internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure, which can be changed with heat.
Why Steel's Properties Can Be Changed
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. Heating the steel above a critical temperature rearranges its atoms into a structure called austenite, which can dissolve carbon.
The final properties of the steel are determined by what happens to this austenite structure as it cools.
The Role of Temperature and Cooling Rate
The rate of cooling is the most critical variable in heat treatment. A slow cooling rate allows the atoms to rearrange into soft, ductile structures, while a very rapid cooling rate traps them in a hard, brittle structure.
The Four Foundational Heat Treatment Processes
These four processes represent a spectrum of outcomes, from the softest and most workable state to the hardest and most wear-resistant.
1. Annealing: Resetting and Softening the Steel
Annealing is a process used to make steel as soft, ductile, and easy to machine as possible. It refines the grain structure, relieves internal stresses, and improves electrical conductivity.
The process involves heating the steel above its critical temperature and then cooling it as slowly as possible, often by leaving it inside the turned-off furnace to cool over many hours.
2. Normalizing: Refining the Grain Structure
Normalizing is often used to produce a uniform and fine-grained microstructure that provides a predictable starting point for further hardening. It results in steel that is stronger and harder than annealed steel.
Like annealing, it involves heating above the critical temperature. However, the cooling is done in still air, which is faster than furnace cooling but much slower than a quench.
3. Hardening (Quenching): Achieving Maximum Hardness
The goal of hardening is to make steel extremely hard and wear-resistant. This is achieved by forming a very hard, brittle microstructure called martensite.
This requires heating the steel to its austenitic range and then cooling it very rapidly by plunging it into a quenching medium like water, oil, or brine. The resulting steel is exceptionally hard but also very brittle.
4. Tempering: Gaining Toughness by Sacrificing Hardness
A hardened part is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary process performed after hardening to reduce that brittleness and increase toughness.
The process involves re-heating the hardened part to a lower temperature (well below the critical point) and holding it for a set time. This process trades some of the extreme hardness gained during quenching for a significant increase in toughness and impact resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process is always an exercise in balancing competing properties. No single process is "best"; it is only best for a specific goal.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Hardness is the ability to resist scratching and wear. Toughness is the ability to absorb energy and resist fracture.
A fully hardened, untempered steel file is extremely hard but will shatter if dropped. A steel spring is tempered to be less hard but much tougher, allowing it to flex without breaking.
The Impact on Machinability
A softer material is easier to machine, cut, and form. Annealing is often performed specifically to make a part easy to work with before it undergoes a final hardening process. Trying to machine a fully hardened piece of steel is extremely difficult and requires specialized tooling.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The extreme temperature changes involved in hardening, specifically rapid quenching, create immense internal stresses. These stresses can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack, particularly in complex geometries. This risk must be managed through proper technique and process control.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the intended function of the steel component.
- If your primary focus is maximum workability and machinability: Choose annealing to make the steel as soft and ductile as possible before fabrication.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and ductility for structural use: Choose normalizing to create a uniform, refined, and reliable grain structure.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and surface hardness: Use a hardening (quench) and tempering cycle to achieve high hardness with the necessary toughness to prevent fracture.
- If your primary focus is a wear-resistant surface with a shock-resistant core: Use a specialized surface treatment like case hardening, where only the outer layer is hardened.
Understanding these fundamental processes empowers you to specify not just a material, but a material conditioned for optimal performance in its intended role.
Summary Table:
| Process | Goal | Heating | Cooling | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften & relieve stress | Above critical temperature | Very slow (furnace cool) | Soft, ductile, easy to machine |
| Normalizing | Refine grain structure | Above critical temperature | Moderate (still air) | Uniform, stronger than annealed |
| Hardening | Maximize hardness | Above critical temperature | Very rapid (quench) | Extremely hard but brittle |
| Tempering | Increase toughness | Below critical temperature | Air cool after hold | Reduces brittleness, improves toughness |
Ready to achieve precise material properties in your lab? The right heat treatment requires precise temperature control. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment for annealing, hardening, tempering, and more. Our solutions help you achieve consistent, reliable results for your material testing and R&D needs.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect furnace for your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















