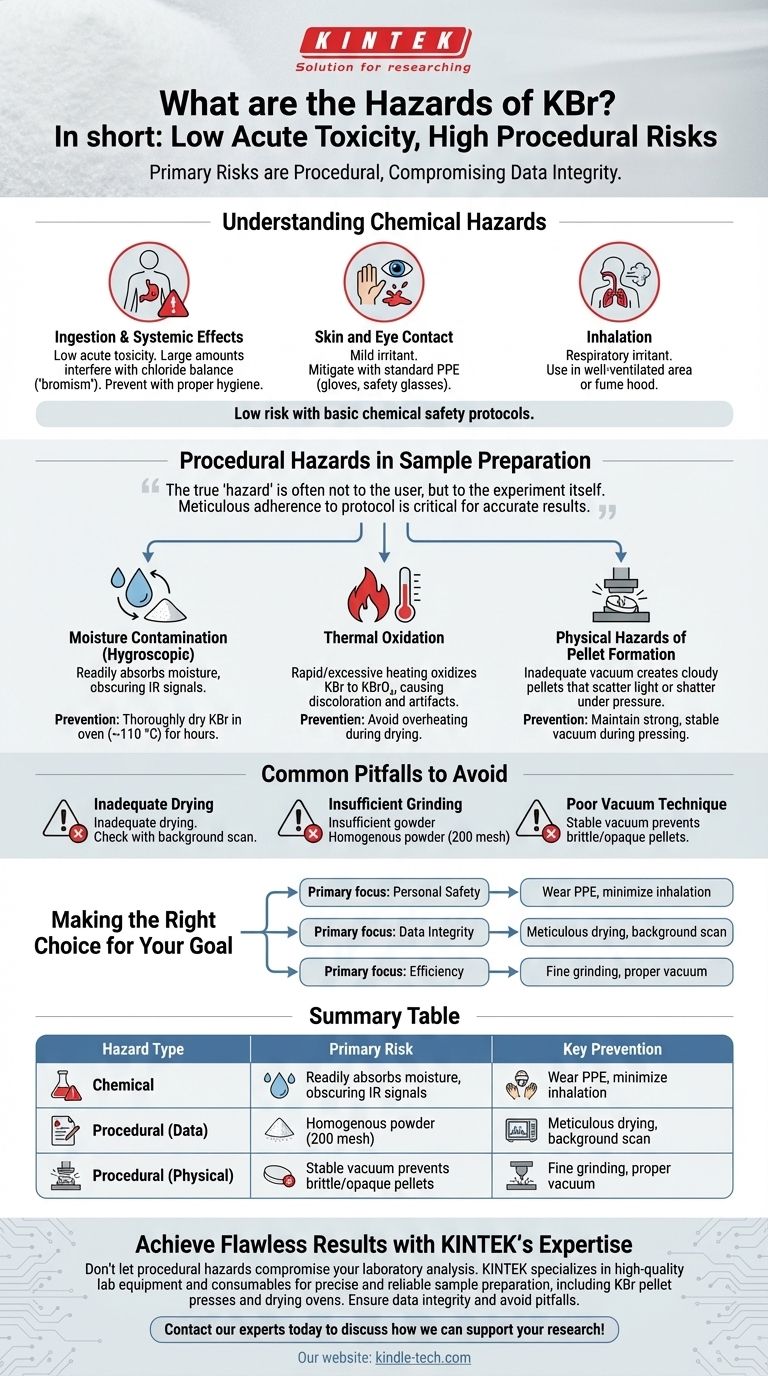
In short, Potassium Bromide (KBr) is a salt with low acute toxicity, but its primary hazards in a laboratory setting are procedural. While it can cause mild irritation upon contact and is harmful if ingested in large amounts, the more common risks involve procedural errors during sample preparation—such as using wet material or overheating—which compromise the integrity of your results.
The true "hazard" of using KBr is often not to the user, but to the experiment itself. While basic chemical safety is necessary, meticulous adherence to preparation protocol is the most critical factor for achieving accurate, repeatable results.

Understanding the Chemical Hazards
While KBr is not highly dangerous, it's essential to follow standard laboratory safety protocols. Its risks are comparable to those of many common laboratory salts.
Ingestion and Systemic Effects
KBr has a low level of acute toxicity. However, ingesting large quantities can interfere with the body's chloride balance and lead to a condition called "bromism," with symptoms like depression, confusion, and neurological issues. This is not a risk with proper lab hygiene.
Skin and Eye Contact
As a salt, KBr can act as a mild irritant to the skin and, more significantly, the eyes. Wearing standard personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves and safety glasses, is sufficient to mitigate this risk.
Inhalation
Inhaling KBr powder can cause irritation to the respiratory tract. Handling the fine powder in a well-ventilated area or using a fume hood for transfers can prevent this.
Procedural Hazards in Sample Preparation
For applications like infrared (IR) spectroscopy, the most significant "hazards" are the procedural mistakes that ruin your sample and invalidate your data. These are the risks that demand the most attention in practice.
The Risk of Moisture Contamination
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. If wet KBr is used to make a pellet, the trapped water will produce broad, strong absorption bands in your IR spectrum, potentially obscuring the signals from your actual sample.
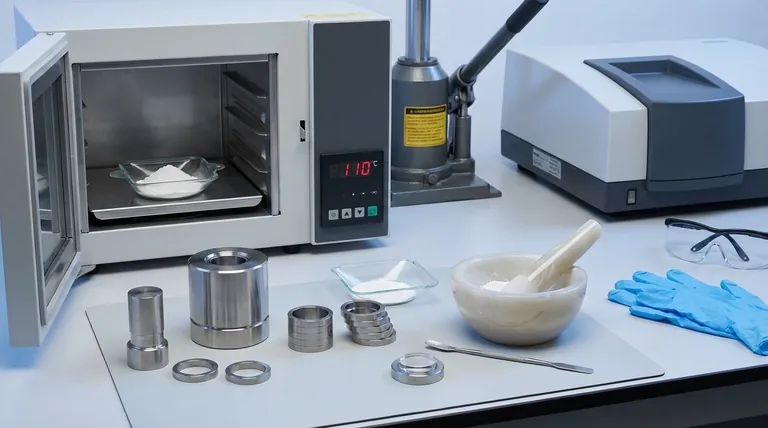
This is why KBr must be thoroughly dried in an oven at around 110 °C for several hours before use.
The Hazard of Thermal Oxidation
While drying is critical, rapid or excessive heating of KBr can cause it to oxidize into potassium bromate (KBrO₃).
This unwanted chemical change can cause discoloration of the pellet and introduce artifacts into your analysis. It represents a hazard to the chemical purity of your blank and the accuracy of your results.
Physical Hazards of Pellet Formation
Creating a KBr pellet requires a high-pressure press and a vacuum to remove trapped air. An inadequate vacuum can lead to a cloudy, opaque pellet that scatters light, degrading the quality of your spectrum.
More importantly, a poorly formed or brittle pellet can shatter under pressure, which is a minor physical safety risk and a major source of wasted time and sample material.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Success with KBr requires balancing competing procedural demands. Avoiding these common mistakes is key.
Inadequate Drying
Failing to dry the KBr powder sufficiently is the most common error. Always perform a background measurement with a pellet made of only your dried KBr to check for the characteristic broad peaks of water contamination.
Insufficient Grinding
The KBr and sample must be pulverized into an extremely fine, homogenous powder (ideally 200 mesh or finer). Coarse particles lead to light scattering, which causes a sloping baseline and poor-quality spectra.
Poor Vacuum Technique
Applying pressure without maintaining a strong, stable vacuum is a frequent mistake. Trapped air makes the pellet brittle and opaque, compromising the measurement and increasing the risk of the pellet breaking during handling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific safety and handling focus depends on what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Wear standard PPE (gloves and safety glasses) and handle the powder in a way that minimizes inhalation.
- If your primary focus is data integrity: Prioritize meticulous drying of the KBr powder and run a background scan on a KBr-only pellet to confirm the absence of water.
- If your primary focus is efficiency: Ensure your KBr is finely ground and you use proper vacuum technique to avoid having to remake broken or opaque pellets.
Ultimately, mastering the procedure for handling KBr is the key to ensuring both personal safety and the success of your experiment.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Type | Primary Risk | Key Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Mild skin/eye irritation, harmful if ingested | Wear standard PPE (gloves, safety glasses) |
| Procedural (Data) | Moisture contamination, thermal oxidation, poor pellet formation | Dry KBr thoroughly, avoid overheating, use proper vacuum technique |
| Procedural (Physical) | Pellet shattering under pressure | Ensure stable vacuum during pressing |
Achieve Flawless Results with KINTEK's Expertise
Don't let procedural hazards compromise your laboratory analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for precise and reliable sample preparation, including KBr pellet presses and drying ovens. Our products are designed to help you avoid common pitfalls like moisture contamination and thermal oxidation, ensuring the integrity of your IR spectroscopy data.
Whether you are setting up a new lab or optimizing your current processes, KINTEK is your trusted partner for all your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research and ensure your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the size range of pellets? From 1mm to 25mm, Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What is a KBr pellet? A Guide to Preparing Solid Samples for IR Spectroscopy
- Why only KBr is used in IR spectroscopy? The Truth About the Best Material for Your Sample
- Why use KBr to make the pellet? Achieve Clear, Accurate IR Spectroscopy Results
- How do you do the KBr pellet method? A Step-by-Step Guide to Perfect FTIR Sample Preparation










