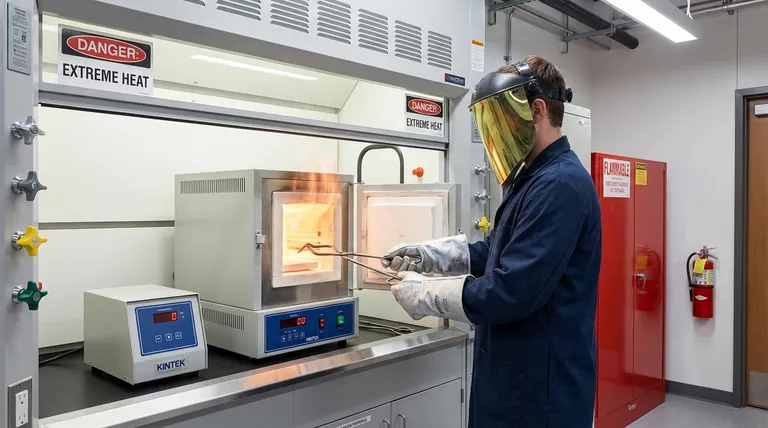
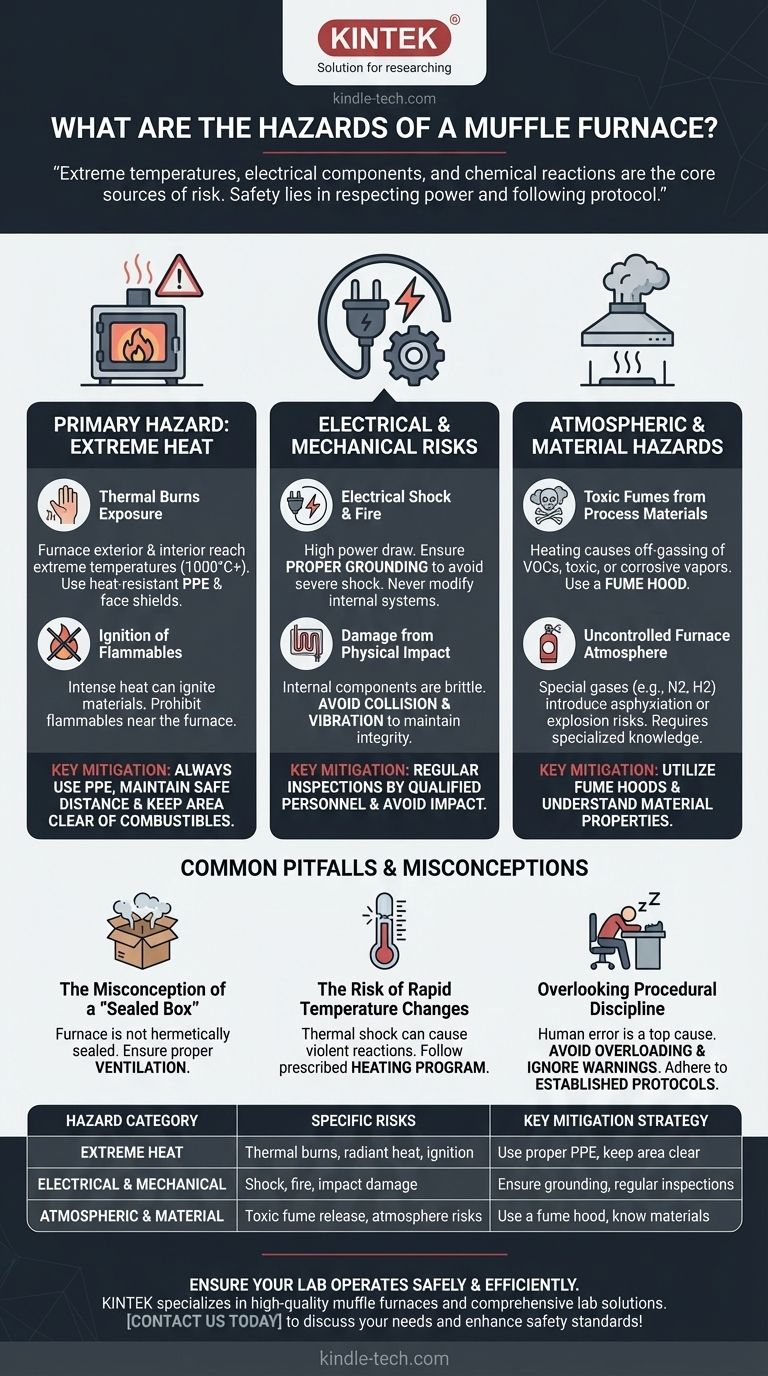
At its core, a muffle furnace presents three primary hazards: extreme heat capable of causing severe burns and igniting nearby materials, the risk of electrical shock or fire from its high-power components, and the potential for releasing toxic fumes depending on the materials being processed. Safe operation requires a disciplined approach to managing these fundamental risks.
While muffle furnaces are generally reliable and designed for safety, the real hazards emerge not from the furnace itself, but from the extreme temperatures it generates and the chemical reactions it facilitates. The key to safety is respecting the power of the tool and rigorously following operational protocol.

The Primary Hazard: Extreme Heat
The most obvious and immediate danger of a muffle furnace is its ability to reach and maintain extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F). This heat presents several risks.
Thermal Burns from Contact
Even with advanced insulation, the exterior surfaces of a furnace can become hot enough to cause serious burns. The interior and the door are at extreme temperatures during and after operation. Always use appropriate thermal-resistant personal protective equipment (PPE), such as heat-resistant gloves and face shields.
Radiant Heat Exposure
Working near an operating furnace, especially when the door is open, exposes you to intense radiant heat. This can cause skin damage and heat stress over time. Limit exposure and maintain a safe distance whenever possible.
Ignition of Flammable Materials
The intense heat can easily ignite combustible materials. It is critical to prohibit placing flammable or combustible materials anywhere near the furnace. This includes solvents, paper, cleaning rags, and certain plastics. The operational area must be kept clear.
Electrical and Mechanical Risks
A muffle furnace is a powerful piece of electrical equipment that requires respect for its internal systems and physical structure.
Electrical Shock and Fire
Muffle furnaces draw significant electrical power. A fault in the wiring or a failure to ensure the unit is properly grounded can create a severe risk of electrical shock. Regular equipment checks by qualified personnel are essential, and you should never attempt to privately modify the furnace's electrical systems.
Damage from Physical Impact
The internal components, particularly the heating elements and insulation, can be brittle. Avoiding collision and vibration is crucial for maintaining the furnace's integrity. A cracked heating element or damaged insulation compromises both performance and safety.
Atmospheric and Material Hazards
Some of the most overlooked hazards are not from the furnace itself, but from the materials you put inside it and the atmosphere you create.
Toxic Fumes from Process Materials
Heating materials—a process known as off-gassing—can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), toxic fumes, or corrosive vapors. This is a primary reason why placing the furnace in a fume hood is recommended, especially if the materials being processed are unknown or known to be hazardous when heated.
Uncontrolled Furnace Atmosphere
Some processes require using specific gases like nitrogen or hydrogen to create a controlled atmosphere. These gases introduce their own risks, such as asphyxiation (in the case of nitrogen) or flammability and explosion (in the case of hydrogen). Managing the furnace atmosphere requires specialized knowledge and procedures.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Trusting the equipment implicitly without understanding its operational limits is a common source of incidents. Adhering to protocol is non-negotiable.
The Misconception of a "Sealed Box"
While well-insulated, a furnace is not a hermetically sealed containment unit. A malfunction, improper door seal, or rapid off-gassing from a sample can cause hazardous fumes to leak into the lab environment. Always ensure proper ventilation is available.
The Risk of Rapid Temperature Changes
Subjecting the furnace or the material inside to thermal shock is dangerous. Following the prescribed heating program and avoiding rapid cooling prevents damage to the furnace's ceramic lining. It also prevents violent, unexpected reactions or shattering of the material being processed.
Overlooking Procedural Discipline
The most common cause of furnace-related incidents is human error. Overloading the furnace, failing to properly train operators, ignoring safety warnings, or becoming complacent are direct paths to accidents. Strict adherence to established safety protocols is the single most effective risk mitigation tool.
Making the Right Choice for Safe Operation
Your operational focus will determine which safety protocols are most critical. Prioritize your procedures based on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Enforce mandatory use of PPE, provide comprehensive training on all procedures, and ensure the area is well-ventilated and clear of all combustibles.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Strictly follow programmed heating and cooling rates, perform regular electrical and mechanical inspections, and protect the unit from any physical impact.
- If your primary focus is process integrity and air quality: Thoroughly understand the off-gassing properties of your materials and utilize a fume hood whenever there is a risk of releasing hazardous fumes.
Ultimately, treating the muffle furnace as the powerful and precise tool it is ensures both safety and successful results.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Specific Risks | Key Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Heat | Thermal burns, radiant heat exposure, ignition of flammables | Use proper PPE, keep area clear of combustibles |
| Electrical & Mechanical | Electrical shock, fire, damage from impact | Ensure proper grounding, regular inspections, avoid physical impact |
| Atmospheric & Material | Toxic fume release, risks from controlled atmospheres | Use a fume hood, understand material properties |
Ensure your lab operates safely and efficiently with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality, reliable muffle furnaces and comprehensive lab equipment solutions designed with safety in mind. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace for your specific application and provide guidance on safe operation protocols. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and enhance your safety standards!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the 3 official methods in determining ash and water content? A Guide to Proximate Analysis
- What causes increase in ash content? Uncover the hidden culprits that harm your equipment.
- What is the muffle furnace used for ash content? Achieve Accurate Gravimetric Analysis
- What is the ashing method of muffle furnace? A Guide to Accurate Sample Analysis
- How is ash content determined using muffle furnace? Achieve Accurate Mineral Analysis



















