For operating in high-temperature oxidizing environments, your primary material choices are metallic iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) and nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloys, or ceramic silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements. Each material functions by forming a stable, protective oxide layer on its surface that prevents the underlying element from rapidly degrading in air. The best choice depends entirely on your maximum required temperature, budget, and operational demands.
The selection of a heating element is not merely a question of withstanding heat. It is a calculated trade-off between a material's maximum operating temperature, its initial cost, its expected lifespan, and its specific vulnerabilities in a given furnace environment.

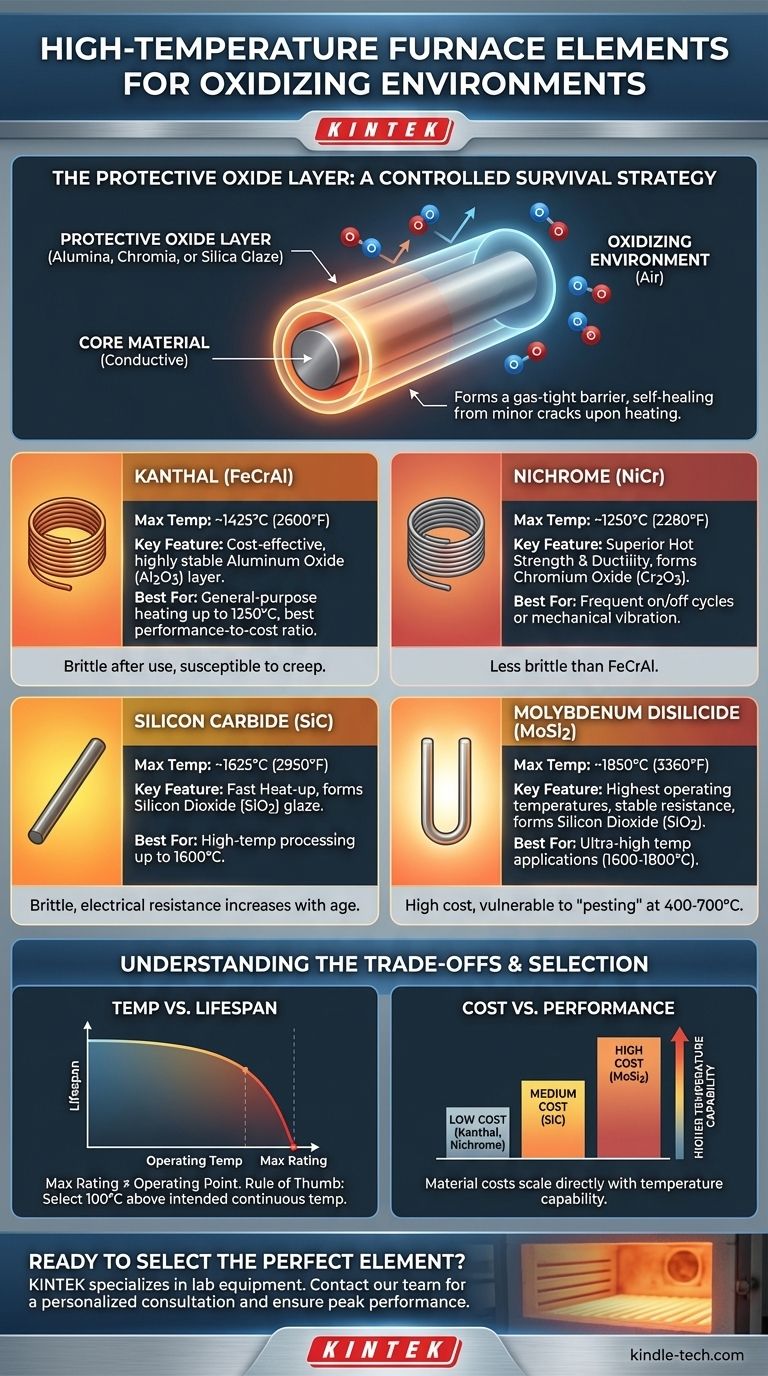
The Critical Role of the Protective Oxide Layer
All high-temperature elements designed for air use share a common survival strategy: they embrace oxidation, but in a controlled manner.
How Self-Protection Works
These materials do not resist oxidation; they are specifically designed to form a thin, stable, and electrically non-conductive oxide layer when first heated. For FeCrAl alloys, this is an aluminum oxide (alumina) layer. For NiCr, it is chromium oxide. For SiC and MoSi2, it is a silicon dioxide (silica) "glaze."
This layer acts as a gas-tight barrier, protecting the core conductive material from further, destructive oxidation. A good element is, in effect, self-healing, as minor cracks in the oxide layer can be repaired upon subsequent heating.
The Enemies of the Oxide Layer
The protective oxide layer is robust but not invincible. Chemical attack from contaminants within the furnace, such as certain salts or metals, can flux and destroy the layer.
Likewise, operating in a reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen or dissociated ammonia), even for a short time, is catastrophic. These gases will strip the oxygen from the protective layer, leading to rapid element failure.
A Breakdown of Common Heating Element Materials
Your choice of material is primarily dictated by your required operating temperature.
Kanthal (FeCrAl) Alloys
Kanthal and similar FeCrAl alloys are the workhorses of the industry for general-purpose heating in air. They form a highly stable aluminum oxide (Al2O3) protective layer.
Their maximum element temperature is typically around 1425°C (2600°F). They offer the best performance-to-cost ratio of any metallic element but become brittle after their first use and are susceptible to creep (sagging at high temperatures), requiring proper support.
Nichrome (NiCr) Alloys
Nichrome alloys form a chromium oxide (Cr2O3) layer. They have a lower maximum operating temperature than Kanthal, generally around 1250°C (2280°F).
Their key advantage is superior hot strength and ductility. They remain less brittle than FeCrAl alloys after thermal cycling, making them a better choice for applications involving frequent on/off cycles or mechanical vibration.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are rigid, self-supporting ceramic rods or tubes. They operate by forming a silicon dioxide (SiO2) protective layer and can be used up to 1625°C (2950°F).
SiC provides very fast heat-up times. However, the elements are brittle and sensitive to thermal shock. Critically, their electrical resistance increases with age, which requires a more complex power supply (typically a multi-tap transformer or an SCR) to maintain consistent power output over the element's life.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements offer the highest operating temperatures in air, up to 1850°C (3360°F). They also form a protective silicon dioxide (SiO2) glaze.
These elements have a stable resistance over their long lifespan. Their major drawbacks are high cost and extreme brittleness at room temperature. They are also vulnerable to a catastrophic low-temperature oxidation phenomenon known as "pesting" between 400-700°C, which requires heating them through this range very quickly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an element is an engineering decision that balances competing factors.
Temperature vs. Lifespan
An element's maximum rated temperature is a limit, not a recommended operating point. Operating an element continuously near its maximum temperature will dramatically shorten its life.
For a reasonable service life, a good rule of thumb is to select an element with a maximum rating at least 100°C above your intended continuous operating temperature.
Cost vs. Performance
The material costs scale directly with temperature capability.
- Low Cost: Kanthal (FeCrAl) & Nichrome (NiCr)
- Medium Cost: Silicon Carbide (SiC)
- High Cost: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
You are paying for the ability to operate reliably at extreme temperatures. Attempting to save money by pushing a lower-rated element beyond its limits will always result in premature failure and higher long-term costs.
Mechanical Properties and Installation
Metallic elements like Kanthal and Nichrome are supplied as wire or ribbon and can be formed into coils. They are ductile before use but require careful ceramic supports to prevent sagging and short-circuiting during operation.
Ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi2 are rigid and brittle. They must be handled with extreme care and mounted precisely according to the manufacturer's specifications to avoid stress fractures.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Base your decision on your single most important operational requirement.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heating up to 1350°C: Kanthal (FeCrAl) is the standard and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is durability under frequent cycling below 1200°C: Nichrome (NiCr) provides better fatigue resistance than Kanthal.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature processing up to 1600°C: Silicon Carbide (SiC) is the industry workhorse, provided you can manage its aging resistance.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (1600-1800°C) in air: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is the premier solution, justifying its high cost and specific handling needs.
By understanding the underlying principles of how these materials function, you can confidently specify the right element that ensures both performance and reliability for your furnace.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temp (°C) | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kanthal (FeCrAl) | ~1425°C | Cost-effective | General heating up to 1350°C |
| Nichrome (NiCr) | ~1250°C | Excellent hot strength | Frequent on/off cycles |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | ~1625°C | Fast heat-up | High-temp work up to 1600°C |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | ~1850°C | Highest temperature | Ultra-high temp applications |
Ready to select the perfect heating element for your high-temperature furnace? The right choice is critical for performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between FeCrAl, NiCr, SiC, and MoSi2 to ensure you get a solution perfectly matched to your temperature requirements, operational demands, and budget. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and ensure your furnace operates at peak performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs



















