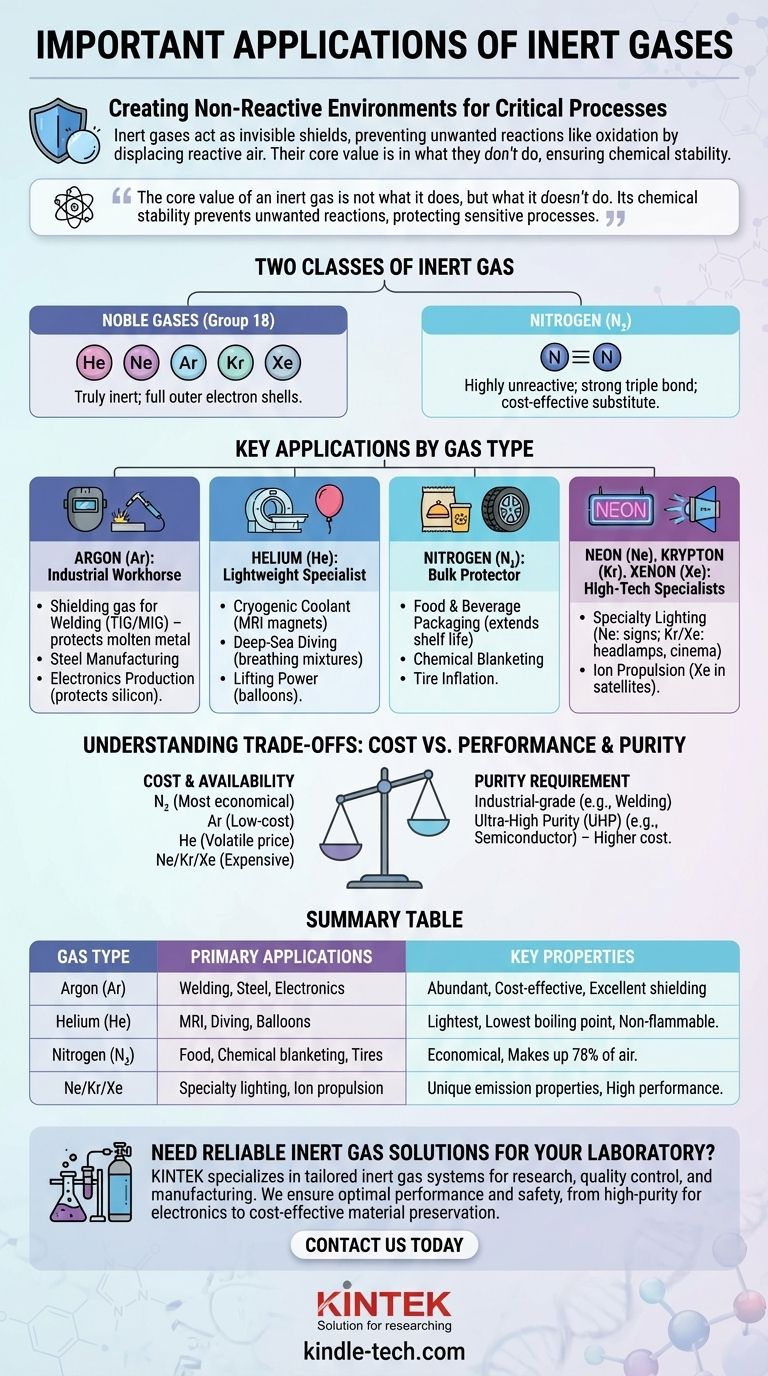
In short, inert gases are critical for creating non-reactive environments in countless industrial, scientific, and commercial processes. Their primary applications include welding and metal fabrication, manufacturing sensitive electronics, preserving food and beverages, and powering specialized lighting and medical equipment. They serve as invisible shields, protecting materials from an unwanted chemical reaction like oxidation.
The core value of an inert gas is not what it does, but what it doesn't do. Its chemical stability prevents unwanted reactions, protecting sensitive processes and materials, making it an essential enabler for modern technology from semiconductor chips to fresh-packaged foods.

The Core Principle: Why "Inert" Matters
The Power of Non-Reactivity
The term "inert" refers to a substance that is chemically non-reactive. For the noble gases (like helium, neon, and argon), this is because their outermost electron shells are completely full, leaving them with no tendency to share, gain, or lose electrons.
This stability is their superpower. In many processes, the oxygen and moisture in the ambient air are destructive, causing oxidation (like rust), combustion, or other degradations. Inert gases are used to displace this reactive air, creating a protective atmosphere.
The Two Classes of Inert Gas
We can group these gases into two categories. The first is the noble gases (Group 18 of the periodic table), which are truly inert.
The second is a gas like nitrogen (N₂), which is not a noble gas but is highly unreactive under many conditions due to the strong triple bond holding its two atoms together. It is often used as a cost-effective substitute for noble gases.
Key Applications by Gas Type
Argon (Ar): The Industrial Workhorse
Argon is the most widely used inert gas, primarily because it is abundant and low-cost. As the references note, it is readily obtained by separating it from the air.
Its most common application is as a shielding gas in welding (like TIG and MIG welding). It protects the molten metal weld pool from oxygen and water vapor, preventing defects and ensuring a strong, clean weld. It's also used in steel manufacturing and in the production of sensitive electronics to protect silicon crystals from impurities.
Helium (He): The Lightweight Specialist
Helium has two unique properties: it is the second-lightest element and it has the lowest boiling point of any substance. This makes it irreplaceable for specific, high-value applications.
Its primary use is as a cryogenic coolant for the superconducting magnets in MRI machines and NMR spectrometers. It is also used in deep-sea diving breathing mixtures to replace nitrogen and prevent nitrogen narcosis, and for its lifting power in high-altitude balloons. Unlike other inert gases, helium is sourced from natural gas deposits.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Bulk Protector
While not a noble gas, nitrogen is often the most economical choice for creating an inert atmosphere. It makes up 78% of the air we breathe.
Its most visible application is in food and beverage packaging, where it displaces oxygen to extend shelf life and prevent spoilage. It is also used to inflate aircraft and race car tires, as it is less prone to pressure changes with temperature, and to provide a "blanket" over flammable chemicals in industrial settings.
Neon (Ne), Krypton (Kr), and Xenon (Xe): The High-Tech Specialists
These are the rarer and more expensive noble gases, reserved for applications where their unique properties are essential.
Neon is famous for its use in creating brilliant reddish-orange advertising signs. Krypton and Xenon are used in high-performance lighting, such as long-lasting incandescent bulbs, car headlamps, and cinema projectors, because they slow the evaporation of the filament. Xenon is also finding increasing use in satellite ion propulsion systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
Cost and Availability
The choice of an inert gas is often a balance between its required properties and its cost.
As noted in the references, Argon is relatively inexpensive due to its high natural abundance in the air. Nitrogen is even more economical.
Helium's price is more volatile, as it is a finite resource extracted from natural gas. The rarer gases—Neon, Krypton, and Xenon—are significantly more expensive due to their extremely low concentrations in the atmosphere, limiting their use to niche applications.
The Purity Requirement
For general-purpose shielding like in welding, standard industrial-grade purity is sufficient.
However, for high-tech applications like semiconductor manufacturing, ultra-high purity (UHP) gas is mandatory. Even minuscule impurities can ruin a multi-million dollar batch of microchips. This higher purity level, often produced by specialized on-site generators, significantly increases the cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct inert gas requires aligning its specific properties with your technical needs and budget.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose shielding: Nitrogen is the most economical choice for blanketing, while Argon is the standard for high-quality welding.
- If your primary focus is achieving extremely low temperatures or lifting: Helium is the only technically viable option due to its unique physical properties.
- If your primary focus is high-performance lighting or propulsion: The unique atomic properties of Xenon and Krypton are necessary, justifying their high cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum inertness for sensitive materials: Argon is a safer bet than Nitrogen, which can react and form nitrides at very high temperatures.
Ultimately, understanding the role of these invisible gases is key to controlling the outcome of countless critical processes.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Applications | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | Welding, steel manufacturing, electronics | Abundant, cost-effective, excellent shielding |
| Helium (He) | MRI cooling, deep-sea diving, balloons | Lightest, lowest boiling point, non-flammable |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Food packaging, chemical blanketing, tires | Economical, makes up 78% of air |
| Neon/Krypton/Xenon | Specialty lighting, ion propulsion | Unique emission properties, high performance |
Need Reliable Inert Gas Solutions for Your Laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored inert gas systems for research, quality control, and manufacturing processes. Whether you require high-purity gases for sensitive electronics or cost-effective solutions for material preservation, our expertise ensures optimal performance and safety.
Contact us today to discuss how our inert gas solutions can protect your processes and enhance your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- 50L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere



















