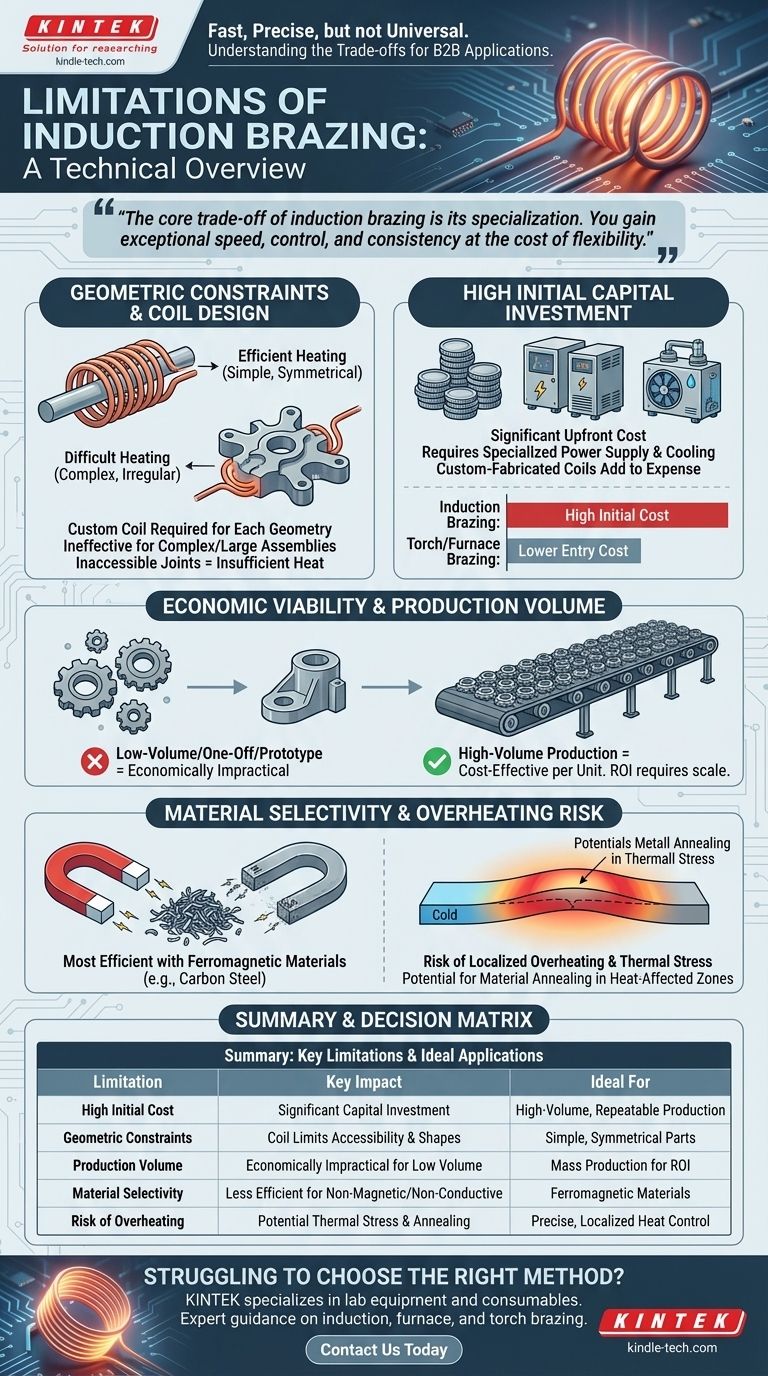
While incredibly fast and precise, induction brazing is not a universal solution. Its primary limitations revolve around the high initial equipment cost, the geometric constraints imposed by the induction coil, and its unsuitability for low-volume or highly complex assemblies. This method excels with simple, repeatable joints in high-volume production but becomes less practical for custom or intricate work.
The core trade-off of induction brazing is its specialization. You gain exceptional speed, control, and consistency at the cost of flexibility, making it a powerful tool for the right application but an expensive and restrictive one for the wrong one.
The Fundamental Challenge: Geometry and Coil Design
Induction brazing relies on a magnetic field to generate heat. The shape and proximity of the induction coil to the part are therefore the most critical factors for success, which introduces significant constraints.
The Central Role of the Induction Coil
The induction coil is not a generic component; it is a custom-designed tool. Each unique joint geometry requires a specifically shaped coil to deliver heat evenly and efficiently to the target area.
This custom engineering adds to the initial setup time and cost for every new part you intend to braze.
Limitations with Complex Shapes
Induction heating is most effective on relatively simple, symmetrical geometries like shafts and fittings. Large, irregularly shaped assemblies are very difficult to heat evenly with a single coil.
Parts with many protrusions or varied thicknesses can lead to hot spots and incomplete filler metal flow, compromising joint integrity.
Issues with Inaccessible Joints
The magnetic field's strength decreases rapidly with distance. If the joint is buried deep within an assembly or physically shielded by other parts of the component, the induction coil cannot generate sufficient heat in the right place.
Economic and Equipment Considerations
Beyond the physics of the process, the economic model fatores heavily into whether induction brazing is a viable choice. It is a process that demands scale to be cost-effective.
High Initial Capital Investment
The power supply, water cooling system, and custom-fabricated coils represent a significant capital investment. This upfront cost is much higher than that of manual torch brazing or even some furnace brazing setups.
Justification Through Production Volume
Induction brazing's high speed and automation potential provide a return on investment only at high production volumes. The cost per-unit drops戏剧ically with thousands of repeatable parts.
For low-volume, one-off, or prototype work, the setup costs and custom tooling make it economically impractical.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Constraints
Every engineering process involves compromises. Understanding the inherent trade-offs of induction brazing is key to avoiding costly application errors.
The Need for Precise Joint Design
Like most brazing methods, induction requires a clean, precisely controlled gap between the parts. This gap, typically 0.002 to 0.005 inches (0.05 to 0.13 mm), is critical for capillary action to pull the molten filler metal into the joint.
Poorly designed or inconsistent joints will result in voids and weak bonds, regardless of the heating method's quality.
Material Selectivity
Induction works by inducing current in electrically conductive materials. It is most efficient with ferromagnetic materials like carbon steel.
Non-magnetic but conductive metals like aluminum or copper can be heated, but often require different frequencies and more power. Brazing non-conductive materials like ceramics requires a completely different approach, such as using a conductive susceptor to transfer heat.
Risk of Localized Overheating
The heating is extremely fast and localized. Without precise control, it is easy to overheat and damage thin sections of a part or create thermal stress, especially when joining dissimilar metals with different expansion rates.
Potential for Material Property Changes
While the heating is localized, the base metal in the heat-affected zone will be heated above its critical temperature. This can cause annealing (softening) or other undesirable changes to the material's temper and hardness, which must be accounted for in the design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must align the method's strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production of simple joints: Induction brazing is an excellent choice, offering unmatched speed and consistency that lowers the cost per part.
- If your primary focus is processing large, complex assemblies or varied, low-volume parts: Furnace brazing or manual torch brazing will provide greater flexibility and a much lower barrier to entry.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials with vastly different masses: Induction can be challenging, and a slower, more uniform heating method like furnace brazing may be required to prevent thermal stress.
Ultimately, choosing the right brazing method requires a clear understanding of your specific part geometry, production volume, and material properties.

Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| High Initial Cost | Significant capital investment in equipment and custom coils | High-volume, repeatable production runs |
| Geometric Constraints | Coil design limits joint accessibility and complex shapes | Simple, symmetrical parts like shafts and fittings |
| Production Volume | Economically impractical for low-volume or one-off jobs | Mass production to justify setup costs |
| Material Selectivity | Less efficient for non-magnetic or non-conductive materials | Ferromagnetic materials (e.g., carbon steel) |
| Risk of Overheating | Potential for thermal stress or annealing in heat-affected zones | Applications requiring precise, localized heat control |
Struggling to choose the right brazing method for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to help you navigate the trade-offs of processes like induction brazing. Whether you're working with high-volume production or complex assemblies, we provide solutions tailored to your materials, geometry, and volume requirements. Contact us today to optimize your brazing process and achieve consistent, reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production



















