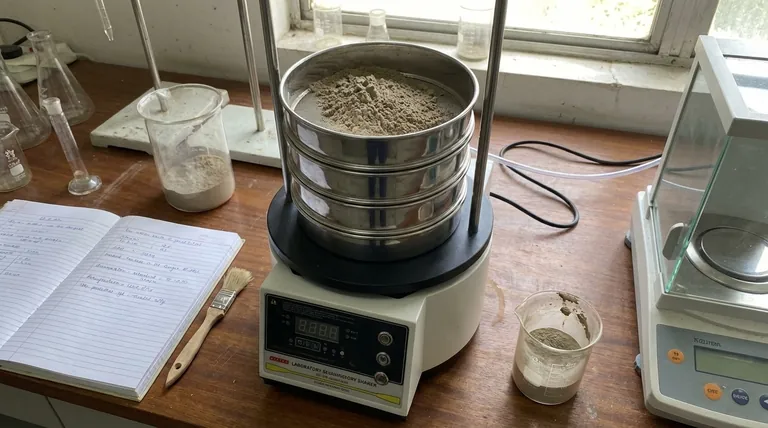
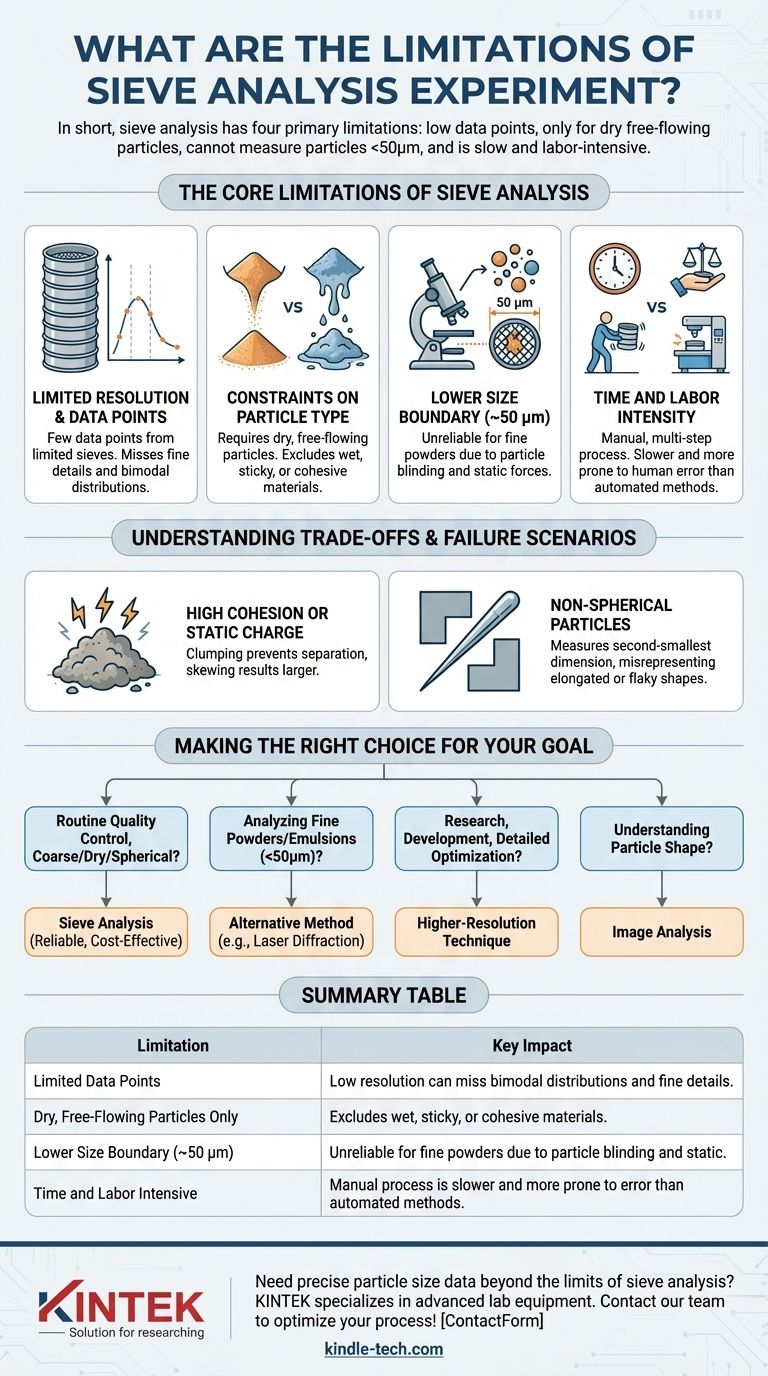
In short, sieve analysis has four primary limitations. The method provides a low number of data points, which limits resolution; it is only suitable for dry, free-flowing particles; it cannot accurately measure particles smaller than approximately 50 micrometers (µm); and the process can be slow and labor-intensive.
Sieve analysis is a foundational and reliable technique for particle size distribution, but its effectiveness is fundamentally constrained by particle characteristics and the level of detail required. It is a workhorse for specific applications, not a universal solution for all particle sizing needs.

The Core Limitations of Sieve Analysis
Sieve analysis, also known as a gradation test, is one of the oldest and most trusted methods for measuring particle size distribution. However, its mechanical simplicity is also the source of its key limitations. Understanding these is crucial for interpreting results correctly and knowing when to choose an alternative method.
Limited Resolution and Data Points
A standard stack of testing sieves typically contains a maximum of eight sieves. This means your entire particle size distribution curve is constructed from just eight data points.
This low resolution provides a broad overview of the size distribution but can easily miss important details. It may fail to identify multiple peaks (bimodal distributions) or subtle variations that are critical for process control and product quality in high-performance materials.
Constraints on Particle Type
The fundamental principle of sieve analysis requires particles to be dry and to flow freely under agitation.
This immediately excludes materials that are wet, sticky, or tend to agglomerate. Cohesive powders will clump together and fail to pass through sieve apertures they otherwise would, leading to a significant overestimation of particle size.
The Lower Size Boundary
Sieve analysis becomes unreliable and impractical for very fine powders, typically below 50 µm.
As particles get smaller, forces like static electricity and intermolecular cohesion (van der Waals forces) become stronger than the gravitational forces pulling them through the mesh. This causes fine particles to stick to each other and to the sieve screen itself, a phenomenon known as blinding, which completely invalidates the results.
Time and Labor Intensity
Compared to modern automated methods like laser diffraction, sieve analysis is a manual, multi-step process.
It requires careful sample preparation, precise weighing of each sieve before and after the test, a lengthy shaking period, and manual data calculation. This makes it time-consuming and introduces a higher potential for human error.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Common Failure Scenarios
The limitations of sieve analysis are not just theoretical. They lead to specific, practical scenarios where the method will produce misleading or entirely incorrect data.
Materials with High Cohesion or Static Charge
If your powder clumps when you handle it or is prone to static cling, sieve analysis is not a suitable method. The clumping will prevent proper separation, skewing the distribution toward a larger particle size.
Non-Spherical or Elongated Particles
A sieve measures the second-smallest dimension of a particle—essentially, whether it can fit through a square hole.
For long, needle-shaped or flaky particles, this is highly problematic. A long fiber can pass through a sieve end-on, registering a size that does not reflect its true length or aspect ratio. For these materials, methods like image analysis are far more appropriate.
Applications Requiring High-Resolution Data
If you are developing a new product or optimizing a manufacturing process, you need detailed data. Sieve analysis cannot provide the granular insight needed to detect small but critical shifts in particle size distribution that might impact product performance, such as dissolution rate, packing density, or reactivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right particle sizing technique depends entirely on your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control for coarse, dry, and roughly spherical materials (e.g., sand, gravel, grains): Sieve analysis is a reliable, cost-effective, and perfectly adequate method.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders, emulsions, or suspensions (< 50 µm): You must use an alternative method like laser diffraction or dynamic light scattering.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or detailed process optimization: The low resolution of sieve analysis is a significant drawback, and a higher-resolution technique is necessary.
- If your primary focus is understanding particle shape and not just size: Sieve analysis is unsuitable; you should use a form of image analysis.
Ultimately, knowing the limitations of a tool is the first step toward using it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Limited Data Points | Low resolution can miss bimodal distributions and fine details. |
| Dry, Free-Flowing Particles Only | Excludes wet, sticky, or cohesive materials. |
| Lower Size Boundary (~50 µm) | Unreliable for fine powders due to particle blinding and static. |
| Time and Labor Intensive | Manual process is slower and more prone to error than automated methods. |
Need precise particle size data beyond the limits of sieve analysis? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for accurate particle characterization. Our experts can help you select the right technology—from laser diffraction to image analysis—to ensure reliable results for your specific materials and R&D or quality control goals. Contact our team today to optimize your particle sizing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity



















