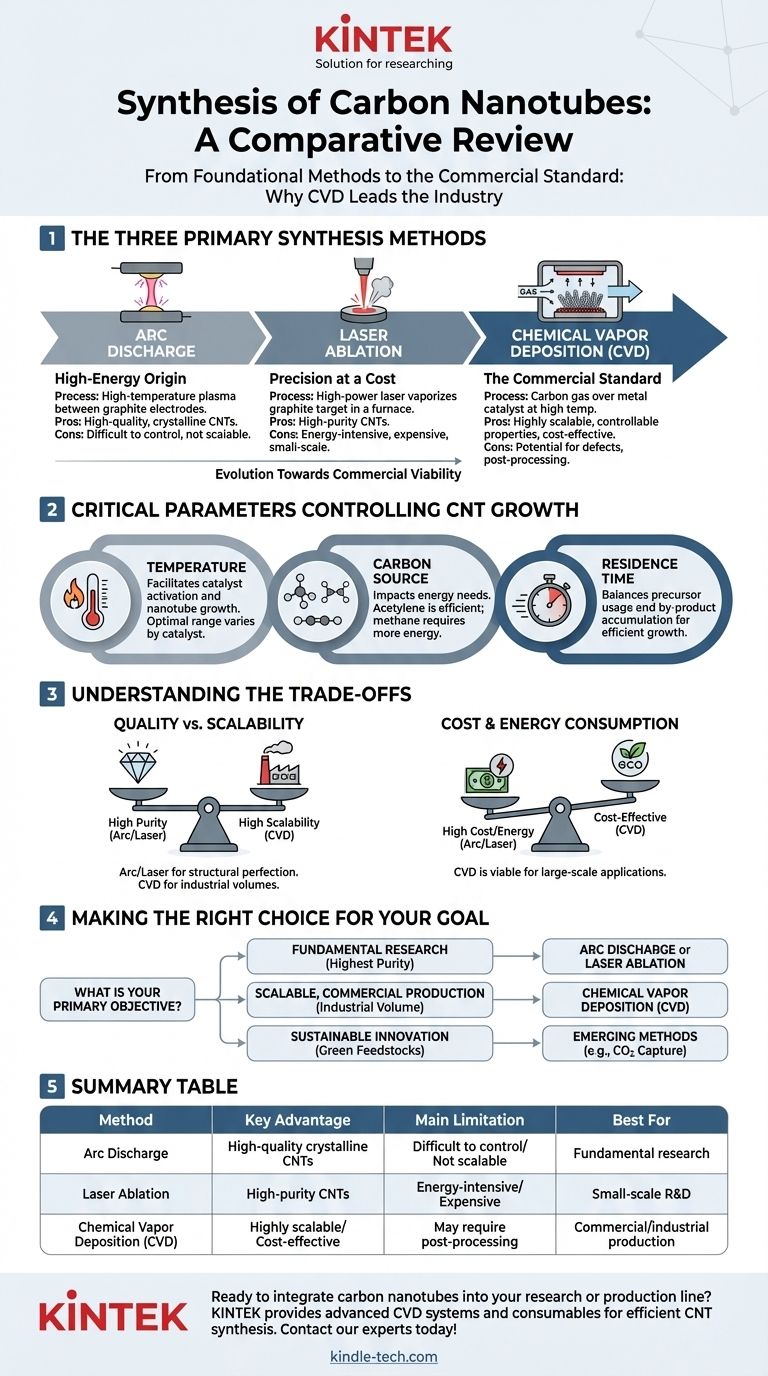
For decades, the synthesis of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) has been pursued through three primary techniques: arc discharge, laser ablation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). While the first two methods were foundational, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the dominant and most commercially viable process used today due to its superior scalability and control over the final product structure.
The central challenge in carbon nanotube synthesis is not simply creating them, but doing so with the desired quality, at a reasonable cost, and at a scale that meets industrial demand. While older methods produce high-purity CNTs, CVD offers the best overall balance for most modern applications.
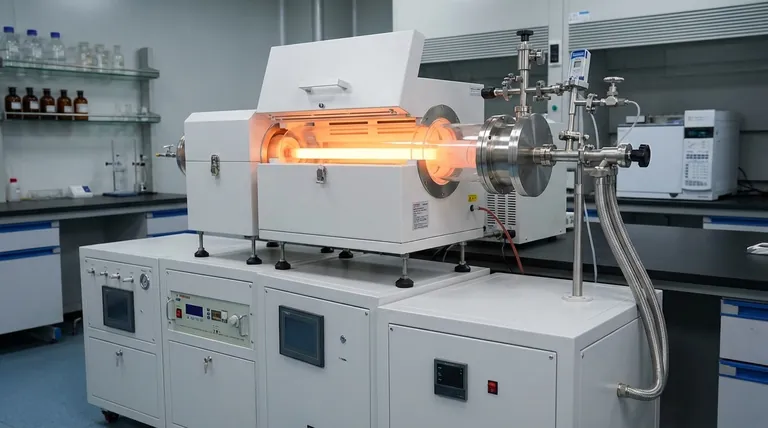

The Three Primary Synthesis Methods
Understanding the evolution of CNT synthesis provides context for why CVD became the industry standard. Each method operates on a different principle, offering a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages.
Arc Discharge: The High-Energy Origin
The arc discharge method was one of the first techniques used to produce CNTs. It involves creating a high-temperature plasma arc between two graphite electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere.
The intense heat vaporizes the carbon from the anode, which then condenses to form CNTs on the cooler cathode. While capable of producing high-quality, crystalline nanotubes, the process is difficult to control and does not scale efficiently for mass production.
Laser Ablation: Precision at a Cost
Similar to arc discharge, laser ablation uses high energy to create CNTs. A high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target inside a high-temperature furnace, vaporizing the carbon.
An inert gas sweeps the vaporized carbon from the hot zone to a cooler surface where the CNTs grow. This method yields high-purity CNTs but is extremely energy-intensive and expensive, limiting its use to small-scale research applications.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Commercial Standard
CVD is the workhorse of the modern CNT industry. In this process, a carbon-containing gas (a hydrocarbon feedstock) is passed over a substrate coated with a metal catalyst at high temperatures.
The catalyst breaks down the hydrocarbon molecules, and the liberated carbon atoms assemble into nanotube structures. The key advantage of CVD is its scalability and the ability to control CNT properties like diameter, length, and alignment by tuning the process parameters.
Critical Parameters Controlling CNT Growth
The success of any synthesis method, particularly CVD, hinges on the precise control of several key operating parameters. These variables directly influence the quality, yield, and cost of the final product.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is a critical factor. It must be high enough to facilitate the catalytic decomposition of the carbon source and promote the growth of the nanotube structure. The optimal temperature varies depending on the specific catalyst and carbon feedstock used.
Choosing a Carbon Source
The choice of carbon feedstock significantly impacts energy requirements. Gases like methane require more energy for thermal conversion into CNT precursors compared to ethylene or acetylene.
Acetylene is particularly efficient as it can act as a direct CNT precursor without needing significant additional energy, making the feedstock choice a key economic and energetic consideration.
Optimizing Residence Time
Residence time—the duration the carbon source spends in the reaction zone—must be carefully balanced. If the time is too short, the carbon source is wasted. If it's too long, by-products can accumulate and inhibit further growth. An optimal residence time is crucial for a high, efficient growth rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single synthesis method is perfect. The choice always involves a trade-off between the quality of the nanotubes, the scalability of the process, and the overall cost.
Quality vs. Scalability
Arc discharge and laser ablation are known for producing CNTs with a high degree of structural perfection and few defects. However, these methods are notoriously difficult to scale up for industrial volumes.
CVD, on the other hand, is highly scalable but may produce CNTs with a wider range of diameters and a higher potential for defects. Post-processing purification is often required, adding a step to the workflow.
Cost and Energy Consumption
The high-energy inputs for laser ablation and arc discharge make them inherently expensive. CVD is generally more energy-efficient and cost-effective, especially for large-scale production, making it the only viable choice for commercial applications like composites, batteries, and electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a synthesis method depends entirely on your end goal. Understanding your primary objective will clarify which approach is the most logical and efficient for your needs.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research requiring the highest-purity samples: Arc discharge or laser ablation are suitable for producing small, high-quality batches where cost is not the primary constraint.
- If your primary focus is scalable, commercial production for industrial applications: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the established and most practical pathway for manufacturing large volumes of CNTs.
- If your primary focus is sustainable innovation and next-generation materials: Exploring emerging methods using "green" feedstocks like captured CO2 or methane pyrolysis will be critical for future development.
Ultimately, understanding these methods and their inherent trade-offs empowers you to select the optimal path for turning carbon into advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Advantage | Main Limitation | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | High-quality, crystalline CNTs | Difficult to control, not scalable | Fundamental research |
| Laser Ablation | High-purity CNTs | Energy-intensive, expensive | Small-scale R&D |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Highly scalable, cost-effective | May require post-processing | Commercial/industrial production |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your research or production line? The right synthesis method is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables—including CVD systems—needed for efficient and scalable CNT synthesis. Our experts can help you select the ideal setup to achieve your goals for quality, volume, and cost. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and how we can support your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How many types of sputter are there? A Guide to DC, RF, Magnetron & Reactive Sputtering
- How is graphene made from CVD? Unlocking Industrial-Scale Production of High-Quality Graphene
- How does a continuous, single layer of graphene form from carbon species? Master the 4 Stages of Graphene Growth
- What is the process of RF sputtering? A Guide to Coating Insulating Materials
- What is vacuum vapor deposition of gold? A Guide to CVD vs. PVD Methods
- Which of the following methods used to deposit thin film? A Guide to PVD, CVD, and Liquid-Phase Techniques
- What are the parameters of CVD? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Flow for Perfect Films
- What is the chemical vapor deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Deposition



















