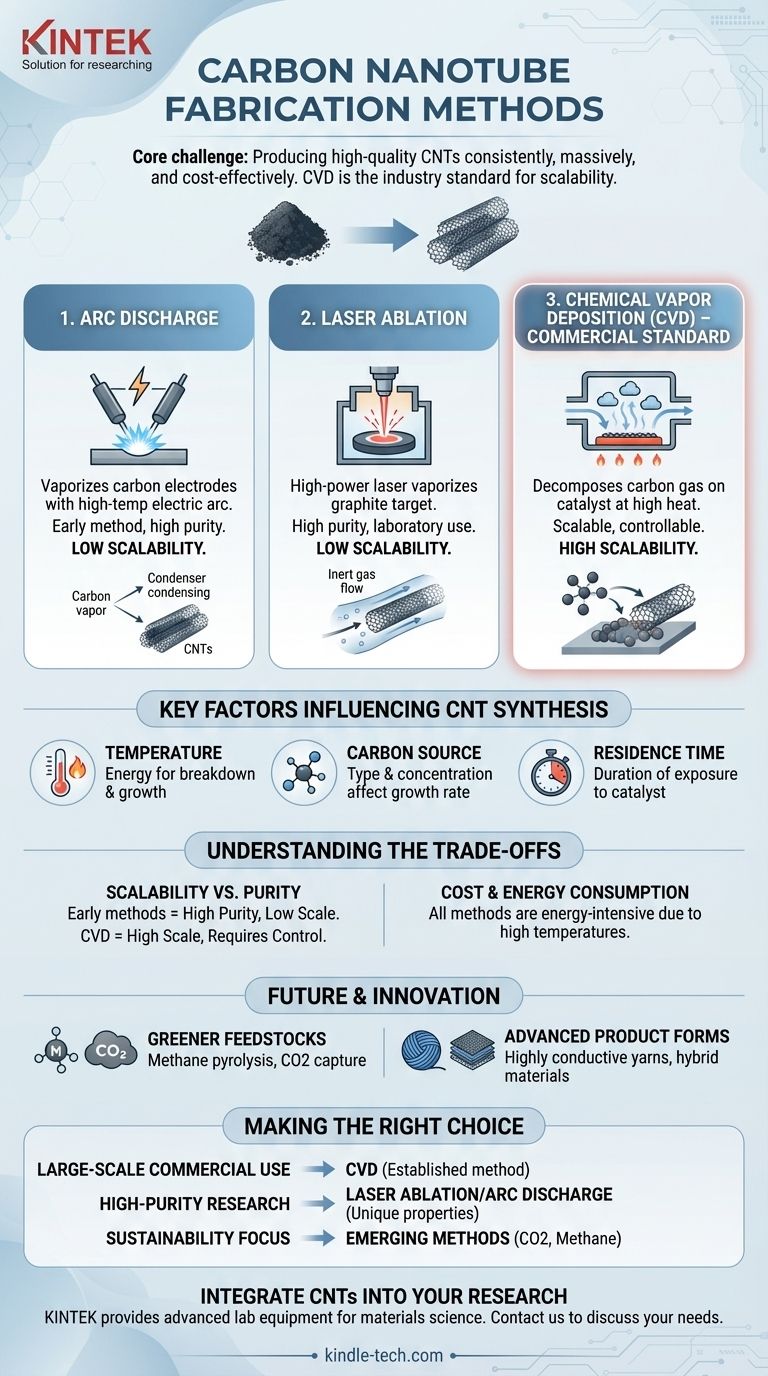
At its core, carbon nanotube fabrication involves transforming a carbon source into a cylindrical nanostructure. The three primary methods for this are arc discharge, laser ablation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). While the first two were foundational, CVD has become the dominant commercial process due to its scalability and control over the final product.
The central challenge in carbon nanotube (CNT) production is not simply creating them, but doing so with consistent quality, at a massive scale, and in a cost-effective manner. For this reason, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) has emerged as the industry standard, even as research pivots toward more sustainable feedstocks.

The Three Core Fabrication Methods
Understanding the evolution of CNT synthesis from early, high-energy methods to modern, scalable processes is key to appreciating the current state of the industry. Each method operates on a different principle for converting a carbon source into nanotubes.
Arc Discharge
This was one of the earliest techniques developed. It involves creating a high-temperature electric arc between two carbon electrodes, which vaporizes the carbon. In the presence of a catalyst, this carbon vapor condenses to form CNTs.
Laser Ablation
Similar to arc discharge, laser ablation uses brute force. A high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target in a high-temperature furnace. The laser vaporizes the carbon from the target, which then forms into nanotubes as it cools within an inert gas flow.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Commercial Standard
CVD is the most prevalent method for large-scale industrial production. It involves passing a carbon-containing gas (a hydrocarbon feedstock) over a substrate coated with catalyst particles at high temperatures. The catalyst breaks down the gas, and the carbon atoms reassemble on the catalyst particles, "growing" into nanotubes.
Key Factors Influencing CNT Synthesis
The success of any fabrication method, particularly CVD, depends on the precise control of several operating parameters. These variables directly impact the quality, length, and purity of the nanotubes produced.
The Role of Temperature
Synthesis is a high-temperature process. The heat provides the necessary energy to break down the carbon source and facilitate the growth of the nanotube structure on the catalyst.
Carbon Source and Concentration
The type of carbon-containing gas and its concentration are critical. These factors determine the rate of growth and can influence the diameter and number of walls in the final nanotubes.
Residence Time
This refers to how long the carbon source is exposed to the catalyst at the reaction temperature. Controlling residence time is essential for achieving desired lengths and preventing the formation of unwanted carbon byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single production method is perfect. The choice often involves balancing scalability, cost, and the specific properties required for the end application.
Scalability vs. Purity
Early methods like arc discharge and laser ablation can produce very high-quality CNTs but are difficult and expensive to scale up for industrial volumes. CVD offers that scalability but requires meticulous process control to maintain high purity and consistency across large batches.
Cost and Energy Consumption
All current methods are energy-intensive due to the high temperatures required. This high energy cost is a significant factor in the final price of CNTs and is a primary driver for innovation in the field.
The Future of CNT Production: Sustainability and Innovation
The industry is actively moving beyond traditional methods to address cost, environmental impact, and the demands of new applications.
Greener Feedstocks
A major area of research is the use of alternative carbon sources. This includes processes like methane pyrolysis (splitting natural gas into hydrogen and solid carbon) and using carbon dioxide captured from industrial processes as the primary feedstock.
Advanced Product Forms
Innovation is also focused on the final product. Efforts are underway to form CNTs into highly conductive continuous yarns for electronics or to create hybrid materials where CNTs are integrated with other additives to enhance polymers, concrete, or metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal fabrication method is directly tied to your end goal, whether you are developing a new battery technology or conducting fundamental research.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial use (e.g., batteries, composites): CVD is the only viable pathway, as it is the established method for producing the necessary volume and consistency.
- If your primary focus is high-purity research or niche electronics: Traditional methods like laser ablation may still be relevant in a laboratory setting where unique properties are prioritized over production volume.
- If your primary focus is sustainability or next-generation materials: Keep a close watch on emerging methods using feedstocks like captured CO2 or methane, as these represent the future of CNT manufacturing.
Understanding the production method is the first step in leveraging the unique conductive and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Principle | Scalability | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | Vaporizes carbon electrodes with an electric arc | Low | Early research, high-purity samples |
| Laser Ablation | Vaporizes graphite target with a high-power laser | Low | Laboratory research, niche electronics |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Decomposes carbon gas on a catalyst at high heat | High (Commercial Standard) | Large-scale industrial production (batteries, composites) |
Ready to Integrate Carbon Nanotubes into Your Research or Product Development?
The right fabrication method is critical to achieving the specific conductive and mechanical properties your project requires. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for cutting-edge materials science, including CNT research and development.
Our expertise can help you select the optimal tools for your work, whether you're scaling up with CVD or pursuing high-purity synthesis. Let us support your innovation in creating the next generation of advanced materials.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and how we can help you achieve your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor



















