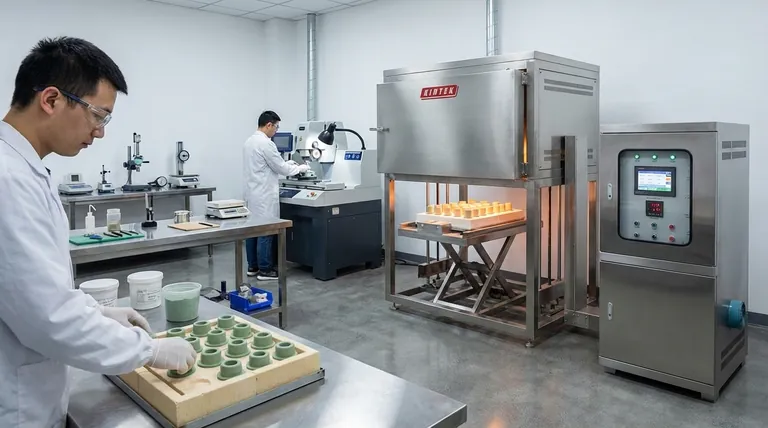
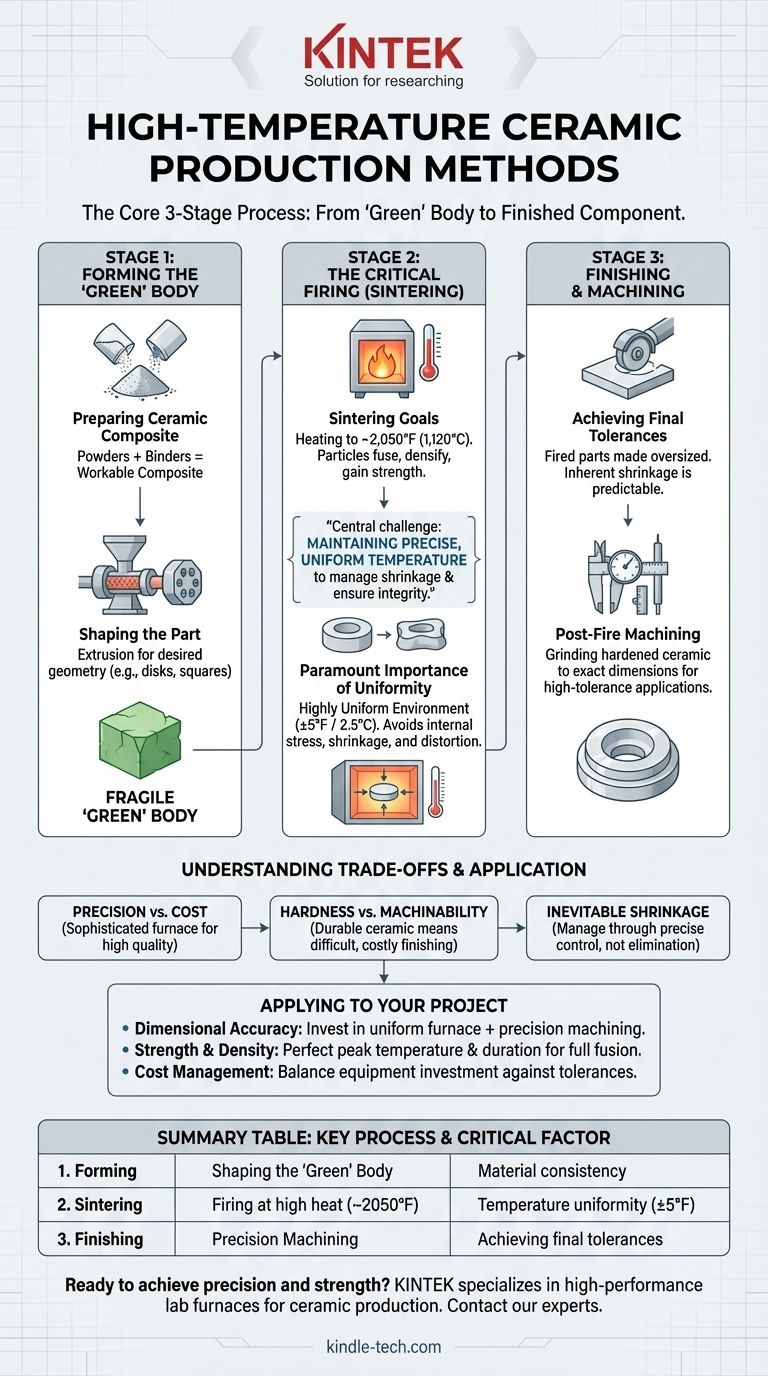
At its core, the production of high-temperature ceramics follows a fundamental three-stage process. First, a ceramic composite is shaped into its initial form; second, it is fired in a highly controlled furnace in a process called sintering; and finally, it is machined to its exact final dimensions.
The central challenge in high-temperature ceramic manufacturing is not merely achieving extreme heat, but maintaining exceptionally precise and uniform temperature control during the firing stage to manage shrinkage and guarantee the final product's structural integrity.

Stage 1: Forming the "Green" Body
The initial stage focuses on preparing the raw ceramic material and giving it a preliminary shape. This pre-fired, fragile piece is often referred to as a "green" body.
Preparing the Ceramic Composite
Before shaping, ceramic powders are mixed with binders or other materials to create a workable composite. This material must have the right consistency for the chosen forming method, such as being extruded into a specific profile.
Shaping the Part
The composite is then formed into the desired geometry. In the case of dental applications, this is often done through extrusion, where the material is forced through a die. The resulting form is then cut into manageable shapes, like disks or squares, for further processing.
Stage 2: The Critical Firing (Sintering) Process
This is the most crucial and sensitive stage, where the shaped part is transformed from a fragile green body into a hard, dense ceramic component.
The Goal of Sintering
Sintering involves heating the ceramic in a furnace to a temperature just below its melting point. For certain dental ceramics, this is around 2,050°F (1,120°C). At this temperature, the individual ceramic particles fuse together, densifying the material and giving it its strength.
The Paramount Importance of Temperature Uniformity
The success of sintering hinges on absolute temperature control. The furnace environment must be kept highly uniform, with variations as low as ±5°F (2.5°C).
Even minor temperature fluctuations across the part can cause uneven heating and cooling. This leads to internal stresses, which result in unacceptable shrinkage or distortion, rendering the component useless.
Stage 3: Finishing and Machining
After firing, the ceramic part is extremely hard but may not have the precise dimensions required for its final application. The final step is to machine it to exact specifications.
Achieving Final Tolerances
Sintering inherently involves some level of shrinkage, which can be difficult to predict with perfect accuracy. Therefore, the fired parts are intentionally made slightly oversized.
Post-fire machining is then used to grind the hardened ceramic down to its finished shape and precise dimensions, a necessary step for high-tolerance applications like custom dental implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The pursuit of quality in high-temperature ceramics involves balancing competing factors. This is where a deep understanding of the process becomes critical for success.
Precision vs. Equipment Cost
Achieving the tight temperature uniformity required for high-quality ceramics necessitates sophisticated and expensive furnace technology. Simpler, less uniform furnaces will produce lower-quality parts with a higher failure rate due to distortion.
Material Hardness vs. Machinability
The very hardness that makes the final ceramic product so durable also makes it difficult and time-consuming to machine. This final finishing step can contribute significantly to the overall cost and production time of the component.
Inevitable Shrinkage
It is essential to recognize that shrinkage during sintering is not a defect to be eliminated, but a natural part of the process. The real engineering challenge is to make this shrinkage predictable and uniform through precise process control.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your manufacturing approach should be dictated by the most critical requirement of your final component.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: You must invest in a highly uniform furnace and incorporate a post-sintering precision machining step into your workflow.
- If your primary focus is strength and density: Your process must perfect the peak sintering temperature and duration to ensure particles fully fuse and minimize internal porosity.
- If your primary focus is managing cost: You must carefully balance the investment in precision equipment against the acceptable tolerance and performance specifications of the final product.
Ultimately, mastering high-temperature ceramic production is an exercise in precise control, transforming a raw composite into a durable, highly engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Critical Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Forming | Shaping the 'Green' Body | Material consistency for extrusion/molding |
| 2. Sintering | Firing at high heat (~2050°F) | Temperature uniformity (±5°F) |
| 3. Finishing | Precision Machining | Achieving final tolerances post-shrinkage |
Ready to achieve precision and strength in your ceramic components? The right lab equipment is critical for mastering the sintering process and ensuring uniform temperature control. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables tailored for high-temperature ceramic production. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing quality and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the inside of a muffle furnace? Discover the Key Components for Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the muffle furnace used for in metallurgy? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- What is the purpose of the muffle furnace? Achieve Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the precaution for muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Lab Excellence



















