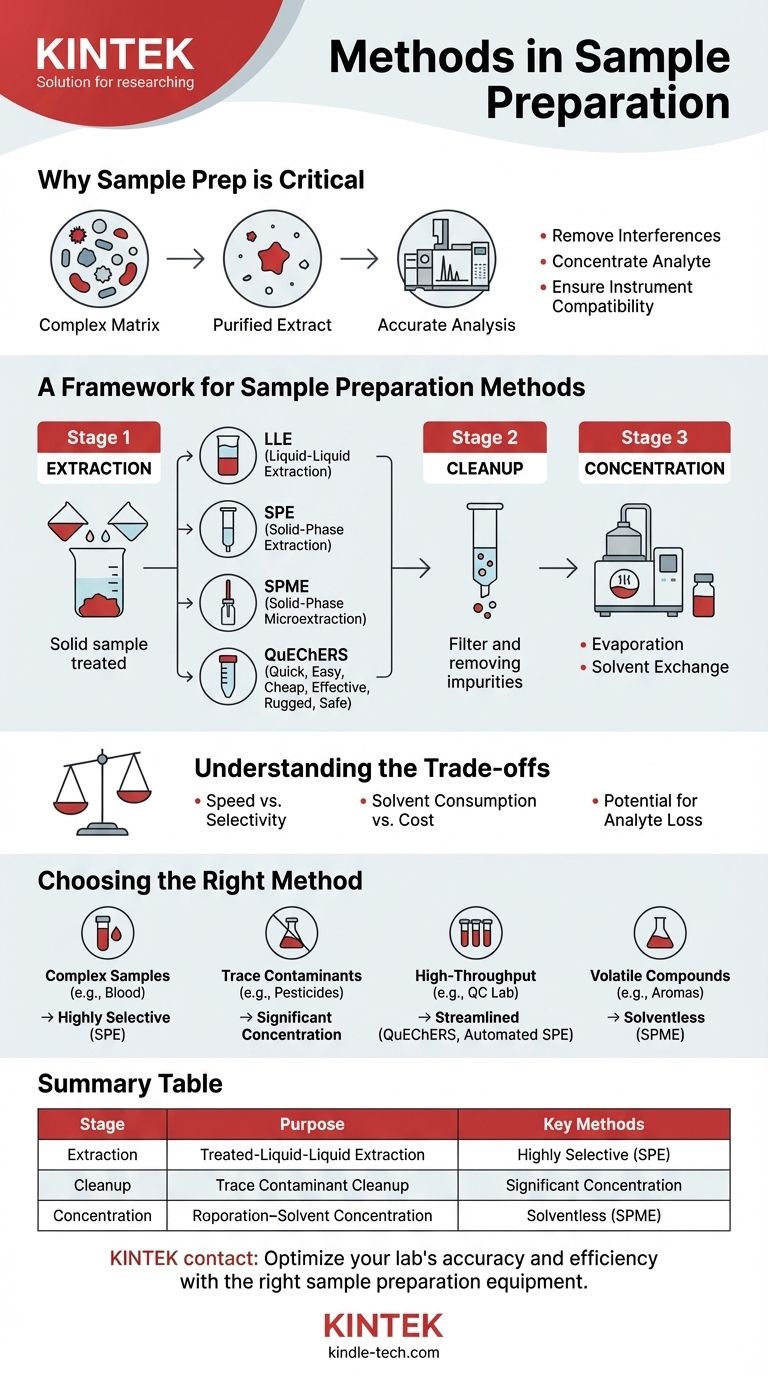
At its core, sample preparation involves a series of processes used to treat a sample before it undergoes analysis. These methods are designed to isolate the compounds of interest (analytes) from the rest of the sample matrix, remove interfering substances, and concentrate the analytes to a level suitable for the analytical instrument. The primary techniques can be broadly categorized into extraction, cleanup, and concentration.
The central goal of sample preparation is to bridge the gap between a complex, "real-world" sample and the precise requirements of a sensitive analytical instrument. A successful preparation ensures that the final analysis is accurate, reliable, and free from interference.

Why Sample Preparation is a Critical Step
Before diving into specific methods, it's crucial to understand why this stage is so important. An analytical instrument, such as a chromatograph or spectrometer, can only measure what it is given.
Removing Interferences
The raw sample (e.g., blood, soil, food) contains thousands of compounds besides your target analyte. These interfering compounds can obscure the signal from your analyte, leading to inaccurate results.
Concentrating the Analyte
Often, the analyte is present in trace amounts, far below the detection limit of the instrument. Sample preparation methods are used to concentrate the analyte, increasing its signal and making detection possible.
Ensuring Instrument Compatibility
The final sample extract must be in a solvent and condition that is compatible with the instrument. For example, a sample for gas chromatography must be volatile, and a sample for liquid chromatography must be dissolved in a suitable mobile phase.
A Framework for Sample Preparation Methods
Instead of viewing sample preparation as a single step, it's more effective to think of it as a workflow with distinct stages. Many techniques can serve multiple purposes within this framework.
Stage 1: Extraction
Extraction is the process of separating the target analyte from the primary sample matrix.
Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) is a classic technique where the sample is dissolved in one solvent, and the analyte is extracted into a second, immiscible solvent in which it has higher solubility.
Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) is a more modern and efficient technique. The sample is passed through a cartridge containing a solid material (the sorbent) that selectively retains either the analyte or the interferences, allowing for their separation.
Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) is a solvent-free method where a coated fiber is exposed to the sample. Analytes adsorb onto the fiber and are then thermally desorbed directly into an instrument, making it ideal for volatile and semi-volatile compounds.
QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe) is a streamlined method popular in food and agricultural testing. It involves an initial extraction with a solvent followed by a cleanup step using various sorbents to remove interferences like fats and pigments.
Stage 2: Cleanup
Cleanup refines the extract from the first stage, removing any co-extracted interferences that could still affect the analysis.
SPE is very commonly used for cleanup. By choosing the right combination of sorbent and solvents, you can selectively wash away interferences while keeping your analyte bound to the cartridge, or vice-versa.
Stage 3: Concentration
This final stage prepares the purified extract for injection into the instrument.
Evaporation under a gentle stream of nitrogen is a common method to remove the extraction solvent. This leaves the concentrated analyte behind.
Solvent Exchange follows evaporation. The dried analyte is redissolved (reconstituted) in a small, precise volume of a different solvent that is better suited for the analytical instrument.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sample preparation method is never about finding a single "best" option; it's about balancing competing factors.
Speed vs. Selectivity
Simpler, faster methods like a basic LLE may not remove all interferences. More complex, multi-step SPE methods offer superior cleanup (high selectivity) but require more time and method development.
Solvent Consumption vs. Cost
Traditional methods like LLE often use large volumes of organic solvents, which are costly and pose environmental concerns. Modern techniques like SPME are solvent-free, and SPE uses significantly less solvent, reducing both waste and expense.
Potential for Analyte Loss
Every transfer, filtration, or evaporation step introduces a risk of losing some of your target analyte. A simpler workflow with fewer steps can sometimes improve recovery and precision, even if the final extract is not perfectly clean.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Analysis
Your choice of method should be dictated by your sample type, your analyte's properties, and your ultimate analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a complex sample with many interferences (e.g., blood plasma, wastewater): A highly selective method like Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) is essential for effective cleanup.
- If your primary focus is detecting trace-level contaminants (e.g., pesticides in food): Your workflow must include a significant concentration step, such as solvent evaporation and reconstitution.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening of many samples (e.g., quality control lab): A streamlined protocol like QuEChERS or the use of automated SPE systems will be most effective.
- If your primary focus is analyzing volatile or semi-volatile compounds (e.g., aromas in coffee): A solventless technique like Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) is ideal to prevent loss of your target analytes.
Ultimately, a well-designed sample preparation strategy is the foundation of any reliable and accurate analytical result.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Purpose | Key Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction | Isolate analyte from sample matrix | Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE), Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE), QuEChERS, Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) |
| Cleanup | Remove co-extracted interferences | Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) |
| Concentration | Increase analyte signal for detection | Solvent Evaporation, Solvent Exchange |
Optimize your lab's accuracy and efficiency with the right sample preparation equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for all your sample prep needs, from Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) cartridges to QuEChERS kits and evaporation systems. Our solutions are designed to help you achieve precise, interference-free results, saving you time and reducing solvent consumption. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific challenges and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
People Also Ask
- How does Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) heating differ from Cold Sintering (CSP)? Thermal vs. Chemical Consolidation
- Why do intrinsic self-healing polymers require heating? Unlock Repeatable Repair with Thermal Activation
- What materials are used in the forging process? Choose the Right Metal for Strength & Performance
- How plasma is generated in magnetron sputtering? The Key to High-Efficiency Thin-Film Deposition
- How do you heat treat metal to make it stronger? Master the Process of Hardening, Quenching, and Tempering
- What is meant by co-pyrolysis? Unlock Synergistic Benefits from Mixed Feedstocks
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- What are the fundamentals of sputtering? Master the Art of High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















