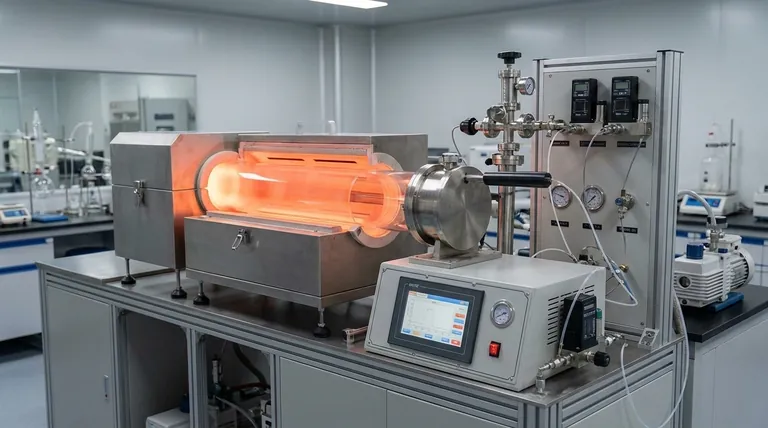
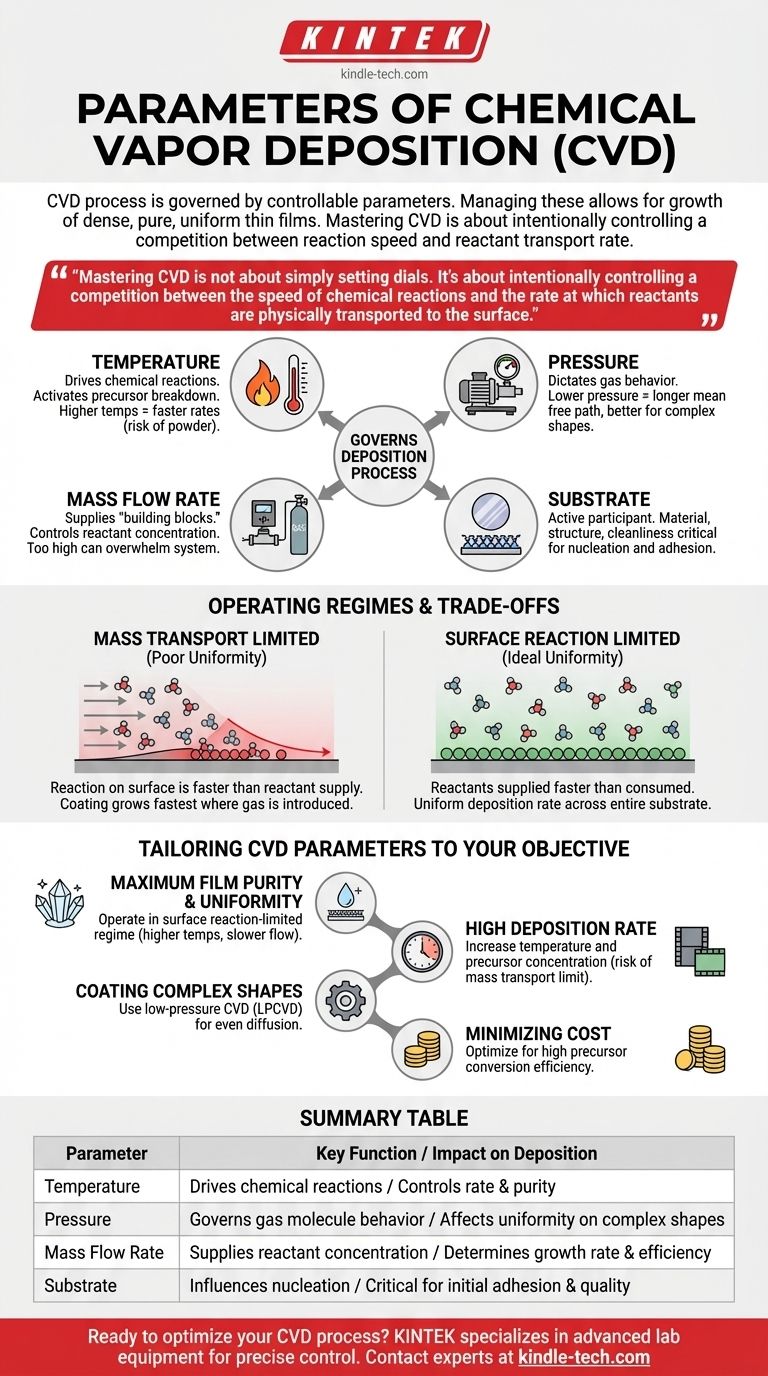
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the process is governed by a core set of controllable parameters. These primary variables are the temperature of the substrate and chamber, the pressure inside the chamber, the mass flow rate of the precursor gases, and the specific material and structure of the substrate being coated. Properly managing these parameters is what allows for the growth of dense, pure, and uniform thin films.
Mastering CVD is not about simply setting dials. It's about intentionally controlling a competition between the speed of chemical reactions and the rate at which reactants are physically transported to the surface. This balance is the single most important factor determining the final quality and properties of your coating.

How Parameters Govern the Deposition Process
Each parameter directly influences a specific stage of the CVD process, from the delivery of source material to the final chemical reaction that forms the coating.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary driver of the chemical reactions. It provides the activation energy needed for the precursor gases to break down and react on the substrate surface.
Higher temperatures generally lead to faster reaction rates, which can increase the deposition rate. However, excessively high temperatures can cause unwanted gas-phase reactions, leading to powder formation instead of a uniform film.
The Impact of Mass Flow
The mass flow rate, managed by precise mass flow controllers, determines the concentration of reactant gases introduced into the chamber.
This parameter directly controls the supply of "building blocks" for the film. A higher flow rate increases the availability of reactants, but if it's too high, it can overwhelm the system and lead to inefficient use of the precursor and non-uniform deposition.
The Function of Pressure
Pressure dictates the behavior of gas molecules within the reaction chamber. It influences both the concentration of reactants and how they travel to the substrate.
Lower pressures increase the mean free path of gas molecules, meaning they travel further before colliding with each other. This is critical for coating complex, three-dimensional shapes, as it allows the reactants to reach all surfaces more uniformly.
The Substrate as the Foundation
The substrate is not a passive element; it is an active part of the deposition process. Its material, crystal structure, and cleanliness are critical.
The initial formation of the film, known as nucleation, is highly dependent on the substrate's surface energy and chemistry. The substrate material can also act as a catalyst, directly participating in and accelerating the deposition reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operating Regimes
The interplay between these parameters creates distinct operating regimes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The goal is to operate in the regime that produces the desired film quality.
Mass Transport vs. Surface Reaction Limits
The most critical trade-off in CVD is the balance between reactant supply and reaction speed.
In a mass transport-limited regime, the chemical reactions on the surface are faster than the rate at which reactants can be supplied. This often leads to poor uniformity, as the coating grows fastest where the gas is first introduced and depletes before reaching other areas.
In a surface reaction-limited regime, reactants are supplied faster than they are consumed. This is the ideal state for high-quality films, as the deposition rate is uniform across the entire substrate, controlled solely by the temperature-dependent surface chemistry.
The Challenge of By-Products and Safety
CVD processes do not consume all reactants. The exhaust gas contains unreacted precursors and chemical by-products, which must be handled carefully.
Many precursors and by-products are toxic, flammable, or corrosive. Furthermore, some processes can generate powders or flaky deposits that can clog exhaust lines. A robust safety and waste-handling protocol is non-negotiable.
Tailoring CVD Parameters to Your Objective
Your ideal parameters depend entirely on the goal of your deposition. There is no single "best" set of conditions; there is only the best set for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity and uniformity: Operate in the surface reaction-limited regime, which typically involves higher temperatures and carefully controlled (often slower) precursor flow rates.
- If your primary focus is a high deposition rate: You will need to increase both temperature and precursor concentration, but you risk entering the mass transport-limited regime and sacrificing film quality.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex, non-flat surface: Use a low-pressure CVD (LPCVD) process to ensure reactants can diffuse evenly across all features of the part.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost: You must optimize for high precursor conversion efficiency, ensuring as much of the gas as possible is converted into film rather than being wasted in the exhaust stream.
Understanding how to manipulate these fundamental variables transforms CVD from a complex chemical process into a precise and powerful manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Key Function | Impact on Deposition |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Drives chemical reactions | Controls deposition rate & film purity |
| Pressure | Governs gas molecule behavior | Affects uniformity on complex shapes |
| Mass Flow Rate | Supplies reactant concentration | Determines growth rate & efficiency |
| Substrate | Influences nucleation & acts as catalyst | Critical for initial film adhesion & quality |
Ready to optimize your Chemical Vapor Deposition process? The precise control of CVD parameters is essential for achieving high-quality, uniform thin films. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary to master temperature, pressure, and flow control for your specific application. Whether your goal is maximum film purity, high deposition rates, or coating complex geometries, our expertise can help you transform CVD into a precise manufacturing tool.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your laboratory's CVD needs and enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















