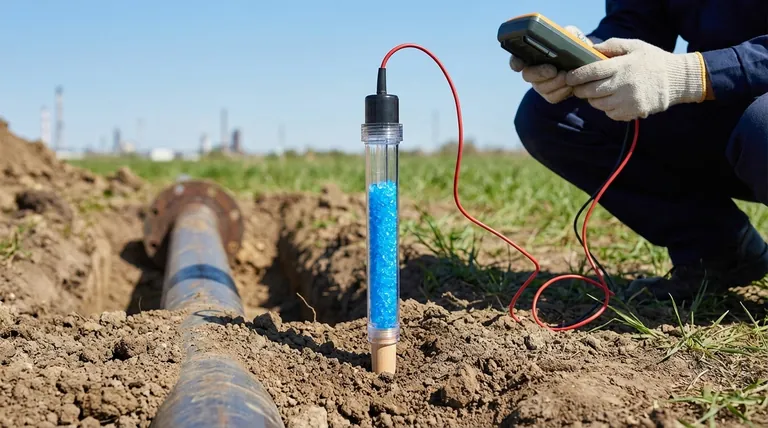
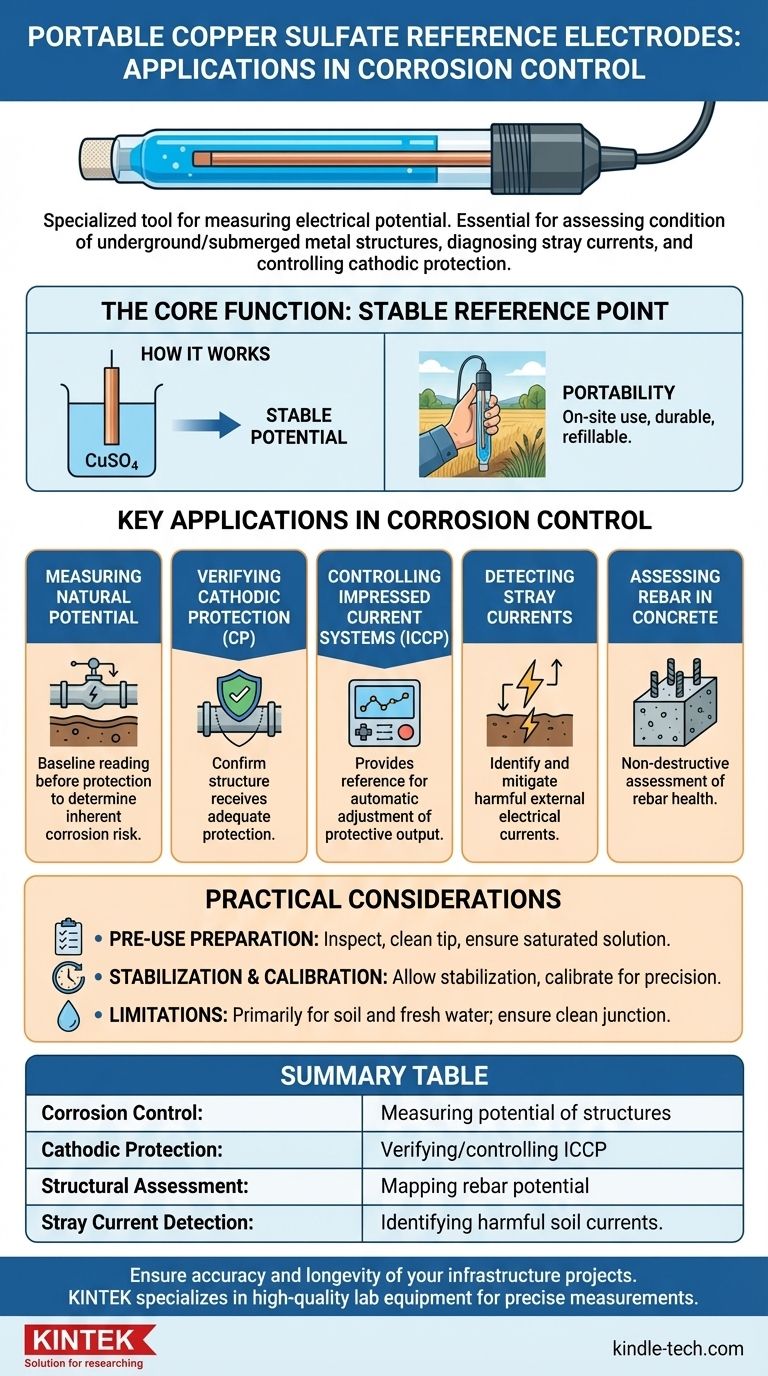
At its core, a portable copper sulfate reference electrode is a specialized tool for measuring electrical potential. Its primary applications are in the field of corrosion control, where it is used to assess the condition of underground or submerged metal structures like pipelines, cable sheaths, and the steel rebar within concrete. It is also used to diagnose stray electrical currents in the soil and to control impressed current cathodic protection systems.
The fundamental purpose of this electrode is to act as a stable, known voltage baseline in field environments. By comparing the unknown electrical potential of a metal structure against this constant reference, engineers can accurately determine if the structure is actively corroding or if it is being effectively protected.

The Core Function: Providing a Stable Reference Point
A reference electrode is the foundation of any electrochemical measurement. Its job is to provide a constant potential that doesn't change, allowing for the accurate measurement of other, unknown potentials.
How a Copper Sulfate Electrode Works
The electrode generates its stable potential through a simple and reliable electrochemical reaction. A high-purity copper rod is immersed in a saturated solution of copper sulfate (CuSO₄).
This specific chemical pairing creates a predictable oxidation-reduction process, producing a stable voltage that serves as a dependable reference point for field measurements.
Why Portability is Key
These electrodes are specifically designed for on-site use. Their construction often includes a transparent body to visually confirm the solution is saturated and a durable, portable design for easy handling.
The internal chamber can be refilled, giving the electrode a long service life and making it a practical tool for repeated field assessments in soil and fresh water.
Key Applications in Corrosion Control
The stable potential provided by the copper sulfate electrode is critical for several diagnostic and monitoring tasks related to preventing corrosion on vital infrastructure.
Measuring Natural Potential
Before any protection system is installed, this electrode is used to measure the "natural potential" of a pipeline or structure relative to the soil. This baseline reading helps determine the inherent risk of corrosion.
Verifying Cathodic Protection
For structures with a cathodic protection (CP) system, the electrode is essential for verifying that the system is working. By measuring the "cathodic protection potential," technicians can confirm the structure is receiving adequate electrical protection against corrosion.
Controlling Impressed Current Systems
In active protection systems known as impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP), the copper sulfate electrode can be used as the reference sensor. It provides the constant potential reading needed for the system to automatically adjust its protective electrical output.
Detecting Stray Currents
Stray electrical currents in the soil, often from nearby DC power systems, can dramatically accelerate corrosion. The electrode is used to map potential gradients in the soil to identify and mitigate these harmful currents.
Assessing Rebar in Concrete
The electrode is also used to measure the potential of steel reinforcement bars (rebar) within concrete structures. This is a non-destructive way to assess the health of the rebar and the risk of corrosion-induced damage to the concrete.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Considerations
While reliable, the accuracy of a portable copper sulfate electrode depends on proper handling and an understanding of its limitations.
Pre-Use Preparation is Crucial
Before any measurement, the electrode must be inspected for damage to its casing or wire. The porous tip must be clean, and the internal copper sulfate solution must be fully saturated with distilled water, with excess crystals visible to confirm saturation.
The Importance of Stabilization and Calibration
The electrode must be immersed in its solution for a period to allow its potential to stabilize. For precise work, it should be calibrated against a known standard to ensure accurate readings.
Material and Environmental Limitations
The liquid junction, often a wood plug or ceramic core, is a critical component. Wood plugs offer a fast response but can be more susceptible to environmental damage or contamination over time. The electrode is designed primarily for use in soil and fresh water.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using this tool effectively means matching its capabilities to your specific objective in the field.
- If your primary focus is routine inspection: Use the electrode for quick and reliable potential measurements to confirm that existing cathodic protection systems are operating within specified limits.
- If your primary focus is diagnostics: Employ the electrode to conduct detailed potential surveys to identify and troubleshoot complex issues like stray current interference or coating holidays on a pipeline.
- If your primary focus is structural assessment: Apply it to map the potential of rebar in concrete structures, allowing you to identify areas at high risk for corrosion before visible damage occurs.
Ultimately, the portable copper sulfate reference electrode is an indispensable instrument for safeguarding the integrity and extending the life of critical metal infrastructure.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Control | Measuring potential of underground/submerged metal structures (pipelines, cable sheaths). | Determines if a structure is actively corroding or protected. |
| Cathodic Protection | Verifying and controlling impressed current systems (ICCP). | Ensures systems are delivering adequate electrical protection. |
| Structural Assessment | Mapping the potential of steel rebar within concrete. | Non-destructive method to assess corrosion risk in concrete. |
| Stray Current Detection | Identifying harmful electrical currents in the soil. | Prevents accelerated corrosion from external DC power sources. |
Ensure the accuracy and longevity of your critical infrastructure projects.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable tools you need for precise field measurements. Whether you are inspecting pipelines, assessing concrete structures, or troubleshooting cathodic protection systems, having the right equipment is paramount.
Let us support your work in corrosion control and structural integrity. Contact our experts today to find the perfect portable reference electrode and other essential laboratory supplies for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the operating principle of a copper sulfate reference electrode? Reliable Potential Measurement Explained
- What are the pre-treatment steps before using a portable copper sulfate reference electrode? Ensure Accurate Corrosion Potential Measurements
- What are the post-treatment procedures after using a copper sulfate reference electrode? Essential Steps for Accuracy & Longevity
- What precautions should be taken when handling and using a copper sulfate reference electrode? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of the wood plug type copper sulfate reference electrode? Speed vs. Durability Explained













