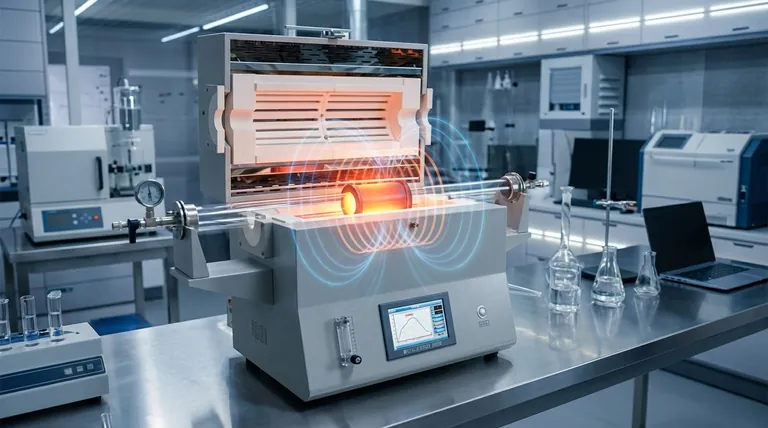
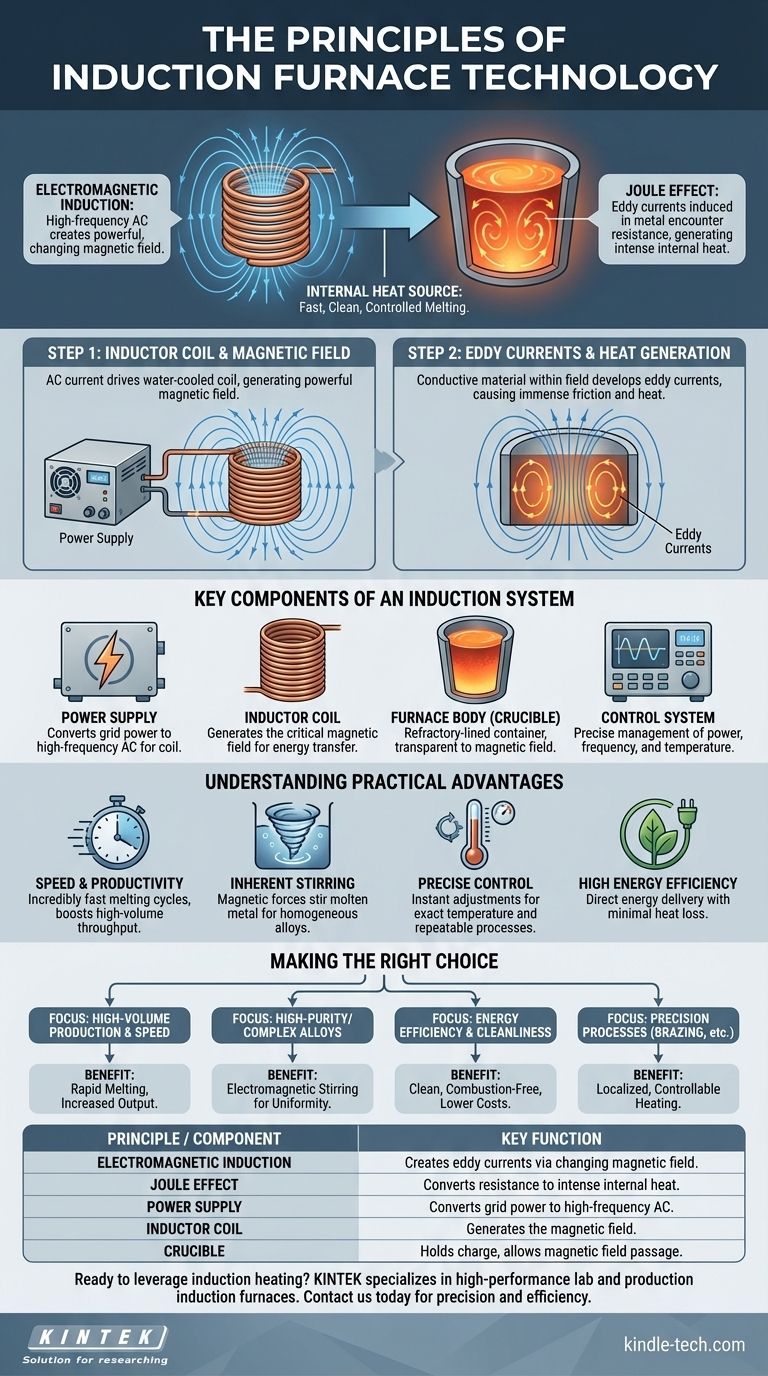
The core principle of an induction furnace is its ability to heat electrically conductive materials without any direct physical contact. This process is fundamentally based on two interconnected physical phenomena: electromagnetic induction, which creates an electric current in the material, and the Joule effect, where the material's resistance to this current generates intense heat.
An induction furnace functions much like a transformer. It uses a powerful, changing magnetic field to turn the metal charge itself into an internal heat source, resulting in faster, cleaner, and more controlled melting compared to conventional heating methods.

How Induction Heating Works: A Two-Step Process
At its heart, the technology converts electrical energy into a magnetic field and then back into electrical energy within the target material to produce heat. This elegant conversion happens in two distinct steps.
Step 1: Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil, known as the inductor, which acts as the primary winding of a transformer. When a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around it.
Step 2: The Joule Effect
When an electrically conductive material, such as metal, is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces strong, circular electrical currents inside the metal. These are called eddy currents. The metal's natural electrical resistance opposes the flow of these currents, causing immense friction on a molecular level and generating rapid, precise heat. This is the Joule effect.
Key Components of an Induction System
Understanding the principle requires knowing the core components that make it possible. The system is more than just a furnace; it's an integrated electrical and mechanical setup.
The Power Supply
This is the brain of the operation. It converts standard AC power from the grid into the high-frequency, high-current power required to drive the inductor coil and create the strong magnetic field.
The Inductor Coil
This copper coil is the "primary winding" in the transformer analogy. It generates the magnetic field, and its shape and size are critical for efficient energy transfer to the material being heated (the "charge").
The Furnace Body (Crucible)
This is the refractory-lined container that holds the metal charge. It is designed to withstand extreme temperatures while being transparent to the magnetic field, allowing the energy to pass through and act directly on the metal inside.
The Control System
Modern induction furnaces rely on sophisticated control systems. These allow operators to precisely manage the power, frequency, and temperature, ensuring a highly repeatable and controlled melting or heating process.
Understanding the Practical Advantages
The principles of induction heating are not just theoretical; they translate directly into significant real-world benefits that drive its adoption in industry.
Unmatched Speed and Productivity
Because heat is generated inside the material itself, the melting process is incredibly fast. This allows facilities to increase their production rates and meet high-volume demands more effectively than with fuel-fired or resistance furnaces.
Inherent Stirring and Uniformity
The magnetic forces that create the eddy currents also exert a physical force on the molten metal. This causes a natural stirring action, ensuring that alloys are mixed thoroughly for a highly uniform and homogeneous final product.
Precise Temperature Control
The heating action can be started, stopped, or adjusted almost instantly by managing the power supply. This allows for exceptionally precise temperature control, which is critical for specialty alloys, investment casting, and heat treatment processes like annealing.
High Energy Efficiency
Induction heating is a highly efficient process. Energy is delivered directly to the target material with minimal heat loss to the surrounding environment, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use an induction furnace is driven by the specific requirements of the industrial process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and speed: The rapid melting cycles inherent to induction furnaces directly boost throughput and overall output.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity or complex alloys: The electromagnetic stirring action is essential for achieving a perfectly uniform and consistent final composition.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and process cleanliness: Induction provides a clean, combustion-free environment and minimizes wasted energy by heating only the target material.
- If your primary focus is precision processes like brazing or shrink-fitting: The rapid, localized, and highly controllable heating allows for unparalleled accuracy and repeatability.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively leverage induction technology for cleaner, faster, and more precise thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Principle / Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | Creates eddy currents inside the metal using a changing magnetic field. |
| Joule Effect | Converts electrical resistance from eddy currents into intense, internal heat. |
| Power Supply | Converts grid power to high-frequency AC for the inductor coil. |
| Inductor Coil | Generates the powerful magnetic field required for induction. |
| Crucible | Holds the metal charge while allowing the magnetic field to pass through. |
Ready to leverage the power of induction heating in your lab or production facility?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for precision, efficiency, and reliability. Whether your focus is R&D, alloy development, or high-volume production, our solutions deliver the clean, fast, and controlled heating you need.
Contact us today to discuss how an induction furnace can transform your thermal processing capabilities and boost your productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















