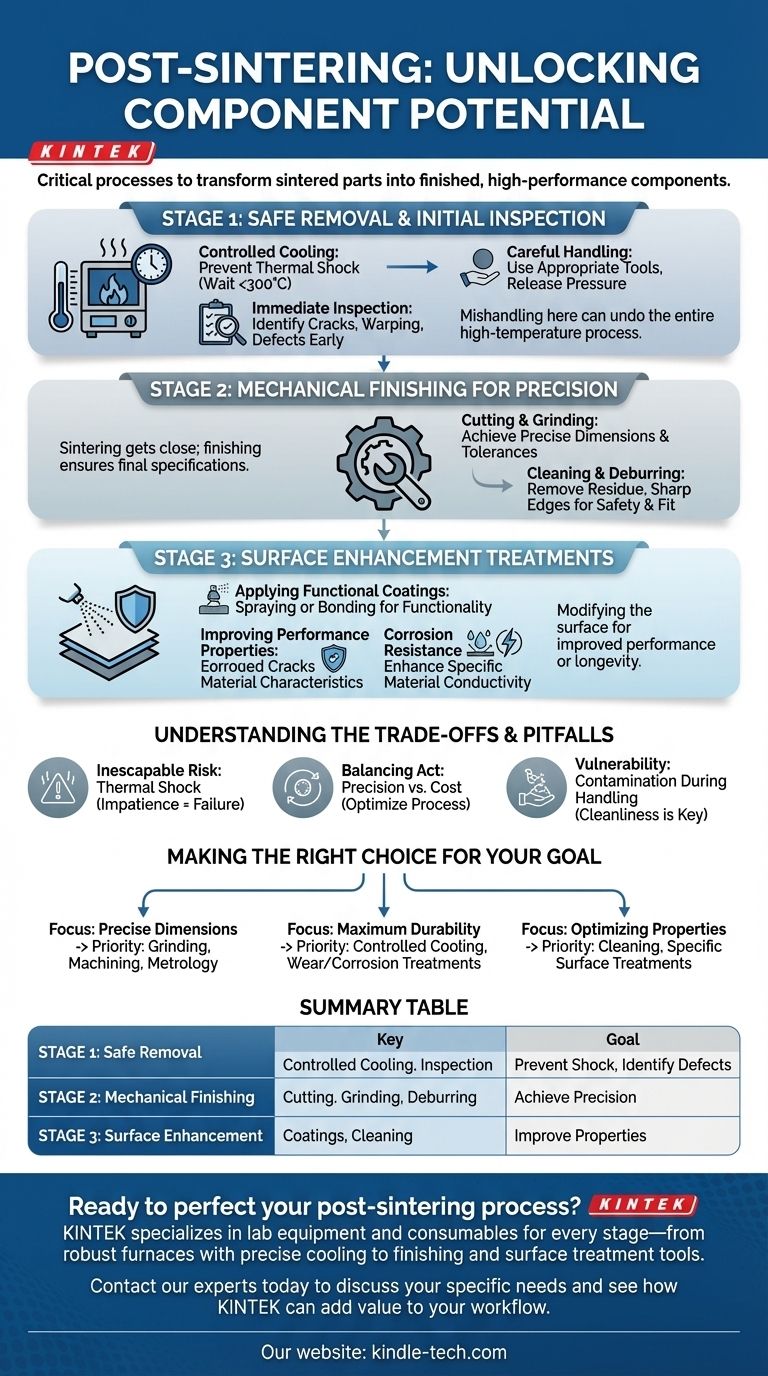
Immediately after sintering is complete, the essential processes involve a controlled cooling period to prevent thermal shock, followed by safe removal of the component. Subsequent steps then focus on mechanical finishing—such as cutting or grinding—and applying specific surface treatments to enhance properties like corrosion resistance or conductivity.
The work is not finished when the furnace turns off. Post-sintering is a critical, multi-stage process that transforms a raw sintered part into a finished component by ensuring its structural integrity, refining its dimensions, and enhancing its surface properties for final application.
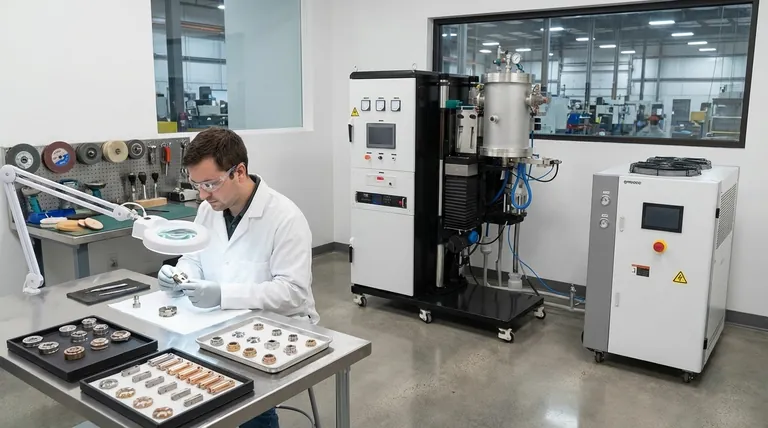

Stage 1: Safe Removal and Initial Inspection
The moments immediately following the sintering cycle are critical for the part's structural integrity. Mishandling at this stage can undo the entire high-temperature process.
Controlled Cooling is Non-Negotiable
The first and most important step is to allow the component to cool down gradually inside the furnace.
Opening the furnace door while the internal temperature is still very high introduces cold air, creating a rapid temperature change. This thermal shock can easily cause cracks in the ceramic or metal part, rendering it useless.
As a rule, wait until the furnace temperature drops below 300°C before opening the door for removal.
Careful Handling and Retrieval
Once cooled, the part can be safely retrieved. If the process involved pressure, such as in hot pressing, ensure all pressure is fully released before attempting to open the chamber.
Handle the newly sintered part carefully, as it may still be brittle depending on the material. Use appropriate tools to remove it from the furnace or press.
Immediate Visual Inspection
Perform a preliminary inspection of the part. Look for obvious defects like cracks, warping, or significant irregularities that may have occurred during sintering or cooling.
This initial check helps identify failed parts early, saving time and resources on subsequent finishing steps.
Stage 2: Mechanical Finishing for Precision
Sintering often results in parts that are close to, but not exactly at, their final required dimensions due to shrinkage. Mechanical finishing is how you achieve final specifications.
Cutting and Grinding
Most sintered components require some form of machining to meet tight dimensional tolerances.
Cutting is used to separate parts or remove support structures, while grinding is used to achieve a precise surface finish and exact dimensions.
Cleaning and Deburring
After machining, parts must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any residual oils, cutting fluids, or debris from the grinding process.
This stage may also involve deburring to remove any sharp edges or small imperfections left over from machining, ensuring the part is safe to handle and fits correctly in an assembly.
Stage 3: Surface Enhancement Treatments
For many applications, the surface of the sintered part must be modified to improve its performance or longevity.
Applying Functional Coatings
Surface treatments often involve applying a coating through processes like spraying or bonding. These coatings are not merely cosmetic; they add critical functionality.
Improving Performance Properties
The primary goal of these treatments is to enhance specific material properties.
Common objectives include improving corrosion resistance for parts exposed to harsh environments or increasing electrical conductivity for electronic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Every step in post-sintering carries its own set of risks and considerations that can impact the final quality of the component.
The Inescapable Risk of Thermal Shock
The single biggest pitfall immediately after sintering is impatience. Opening the furnace too early to save time is the most common cause of component cracking and failure. This risk cannot be overstated.
Balancing Precision and Cost
While post-sintering machining is necessary for precision, it also adds significant time and cost to the manufacturing process. The goal is to optimize the sintering process to minimize the amount of material that needs to be removed later.
Contamination During Handling
The component is vulnerable to contamination after it leaves the furnace. Oils, dirt, or even fingerprints can interfere with the adhesion and performance of subsequent surface treatments. Clean handling is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific post-sintering steps you prioritize will depend entirely on the intended application of the final component.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise dimensions: Your critical path involves meticulous grinding, machining, and metrology to meet tight tolerances.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum durability: Emphasize controlled cooling to prevent micro-cracks and select surface treatments designed for wear and corrosion resistance.
- If your primary focus is optimizing functional properties: Your priority will be the cleaning and surface treatment stages that enhance specific characteristics like conductivity or biocompatibility.
Ultimately, post-sintering processing is what realizes the full engineering potential of a sintered component.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Processes | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Safe Removal | Controlled Cooling, Initial Inspection | Prevent thermal shock, identify defects |
| Stage 2: Mechanical Finishing | Cutting, Grinding, Deburring | Achieve precise dimensions and tolerances |
| Stage 3: Surface Enhancement | Applying Coatings, Cleaning | Improve corrosion resistance, conductivity, etc. |
Ready to perfect your post-sintering process?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for every stage—from robust sintering furnaces with precise cooling controls to tools for finishing and surface treatment. We serve laboratories and manufacturers who require reliable, high-performance components.
Let us help you ensure structural integrity, precise dimensions, and enhanced surface properties for your final application. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and see how KINTEK can add value to your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What affects melting range? Understand the Critical Role of Purity and Structure
- What are the alternatives to crown lengthening? Explore Orthodontic Extrusion & Gingivectomy
- Is biofuel a renewable energy source? Powering a Sustainable Future with Biomass
- How does a high-precision oven contribute to the post-processing of hydrothermal oxidation products? Ensure Data Purity
- Why argon is used in sputtering? The Ideal Gas for Efficient, Pure Thin Film Deposition
- What is a lab oven used for? A Guide to Precise Heating, Sterilization & Drying
- What is preventive maintenance of laboratory equipment? A Proactive Strategy for Data Integrity and Safety
- Why is a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen required during the catalytic pyrolysis of plastics? Maximize Fuel Yield



















