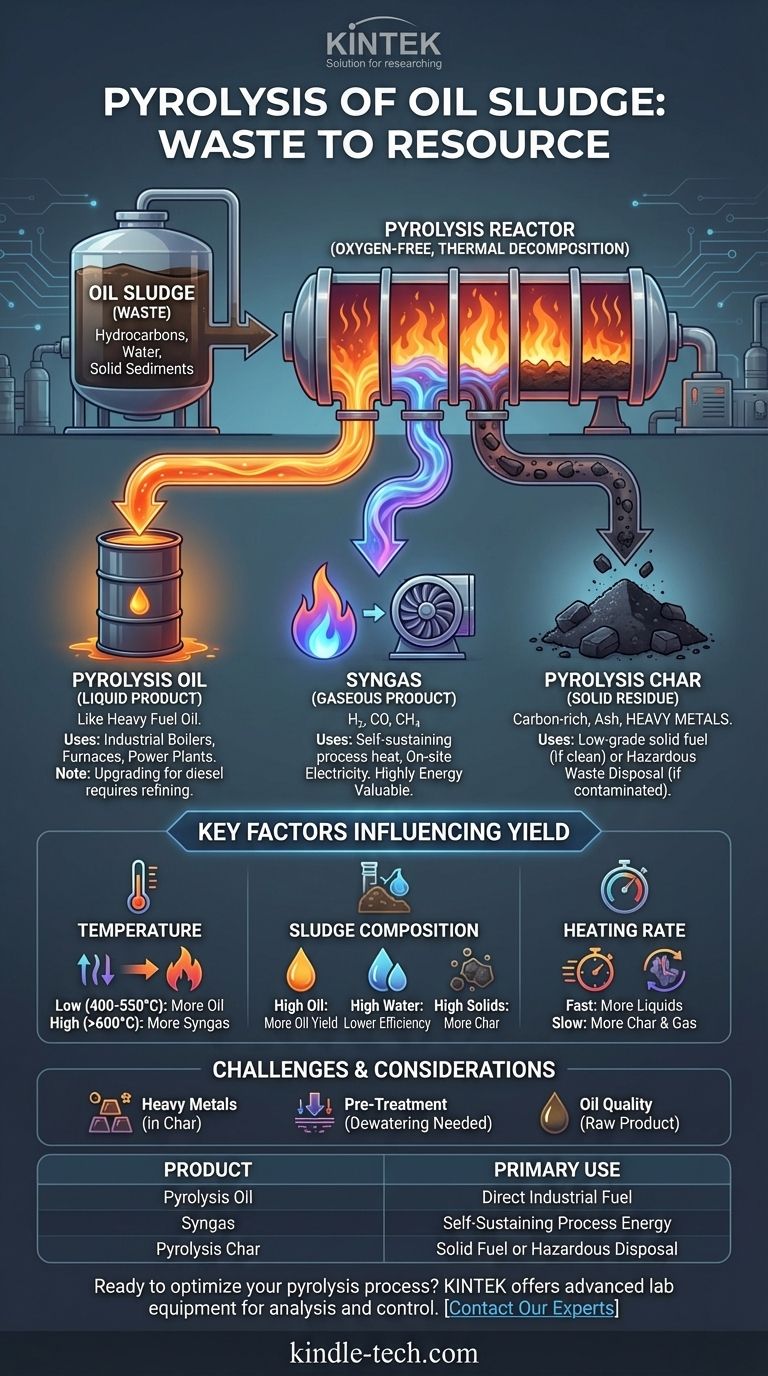
In short, the pyrolysis of oil sludge breaks it down into three primary products: a liquid pyrolysis oil similar to heavy fuel oil, a non-condensable syngas that is typically used to power the process itself, and a solid carbon-rich residue known as pyrolysis char. The specific yield and quality of each product depend heavily on the initial sludge composition and the exact operating conditions of the pyrolysis reactor.
Oil sludge pyrolysis should not be viewed merely as waste disposal, but as a resource recovery process. It transforms a hazardous environmental liability into a set of potentially valuable energy products, but the economic viability hinges on managing the quality and contamination of these outputs.
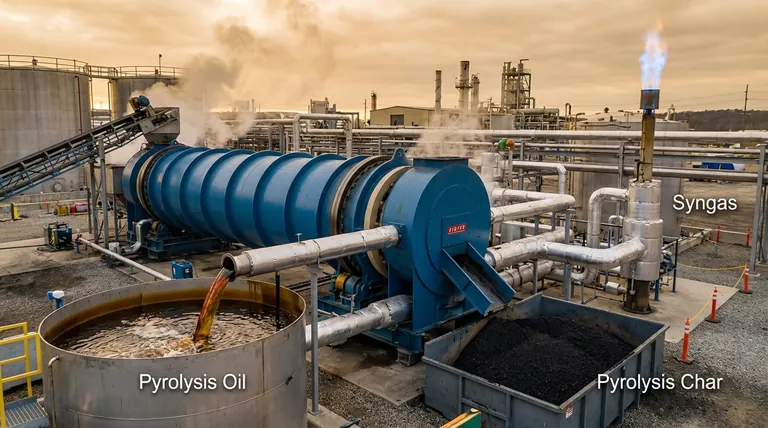

Deconstructing the Outputs: From Waste to Resource
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that occurs in an oxygen-free environment. When applied to oil sludge—a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, water, and solid sediments—it segregates the material into distinct, more manageable streams.
The Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil
This is often the most economically valuable product of the process. It is a dark, viscous liquid created by condensing the volatile organic compounds driven out of the sludge.
The oil's properties are comparable to a heavy industrial fuel oil. It can be used directly in applications like industrial boilers, furnaces, cement kilns, or power plants designed to handle such fuels.
While it can be upgraded into higher-grade fuels like diesel, this requires significant further refining, which adds cost and complexity. The quality and heating value of the oil are directly tied to the hydrocarbon content of the original sludge.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
This is the non-condensable gas stream produced during pyrolysis. It is a mixture of flammable gases including hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), and other light hydrocarbons.
Syngas has a significant energy value, but it is typically not sold. Instead, it is recycled back to the pyrolysis system and burned to provide the heat required for the reaction.
This creates a self-sustaining energy loop, dramatically reducing the external energy costs of the operation. Any excess gas can be used for on-site electricity generation.
The Solid Residue: Pyrolysis Char
After the volatile components (oil and gas) have been removed, a solid, carbon-rich material remains. This char contains the fixed carbon and all of the inorganic materials originally present in the sludge.
This includes sand, sediment, rust, and, most critically, heavy metals. The final use case for this char is entirely dependent on its level of contamination.
If the char is clean, it can be used as a solid fuel similar to low-grade coal or as a material like biochar. However, if it contains high concentrations of heavy metals, it is classified as hazardous waste and requires specialized, costly disposal in a secure landfill.
Key Factors Influencing Product Yield
The ratio and quality of oil, gas, and char are not fixed. They are controlled by several key operational parameters. Understanding these allows for process optimization based on desired outcomes.
Pyrolysis Temperature
Temperature is the most dominant factor.
- Lower temperatures (400-550°C) tend to maximize the yield of liquid pyrolysis oil.
- Higher temperatures (>600°C) cause further "cracking" of the larger hydrocarbon molecules, increasing the yield of syngas at the expense of oil.
Initial Sludge Composition
The "garbage in, garbage out" principle applies directly.
- High Oil Content: Leads to a higher yield of valuable pyrolysis oil.
- High Water Content: Reduces process efficiency, as significant energy is consumed to evaporate the water before pyrolysis can begin. Dewatering is a common pre-treatment step.
- High Solid/Ash Content: Results in a higher yield of solid char.
Heating Rate
The speed at which the sludge is heated also plays a role.
- Fast Pyrolysis (high heating rate): Favors the production of liquids by quickly vaporizing organics before they can further react into char and gas.
- Slow Pyrolysis (low heating rate): Tends to produce more solid char and gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While promising, sludge pyrolysis is not a silver bullet. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its operational challenges.
The Challenge of Heavy Metals
This is the single most critical factor for the environmental and economic viability of the process. Pyrolysis does not destroy metals like lead, mercury, or cadmium. Instead, they become concentrated in the solid char.
If the initial sludge has high metal content, the resulting char may be too hazardous for reuse and will represent a disposal cost, undermining the economics of the entire operation.
The Need for Pre-Treatment
Raw oil sludge can be over 50% water. Feeding this directly into a reactor is highly inefficient. Most successful pyrolysis plants incorporate a pre-treatment stage to dewater and sometimes dry the sludge, adding to the system's capital and operational cost.
Oil Quality and Market Realities
The pyrolysis oil produced is a raw, unrefined product. It is not equivalent to crude oil or standardized fuels. Finding a consistent buyer who can handle its specific properties (e.g., viscosity, sediment, sulfur content) is essential for profitability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to implement oil sludge pyrolysis should be aligned with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is exceptionally effective, converting a large volume of hazardous sludge into a much smaller, more stable solid volume, significantly cutting disposal costs.
- If your primary focus is energy recovery: The process is a proven waste-to-energy technology, capable of powering itself and generating surplus energy from the resulting oil for on-site industrial use.
- If your primary focus is maximizing revenue: Success requires a careful analysis of the sludge composition to ensure high oil yield and low contaminant levels in the char, securing a market for both outputs.
Ultimately, pyrolysis offers a powerful method for transforming an environmental liability into a set of recoverable resources.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil | Viscous liquid similar to heavy fuel oil | Direct fuel for industrial boilers, furnaces |
| Syngas | Flammable gas mix (H₂, CO, CH₄) | Fuel for self-sustaining pyrolysis process |
| Pyrolysis Char | Solid carbon-rich residue with heavy metals | Low-grade fuel or hazardous waste disposal |
Ready to transform your oil sludge into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for analyzing pyrolysis processes and optimizing product yields. Whether you're researching waste-to-energy solutions or scaling up for industrial recovery, our tools help you achieve precise temperature control and analyze output quality. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your lab's needs in sustainable resource recovery.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















