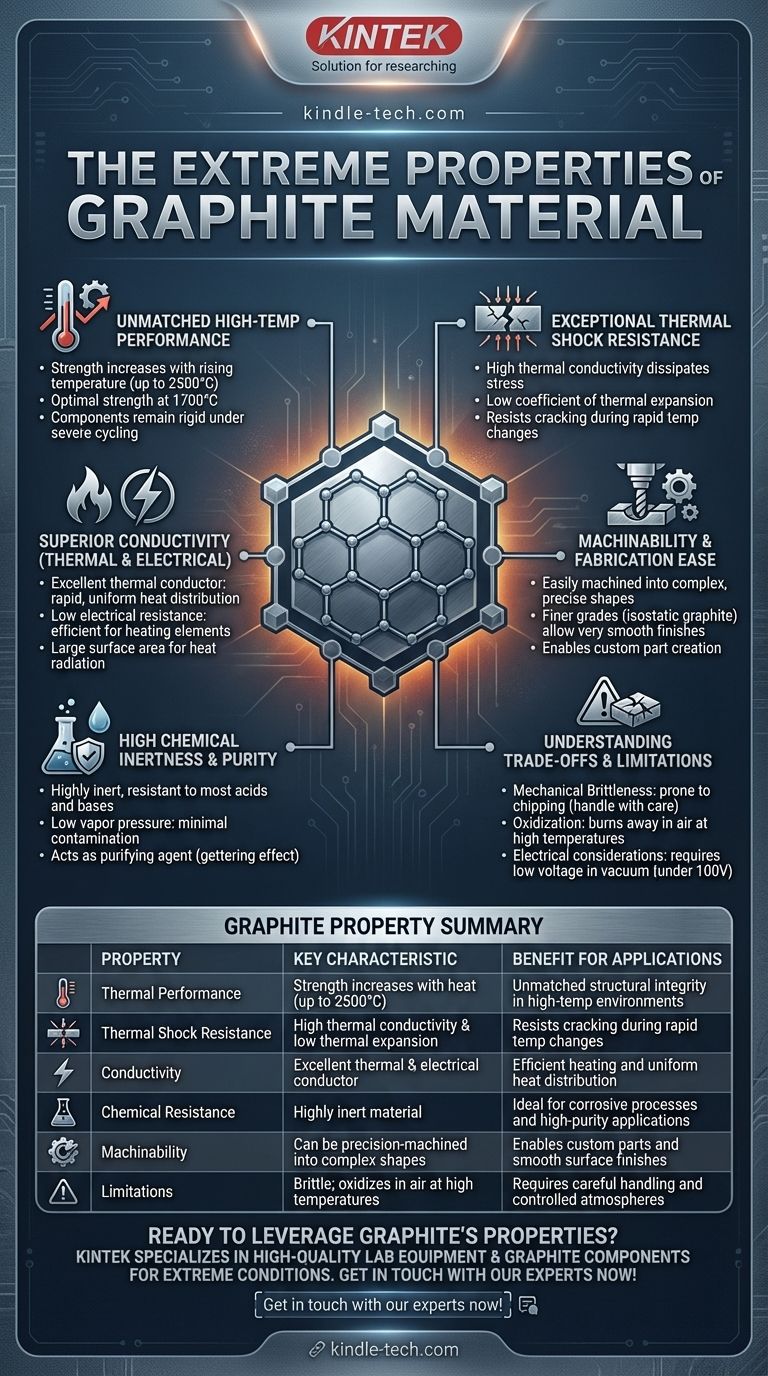
At its core, graphite is a material of extremes, defined by its remarkable performance under intense conditions. Its primary properties include exceptionally high resistance to heat and chemicals, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, and the unique characteristic of becoming stronger as its temperature increases. This combination makes it a critical material for high-temperature industrial applications like vacuum furnaces.
Graphite is the material of choice for environments where other materials fail. It excels due to its ability to withstand extreme heat and thermal shock, but this performance comes with a trade-off: a mechanical brittleness that requires careful handling and design considerations.
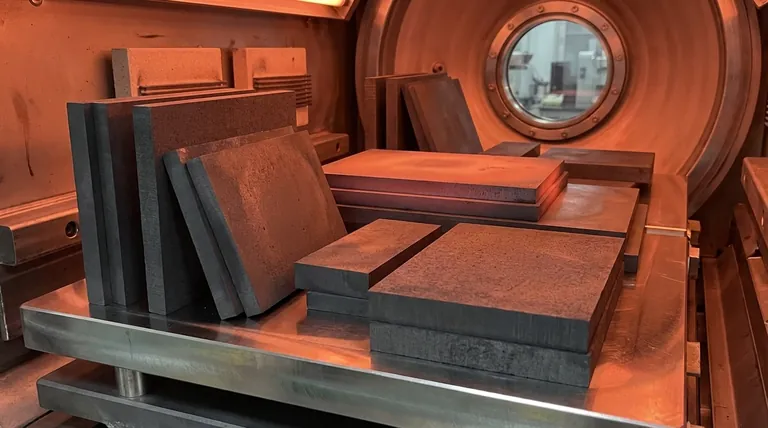

Unmatched Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Graphite's most valuable characteristics emerge under thermal stress. Unlike metals that weaken when heated, graphite's performance improves, making it uniquely suited for the most demanding thermal environments.
Increasing Strength with Heat
The mechanical strength of graphite does not decrease at high temperatures. Instead, it actually increases with rising temperature, with its optimal strength occurring around 1700°C and continuing to perform up to 2500°C.
This counter-intuitive property ensures that components like furnace hearths and fixtures remain rigid and retain their shape almost indefinitely, even under severe thermal cycling.
Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite exhibits an extremely high resistance to thermal shock, which is the tendency of a material to crack during rapid temperature changes.
This is a direct result of two core properties working together: its high thermal conductivity (which dissipates thermal stress quickly) and its low coefficient of thermal expansion (it doesn't expand or contract much when heated or cooled).
High Purity and Stability
In vacuum furnace applications, graphite has a very high melting point and a low vapor pressure, meaning it doesn't readily sublimate and contaminate the environment.
Furthermore, it can act as a purifying agent by reacting with residual oxygen and water vapor. This "gettering" effect helps create a cleaner atmosphere, which can simplify the vacuum system design and reduce costs.
Superior Conductivity and Transfer Properties
Graphite is an excellent conductor of both heat and electricity. This dual capability allows it to be used for both structural components and active heating elements.
High Thermal Conductivity
Graphite's ability to conduct heat efficiently ensures rapid and uniform heat distribution. In furnaces, this minimizes hot spots and can help offset the slower initial heat-up times that might result from its higher mass compared to other materials.
High Electrical Conductivity
With its low electrical resistance, graphite is an effective and low-cost material for non-metal heating elements. It provides a large surface area for heat radiation, making it an efficient method for heat transfer in a vacuum.
Machinability and Chemical Inertness
Beyond its thermal performance, graphite is valued for its stability and ease of fabrication, especially high-purity grades like isostatic graphite.
Ease of Machining
Graphite can be easily machined into complex and precise shapes. Grades made with finer particles, such as isostatic graphite, allow for very smooth surface finishes and the creation of custom parts with specific thicknesses and dimensions.
High Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Graphite is a highly inert material, showing excellent resistance to corrosion and chemical attack from most acids, bases, and organic compounds. This makes it ideal for containers and fixtures used in chemically aggressive processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While graphite's properties are exceptional, it is not without its practical weaknesses. Acknowledging these limitations is critical for successful implementation.
Mechanical Brittleness
The primary drawback of graphite is its brittleness. It is hard and rigid but prone to chipping or cracking if subjected to mechanical shock. Furnace rails and other components must be handled with care during the loading and unloading of heavy parts to prevent damage.
Oxidation and Volatilization
Despite its high-temperature resistance, graphite will oxidize (burn away) when exposed to oxygen at elevated temperatures. This necessitates its use in vacuum or inert gas atmospheres. At very high temperatures, it can also begin to volatilize, or turn into a gas.
Electrical Considerations in Vacuum
When used as a heating element in a vacuum, care must be taken to prevent electrical discharge or arcing. It is often recommended to operate graphite elements at a low voltage (typically under 100V) to ensure stable and safe operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use graphite should be based on a clear understanding of your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural integrity: Graphite is unmatched for furnace fixtures, hearths, and supports due to its increasing strength with heat and thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is efficient and cost-effective heating: Graphite's conductivity, large radiation area, and ease of processing make it an ideal choice for heating elements in vacuum or inert environments.
- If your primary focus is purity and chemical compatibility: High-purity isostatic graphite provides an inert, non-contaminating material for semiconductor manufacturing and handling corrosive substances.
By understanding these distinct properties and their associated trade-offs, you can confidently leverage graphite's exceptional capabilities for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Benefit for Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Performance | Strength increases with heat (up to 2500°C) | Unmatched structural integrity in high-temperature environments |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High thermal conductivity & low thermal expansion | Resists cracking during rapid temperature changes |
| Conductivity | Excellent thermal and electrical conductor | Efficient heating and uniform heat distribution |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly inert material | Ideal for corrosive processes and high-purity applications |
| Machinability | Can be precision-machined into complex shapes | Enables custom parts and smooth surface finishes |
| Limitations | Brittle; oxidizes in air at high temperatures | Requires careful handling and controlled atmospheres |
Ready to leverage graphite's exceptional properties in your lab or process?
Graphite's unique combination of high-temperature strength, superior conductivity, and chemical inertness makes it ideal for demanding applications like vacuum furnaces, semiconductor manufacturing, and high-temperature processing.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including graphite components tailored to withstand extreme conditions. Our expertise ensures you get the right materials for superior performance and longevity.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite solutions can enhance your application's efficiency and reliability.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- What are the advantages of biomass? Unlock Renewable Power from Waste and Crops
- What is the function of graphite material when preparing Ga-LLZO sintered bodies? Ensure Sample Integrity in HIP
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- Is graphite a conductive metal? Discover Why This Non-Metal Powers Modern Technology



















