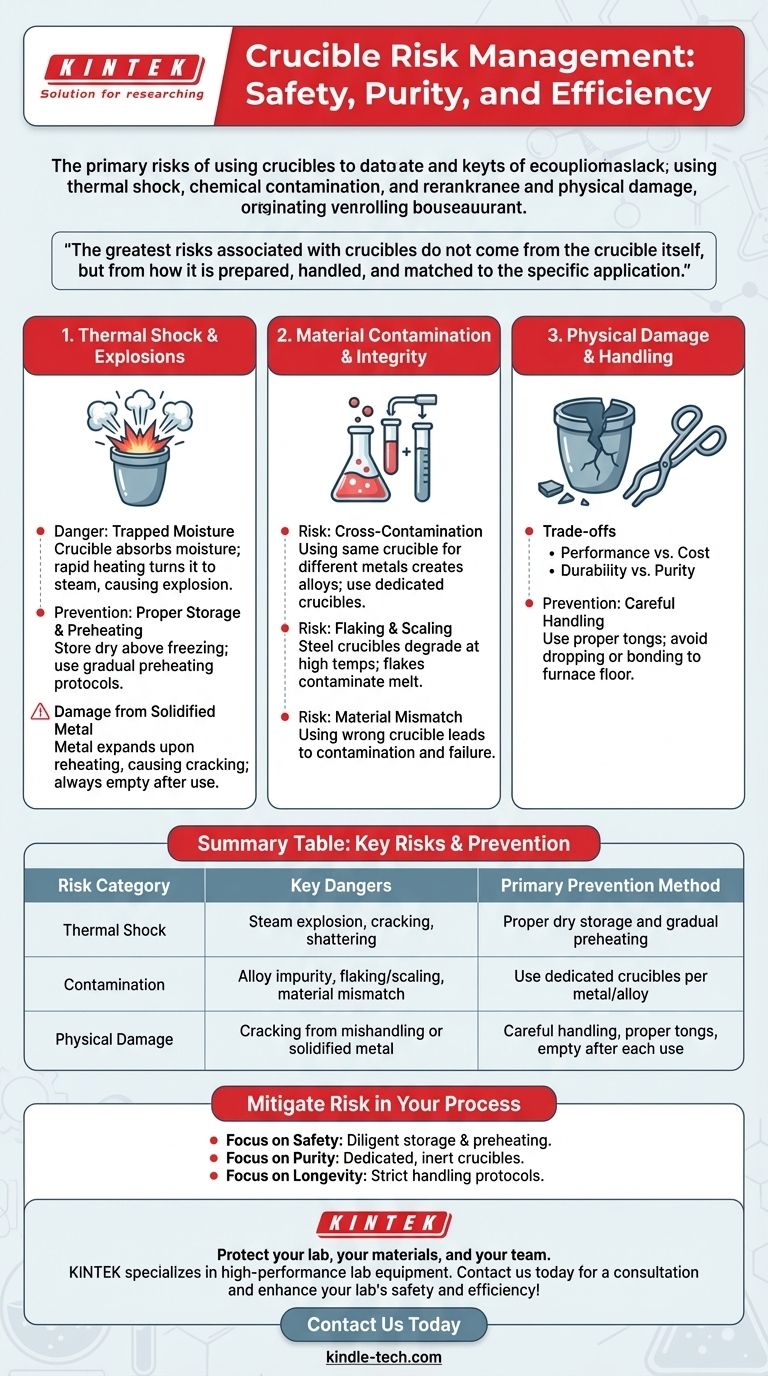
The primary risks of using crucibles are catastrophic failure from thermal shock, chemical contamination of the melt, and physical damage to the equipment itself. These dangers are not inherent to the tool but arise from improper storage, handling, and material selection, making them almost entirely preventable through disciplined procedure.
The greatest risks associated with crucibles do not come from the crucible itself, but from how it is prepared, handled, and matched to the specific application. Mastering these operational details is the key to ensuring both safety and success.

The Critical Risk: Thermal Shock and Explosions
The most severe danger in a foundry environment is a steam explosion caused by the rapid heating of a compromised crucible. This is a violent, dangerous event that must be avoided at all costs.
The Danger of Trapped Moisture
A crucible that is cold or has been stored in a damp environment can absorb moisture. When this crucible is placed into a hot furnace, the trapped water instantly turns to steam, expanding violently.
This rapid expansion can cause the crucible to crack, shatter, or explode, ejecting molten metal and posing a severe hazard to operators and equipment.
The Role of Storage and Preparation
Crucibles must always be stored in a dry area and at a temperature above freezing (32°F / 0°C). A cold or wet crucible must never be placed directly into service.
Proper preheating protocols are essential to gently drive off any residual moisture before the crucible is charged with metal and exposed to high temperatures.
Damage from Solidified Metal
A related risk occurs when metal is left to solidify inside a crucible after a melt. Upon reheating, the metal can expand at a different rate than the crucible material.
This differential expansion exerts immense pressure on the crucible walls, which can lead to cracking and failure. Always empty crucibles completely after each use.
Material Contamination and Crucible Integrity
Beyond immediate safety hazards, improper crucible use can compromise the quality of your work and degrade the equipment itself.
Cross-Contamination Between Metals
Using the same crucible for different metals is a direct path to contamination. Trace amounts of a previous metal can leach into the new melt, creating an unintended alloy.
This can drastically alter the chemical and mechanical properties of your final product. For this reason, dedicated crucibles must be used for each distinct metal or alloy.
Flaking and Scaling
Certain crucible materials, like steel, are prone to degradation at high temperatures. The interior surface can flake or "scale" off.
These flakes fall into the molten metal, introducing impurities. This process also thins the crucible walls over time, weakening its structure and increasing the risk of a breach. Protective coatings can help mitigate this but require regular maintenance.
Material Mismatch
The disadvantages of a specific crucible material often stem from using it in the wrong application. For example, an alumina crucible may be very pure but has lower thermal conductivity than other types.
Using a crucible with a melting point too close to your working temperature or one that reacts chemically with your melt can lead to direct contamination and premature failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" material, only the best choice for a specific task.
Performance vs. Cost
High-purity or high-performance materials like alumina often come at a significantly higher cost. This investment may be necessary for applications requiring extreme purity.
For general-purpose melting of lower-temperature alloys, a more economical crucible may be sufficient, provided its limitations are understood and managed.
Durability vs. Purity
A durable and inexpensive steel crucible might be suitable for melting zinc, but it carries the inherent risk of iron contamination from scaling.
Conversely, a more inert but brittle ceramic crucible might offer superior purity but require more careful handling to prevent cracks and physical damage.
The Importance of Handling
Even the most expensive, perfectly specified crucible can be ruined by improper handling. Using poorly fitting tongs can create stress points that lead to cracks.
Dropping the crucible or allowing it to bond to the furnace floor are common and costly mistakes. Careful handling is a non-negotiable aspect of risk mitigation.
How to Mitigate Risk in Your Process
Your approach to crucible management should be directly tied to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Your highest priority is diligent storage and preheating to eliminate all moisture and prevent thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is melt purity: You must use dedicated crucibles for each alloy and select a crucible material that is inert to your specific metal at working temperatures.
- If your primary focus is crucible longevity and cost-effectiveness: You must enforce strict protocols for handling, emptying the crucible after every use, and inspecting for damage before heating.
Ultimately, crucible safety and effectiveness are a matter of disciplined procedure, not chance.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Dangers | Primary Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock | Steam explosion, cracking, shattering | Proper dry storage and gradual preheating |
| Contamination | Alloy impurity, flaking/scaling, material mismatch | Use dedicated crucibles per metal/alloy |
| Physical Damage | Cracking from mishandling or solidified metal | Careful handling, proper tongs, empty after each use |
Protect your lab, your materials, and your team. The right crucible is essential for safe and effective melting. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering a range of crucibles designed for specific applications and metals. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible to mitigate risks and ensure purity and safety in your processes. Contact us today for a consultation and enhance your lab's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What dual roles do high-purity graphite crucibles play? Expert Insights into Fluoride Salt Testing
- What is the thermal limit of graphite? Unlock Extreme Heat Performance in Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using alumina crucibles for handling KCl-NaCl molten salt electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stability
- What is the maximum temperature for a carbon crucible? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- Selecting Alumina or Zirconia Crucibles for LLZTO Synthesis: Key Factors for Pure Solid-State Electrolytes
- Can you melt steel in a graphite crucible? Understand the critical risks of carbon contamination.
- Can crucibles withstand very high temperatures? Yes, if you choose the right material for your application.
- Do you need to heat the clean crucible before using it? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Process Accuracy



















