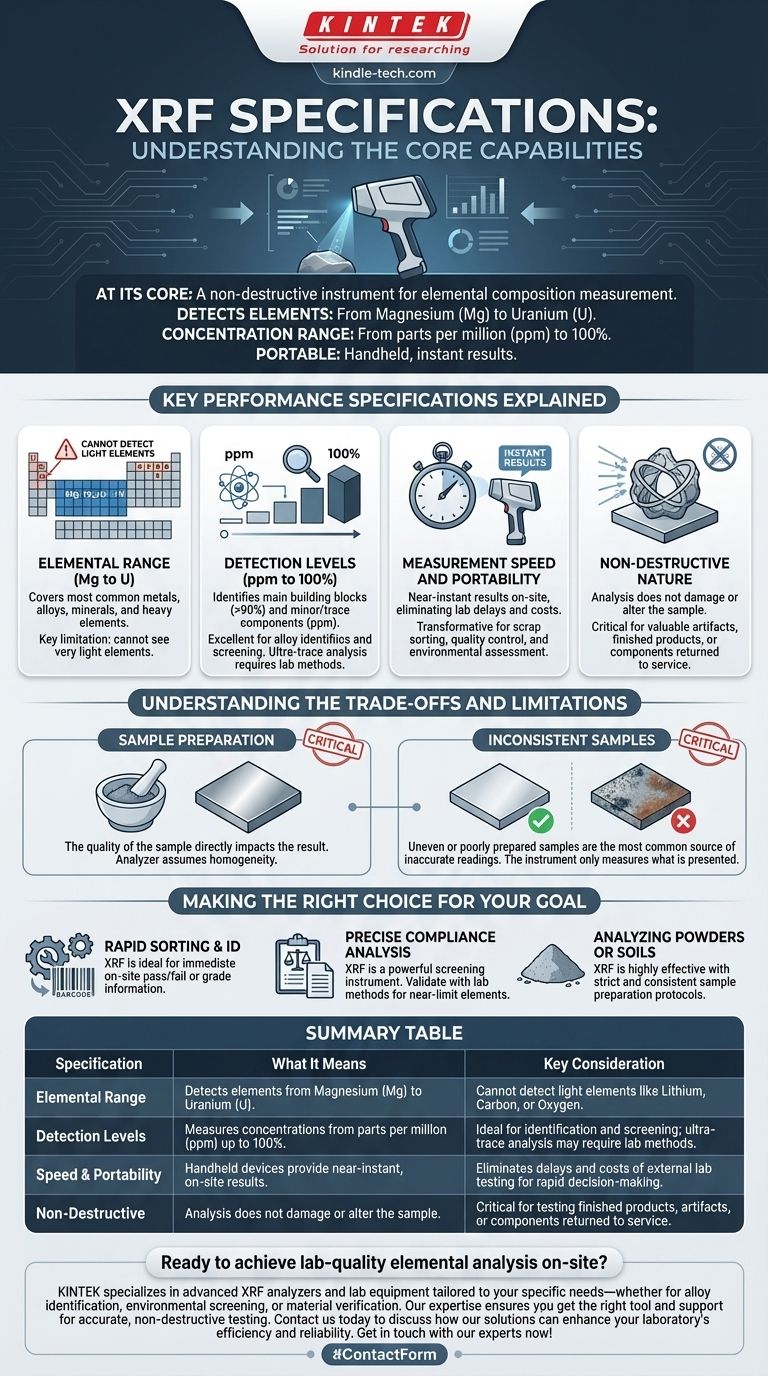
At its core, an X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analyzer is a non-destructive instrument designed to measure the elemental composition of a material. Its primary specifications include the ability to detect elements from Magnesium (Mg) to Uranium (U) in concentrations ranging from a few parts per million (ppm) up to 100%, often in a portable, handheld form factor that delivers results instantly.
While the technical specifications define an XRF analyzer's potential, its true accuracy in any given situation is fundamentally determined by proper sample preparation and an understanding of the material being analyzed.

Key Performance Specifications Explained
To understand if XRF is the right tool for your needs, you must look beyond the numbers and understand what each specification means in practice.
Elemental Range (Mg to U)
This defines which elements the instrument can "see." The range from Magnesium (atomic number 12) to Uranium (atomic number 92) covers most common metals, alloys, minerals, and heavy elements.
However, this specification also highlights a key limitation: XRF cannot detect very light elements. This includes critical elements like Lithium, Beryllium, Carbon, Nitrogen, and Oxygen.
Detection Levels (ppm to 100%)
This specification describes the instrument's sensitivity. It can identify the main building blocks of a material (e.g., Iron in steel at >90%) as well as minor and trace components down to the parts per million level.
This makes XRF excellent for alloy grade identification, mineral exploration, and restricted substance screening. For ultra-trace analysis (parts per billion), more sensitive laboratory methods are typically required.
Measurement Speed and Portability
Modern handheld XRF analyzers provide near-instantaneous results at the point of inspection. This eliminates the delay and cost of sending samples to an external laboratory.
This capability is transformative for applications like scrap metal sorting, quality control on a production line, or environmental site assessments where immediate decisions are necessary.
Non-Destructive Nature
The analysis process does not damage or alter the sample. The X-rays used are low-power and leave the material intact. This is critical when testing finished products, valuable historical artifacts, or components that must be returned to service.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
An analyzer's datasheet only tells part of the story. Achieving "lab-quality" results depends heavily on external factors.
The Critical Role of Sample Preparation
The quality of your sample directly impacts the quality of your result. The analyzer assumes the small area it measures is representative of the whole.
For powders, samples must be finely ground with a consistent particle size to ensure homogeneity. For solid metals, the surface must be clean and flat, free of contaminants, coatings, or corrosion.
Inconsistent Samples Yield Inconsistent Results
An uneven or poorly prepared sample is the most common source of inaccurate XRF readings. The instrument itself may be perfectly calibrated, but it can only measure the sample it is presented with.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use these guidelines to determine if XRF specifications align with your objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid sorting and material identification: XRF is an ideal tool, providing immediate pass/fail or grade information on-site.
- If your primary focus is precise chemical analysis for compliance: XRF is a powerful and reliable screening instrument, but be prepared to validate results with lab methods, especially for elements near specification limits.
- If your primary focus is analyzing powders or soils: XRF is highly effective, but only if you implement a strict and consistent sample preparation protocol.
Ultimately, XRF technology provides an invaluable capability for immediate elemental analysis, so long as its operational principles are understood and respected.
Summary Table:
| Specification | What It Means | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Elemental Range | Detects elements from Magnesium (Mg) to Uranium (U). | Cannot detect light elements like Lithium, Carbon, or Oxygen. |
| Detection Levels | Measures concentrations from parts per million (ppm) up to 100%. | Ideal for identification and screening; ultra-trace analysis may require lab methods. |
| Speed & Portability | Handheld devices provide near-instant, on-site results. | Eliminates delays and costs of external lab testing for rapid decision-making. |
| Non-Destructive | Analysis does not damage or alter the sample. | Critical for testing finished products, artifacts, or components returned to service. |
Ready to achieve lab-quality elemental analysis on-site?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced XRF analyzers and lab equipment tailored to your specific needs—whether for alloy identification, environmental screening, or material verification. Our expertise ensures you get the right tool and support for accurate, non-destructive testing.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and reliability.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the most likely cause of excessive temperature in the hydraulic fluid would be? A Faulty Relief Valve
- What is the size range of pellets? From 1mm to 25mm, Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What is the purpose of using a pre-forming machine for Ni-Co-Al alloy powders? Optimize Your Hot Pressing Workflow
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in biomass analysis? Achieve Precision Pellet Preparation
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for pelletizing metal oxide powders? Unlock Precise Gas-Sensing Data
- What is a hydraulic press made of? Discover the Core Components for Immense Force
- What are the hazards of a hydraulic press? Understanding Crushing, Injection, and Fire Risks
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
















