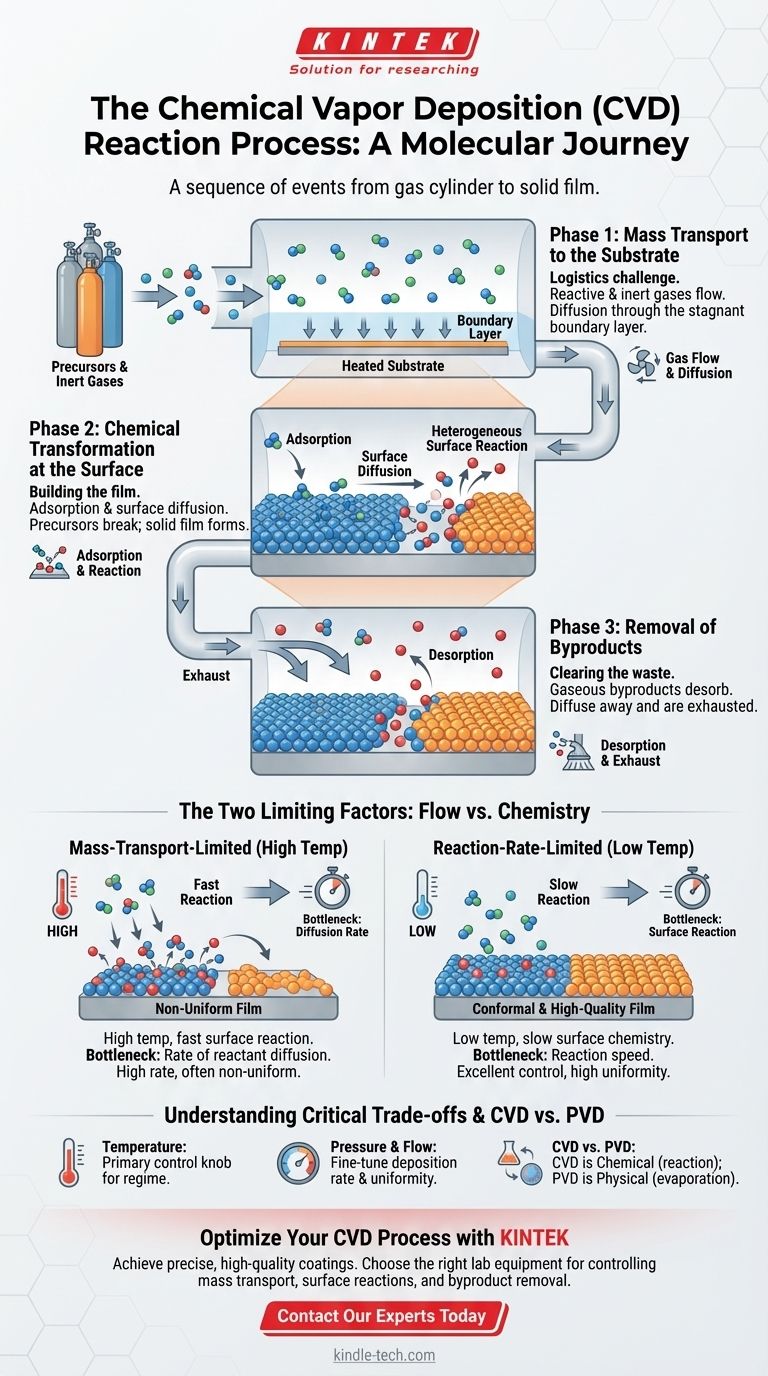
At its core, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is a sequence of events that transports reactive gases to a heated surface, where they react to form a solid thin film, leaving behind gaseous byproducts that are then removed. This journey involves distinct phases of gas transport, surface chemistry, and waste removal.
Understanding CVD is not about memorizing a list of steps, but about seeing it as a continuous supply chain. The final quality of the deposited film is determined by the slowest link in that chain—the process bottleneck—which can be either the delivery of materials or the reaction itself.
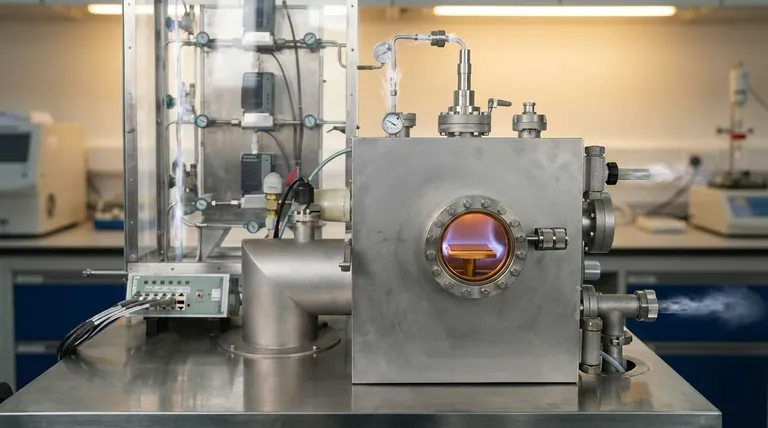

The Three Core Phases of a CVD Reaction
While specific details can vary, every CVD process follows a fundamental, three-phase pathway. Think of it as a molecule's journey from a gas cylinder to becoming part of a solid film.
Phase 1: Mass Transport to the Substrate
This initial phase is about getting the necessary ingredients, or precursors, to the reaction site. It's a logistics challenge on a microscopic scale.
The process begins with the controlled introduction of reactant gases and inert diluent gases into the reaction chamber.
These gases flow toward the substrate, but they don't simply crash into it. A thin, stagnant layer of gas called the boundary layer forms just above the substrate surface.
The final, crucial step of this phase is diffusion. The reactant molecules must travel through this boundary layer to physically reach the surface where the chemistry will happen.
Phase 2: Chemical Transformation at the Surface
This is where the actual film is built. It's a series of rapid chemical and physical events happening directly on the substrate.
First, the precursor molecules must land and stick to the surface, a process called adsorption.
Once adsorbed, these molecules may diffuse across the surface, moving around until they find an energetically favorable location for growth, like the edge of an existing crystal structure.
This is followed by the heterogeneous surface reaction. At the heated surface, the precursor molecules break apart. Some atoms bond to the substrate to form the desired solid film, while other parts of the molecule are liberated as gaseous byproducts.
Phase 3: Removal of Byproducts
For the deposition to continue, the waste products must be efficiently cleared away to make room for new reactants.
The gaseous byproducts created during the surface reaction must detach from the surface, a step known as desorption.
Finally, these byproduct gases diffuse away from the surface, back through the boundary layer, and are carried out of the reaction chamber by the bulk gas flow.
The Two Limiting Factors: Flow vs. Chemistry
The overall rate and quality of your CVD process are governed by which of the above steps is the slowest. This creates two distinct operating regimes.
The Mass-Transport-Limited Regime
At high temperatures, the surface reactions are extremely fast. The reaction consumes precursors almost as soon as they arrive.
In this scenario, the bottleneck is the rate at which new reactants can diffuse through the boundary layer to the surface. It's like a factory with a lightning-fast assembly line that's constantly waiting for parts to be delivered.
This regime yields high deposition rates but often results in non-uniform films, as areas with better gas flow (like the leading edge of the substrate) get coated faster.
The Reaction-Rate-Limited Regime
At lower temperatures, the surface chemistry is the slow step. There are plenty of reactant molecules available at the surface, but the chemical reaction to form the film proceeds slowly.
This is like a factory with a huge pile of parts but a very deliberate, slow-moving assembly line.
This regime gives you excellent control. Because the reaction is slow and uniform everywhere on the surface, it typically produces much more conformal and high-quality films, even if the deposition rate is lower.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Mastering CVD means balancing competing factors to achieve your desired outcome.
Temperature's Dual Role
Temperature is the primary control knob. Increasing it speeds up both mass transport and reaction rates, but it doesn't affect them equally. It's the key factor that determines which limiting regime you are operating in.
Pressure and Flow Rate
Adjusting chamber pressure and gas flow rates changes the concentration of precursors and the thickness of the boundary layer. These are critical secondary controls used to fine-tune the deposition rate and uniformity within a chosen temperature regime.
A Note on CVD vs. PVD
A common point of confusion is the difference between CVD and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). CVD creates a film via a chemical reaction from gaseous precursors on the substrate. In contrast, PVD involves physical processes, such as evaporating a solid source material in a vacuum and letting it condense onto the substrate.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your specific goals will determine how you should approach controlling the CVD reaction steps.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and deposition speed: You will likely operate at higher temperatures in the mass-transport-limited regime, accepting the trade-off of potentially lower film uniformity.
- If your primary focus is film quality and uniformity: You should operate at lower temperatures in the reaction-rate-limited regime, where you have precise control over the slow, steady growth of the film.
- If you are troubleshooting film defects or contamination: Investigate the byproduct removal phase, as inefficient desorption can poison the surface and disrupt stable growth.
By controlling the transport, reaction, and removal of molecules, you can engineer thin films with precision.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Mass Transport | Gas Flow & Diffusion | Reactant gases flow into the chamber and diffuse to the substrate surface. |
| 2. Surface Reaction | Adsorption & Reaction | Molecules adsorb onto the heated surface and react to form the solid film. |
| 3. Byproduct Removal | Desorption & Exhaust | Gaseous byproducts desorb from the surface and are carried out of the chamber. |
Ready to Optimize Your CVD Process for Superior Thin Films?
Understanding the steps of a CVD reaction is the first step to achieving precise, high-quality coatings. Whether your priority is high throughput or exceptional film uniformity, the right lab equipment is crucial for controlling mass transport, surface reactions, and byproduct removal.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect CVD system or components to master your process, ensuring efficient and reliable thin film deposition.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and help you engineer thin films with precision.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















