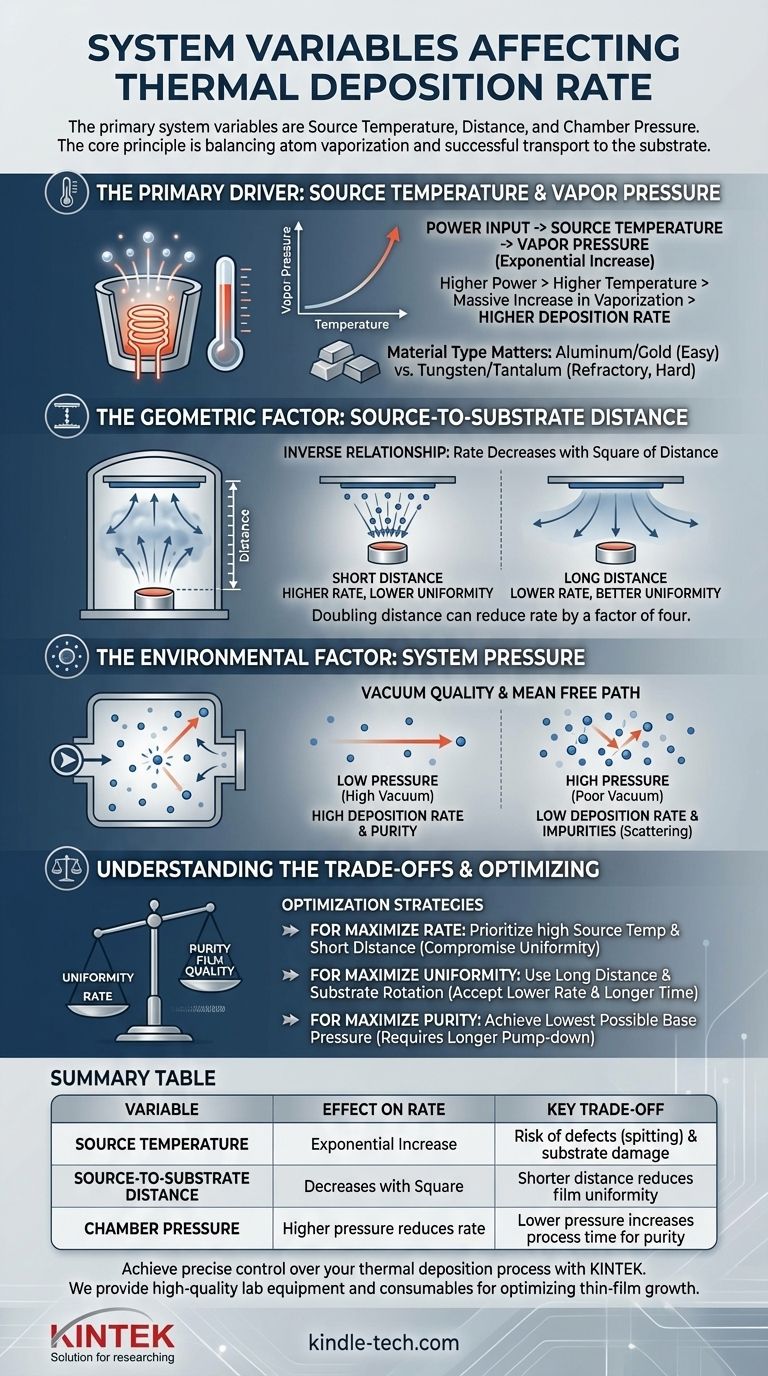
The primary system variables that affect the deposition rate in thermal evaporation are the temperature of the source material, the distance from the source to the substrate, and the pressure within the vacuum chamber. The intrinsic properties of the material being evaporated, specifically its vapor pressure curve, also play a fundamental role in determining the achievable rate.
The core principle is a balance between two factors: how many atoms are vaporized from the source (a function of temperature and material type) and how many of them successfully travel to and stick on the substrate (a function of system geometry and vacuum pressure).
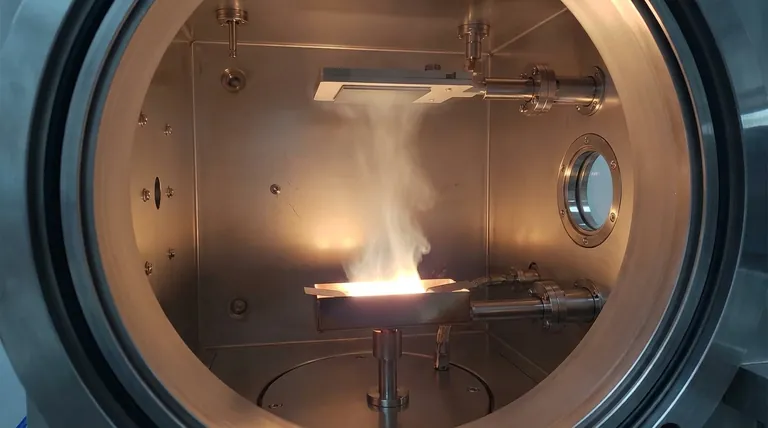

The Primary Driver: Source Temperature and Vapor Pressure
In thermal deposition, you are essentially boiling a material in a vacuum. The rate at which it "boils" or evaporates is the single most important factor, and this is governed by temperature.
The Role of Power Input
The variable you directly control is the electrical power applied to the heating element (like a resistive boat or an electron beam). This power input is what determines the temperature of the source material.
Higher power leads to a higher source temperature.
Understanding Vapor Pressure
Every material has a characteristic vapor pressure, which is the pressure exerted by its gaseous phase. This pressure increases exponentially with temperature.
A small increase in source temperature can cause a massive increase in the vapor pressure, leading to a much higher number of atoms leaving the source per second. This directly translates to a higher deposition rate.
The Material Itself is a Variable
The specific material you are evaporating is a critical variable. Materials like Aluminum and Gold have high vapor pressures at relatively low temperatures and are easy to evaporate.
Refractory materials like Tungsten or Tantalum require extremely high temperatures to achieve the same vapor pressure and, therefore, the same deposition rate.
The Geometric Factor: Source-to-Substrate Distance
The physical layout of your chamber dictates what percentage of the evaporated atoms actually reach their target. The distance between the evaporation source and your substrate is the key geometric parameter.
An Inverse Relationship
The flux of material arriving at the substrate generally decreases with the square of the distance from the source. This means doubling the distance can reduce the deposition rate by a factor of four.
Therefore, a shorter source-to-substrate distance results in a significantly higher deposition rate.
The Effect on Uniformity
While a shorter distance increases the rate, it can harm the thickness uniformity across the substrate. The center of the substrate will be coated much more thickly than the edges.
Increasing the distance allows the vapor cloud to spread more evenly before reaching the substrate, improving uniformity at the cost of a lower deposition rate.
The Environmental Factor: System Pressure
Thermal evaporation must occur in a high vacuum for a simple reason: the evaporated atoms need a clear path to the substrate.
Mean Free Path
The quality of the vacuum is defined by its pressure. This pressure determines the mean free path—the average distance a vaporized atom can travel before colliding with a background gas molecule (like nitrogen or water vapor).
Impact on Rate and Purity
If the system pressure is too high, the mean free path becomes short. Evaporated atoms will collide with background gas, scattering them away from the substrate.
This scattering directly reduces the deposition rate and can also lead to the incorporation of these gas molecules as impurities in your final film, compromising its quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Controlling the deposition rate is not about maximizing a single variable but about finding the optimal balance for your specific goal.
Rate vs. Film Quality
Aggressively increasing the source temperature for a faster rate can cause the molten material to "spit," ejecting microscopic droplets that create defects in the film. It can also cause unwanted radiant heating, potentially damaging sensitive substrates.
Uniformity vs. Rate
The goals of high uniformity and high deposition rate are in direct opposition. Increasing the source-to-substrate distance improves uniformity but drastically reduces the deposition rate, increasing process time and wasting source material.
Pressure vs. Process Time
Achieving a very high vacuum (low pressure) ensures a clean path and high film purity, but it requires long pump-down times. For high-throughput applications, you may need to accept a slightly higher base pressure to reduce the overall cycle time.
Optimizing Your Deposition Process
Your approach should be dictated by the desired properties of your final thin film.
- If your primary focus is maximizing deposition rate: Prioritize increasing the source temperature (power) and using the shortest possible source-to-substrate distance, while accepting potential compromises in uniformity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing film uniformity: Use a long source-to-substrate distance and consider substrate rotation, accepting that this will significantly lower the deposition rate and extend process time.
- If your primary focus is maximizing film purity: Invest time in achieving the lowest possible base pressure in your chamber before beginning the deposition to ensure the longest mean free path.
Mastering these interconnected variables gives you precise control over the growth and final properties of your thin films.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Effect on Deposition Rate | Key Trade-off |
|---|---|---|
| Source Temperature | Exponential increase with higher temperature | Risk of film defects (spitting) and substrate damage |
| Source-to-Substrate Distance | Rate decreases with the square of the distance | Shorter distance reduces film uniformity |
| Chamber Pressure | Higher pressure reduces rate due to atom scattering | Lower pressure increases process time for higher purity |
Achieve precise control over your thermal deposition process. The experts at KINTEK understand that balancing rate, uniformity, and purity is critical for your lab's success. We provide the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to optimize your thin-film growth. Let us help you select the right system for your application—contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Tungsten Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications



















