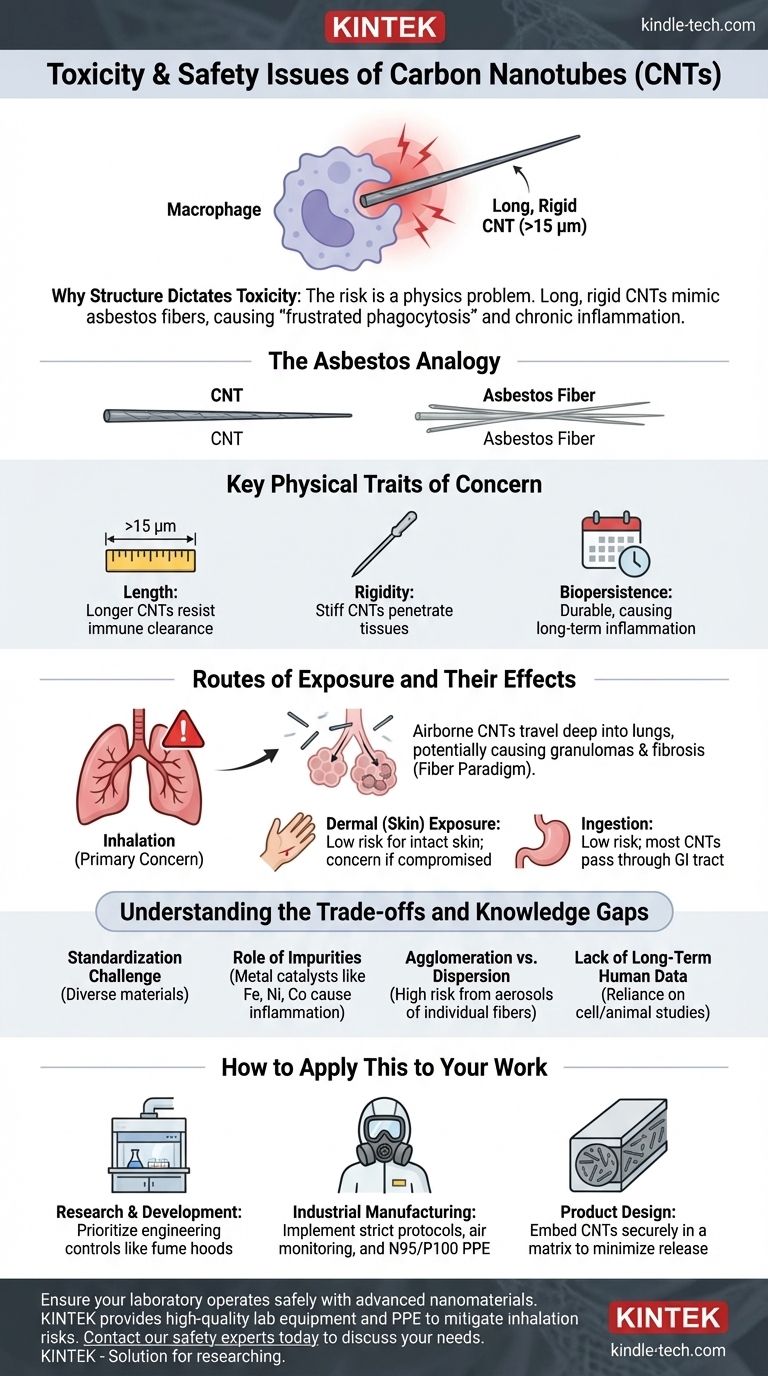
To be clear, the toxicity of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is not due to the carbon itself but is overwhelmingly determined by their physical characteristics. Their needle-like shape, high aspect ratio (length-to-width), and biopersistence can mimic the hazardous properties of asbestos fibers, making inhalation the primary safety concern.
The central issue with carbon nanotube safety is a structural one. Long, rigid, and durable nanotubes that cannot be cleared by the body's immune cells can trigger chronic inflammation, fibrosis, and other serious lung diseases, a mechanism known as the "fiber paradigm."

Why Structure Dictates Toxicity
The potential hazard of CNTs is fundamentally a physics problem, not a chemistry problem. Understanding how their physical form interacts with biological systems is the key to assessing their risk.
The Asbestos Analogy
The most effective way to understand CNT risk is through the asbestos analogy. Asbestos fibers cause diseases like asbestosis and mesothelioma because they are long, thin, and rigid.
The body's immune cells, called macrophages, are responsible for clearing foreign particles. However, they cannot fully engulf fibers longer than their own diameter (typically 15-20 micrometers).
This "frustrated phagocytosis" leads to a state of chronic inflammation. The persistent release of inflammatory signals and reactive oxygen species by struggling macrophages causes tissue damage, scarring (fibrosis), and can eventually lead to cancer.
Key Physical Traits of Concern
Not all CNTs are equally hazardous. The risk is a spectrum defined by specific physical properties:
- Length: Longer CNTs (>15 µm) are more pathogenic as they are too long for macrophages to clear.
- Rigidity: Stiff, needle-like CNTs are more likely to penetrate cell membranes and tissues, causing physical damage and triggering inflammation. Tangled and flexible CNTs are generally less hazardous.
- Biopersistence: CNTs are durable and do not easily break down in the body. This persistence allows inflammatory processes to continue for long periods, increasing the risk of chronic disease.
Routes of Exposure and Their Effects
Understanding how CNTs can enter the body is critical for implementing effective safety controls.
Inhalation: The Primary Concern
The most significant and well-studied route of exposure is inhalation. Due to their small size, airborne CNTs can travel deep into the lungs.
Once in the alveolar region, they can trigger the inflammatory responses described above. Studies in animal models have shown that certain types of CNTs can lead to the formation of granulomas, fibrosis, and, in some cases, pathologies similar to those caused by asbestos.
Dermal (Skin) Exposure
Intact, healthy skin provides a good barrier against CNT penetration. The risk from skin contact is considered low for undamaged skin.
However, if the skin is compromised by cuts or abrasions, CNTs may have a pathway to enter the body. This route is less understood but remains a consideration for workplace safety.
Ingestion
Ingestion is considered a low-risk exposure route. Most ingested CNTs are expected to pass through the gastrointestinal tract without being absorbed into the bloodstream.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Knowledge Gaps
While the fundamental risks are understood, the field of nanotoxicology is still evolving, and significant uncertainties remain.
The Challenge of Standardization
A major difficulty in assessing CNT toxicity is the vast diversity of materials. CNTs produced by different methods vary in length, diameter, purity, and surface chemistry. This makes it challenging to compare results across studies and establish universal safety standards.
The Role of Impurities
The toxicity of a CNT sample can be significantly influenced by impurities, particularly residual metal catalysts (e.g., iron, nickel, cobalt) left over from the manufacturing process. These metals can independently cause oxidative stress and inflammation, confounding the assessment of the nanotubes themselves.
Agglomeration vs. Dispersion
In their raw form, CNTs tend to clump together into large agglomerates. These clumps are often too large to be inhaled into the deep lung.
The highest risk comes from processes that generate energy to break up these agglomerates, creating an aerosol of individual, respirable fibers.
Lack of Long-Term Human Data
Nearly all current knowledge is based on cell culture (in-vitro) and animal (in-vivo) studies. There is a critical lack of long-term epidemiological data from human workers who have been exposed to CNTs, making definitive conclusions about human disease risk difficult.
How to Apply This to Your Work
Managing the risks of CNTs requires a proactive approach centered on preventing exposure, particularly through inhalation.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize engineering controls like certified fume hoods or glove boxes to contain CNT powders and prevent them from becoming airborne.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing: Implement a comprehensive safety program that includes air monitoring, strict handling protocols, and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as N95 or P100 respirators.
- If your primary focus is product design: Minimize future risk by embedding CNTs securely within a solid matrix (e.g., a polymer composite), which drastically reduces the chance of them being released and inhaled during the product's use or disposal.
By understanding that the danger lies in the physical form, you can make informed decisions to engineer safer materials and implement controls that effectively mitigate risk.
Summary Table:
| Risk Factor | Key Insight | Primary Concern |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Needle-like shape mimics asbestos fibers | Inhalation leading to chronic inflammation & fibrosis |
| Length & Rigidity | Fibers >15 µm resist immune clearance | Frustrated phagocytosis & tissue damage |
| Biopersistence | Durable fibers persist in the body | Long-term inflammatory response & disease risk |
| Exposure Route | Inhalation is the primary hazard | Deep lung penetration & granuloma formation |
Ensure your laboratory operates safely with advanced nanomaterials. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for handling nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes. From certified fume hoods to specialized PPE, we help you implement the engineering controls and safety protocols necessary to mitigate inhalation risks and protect your team.
Contact our safety experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can support your research or manufacturing processes with confidence and compliance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















