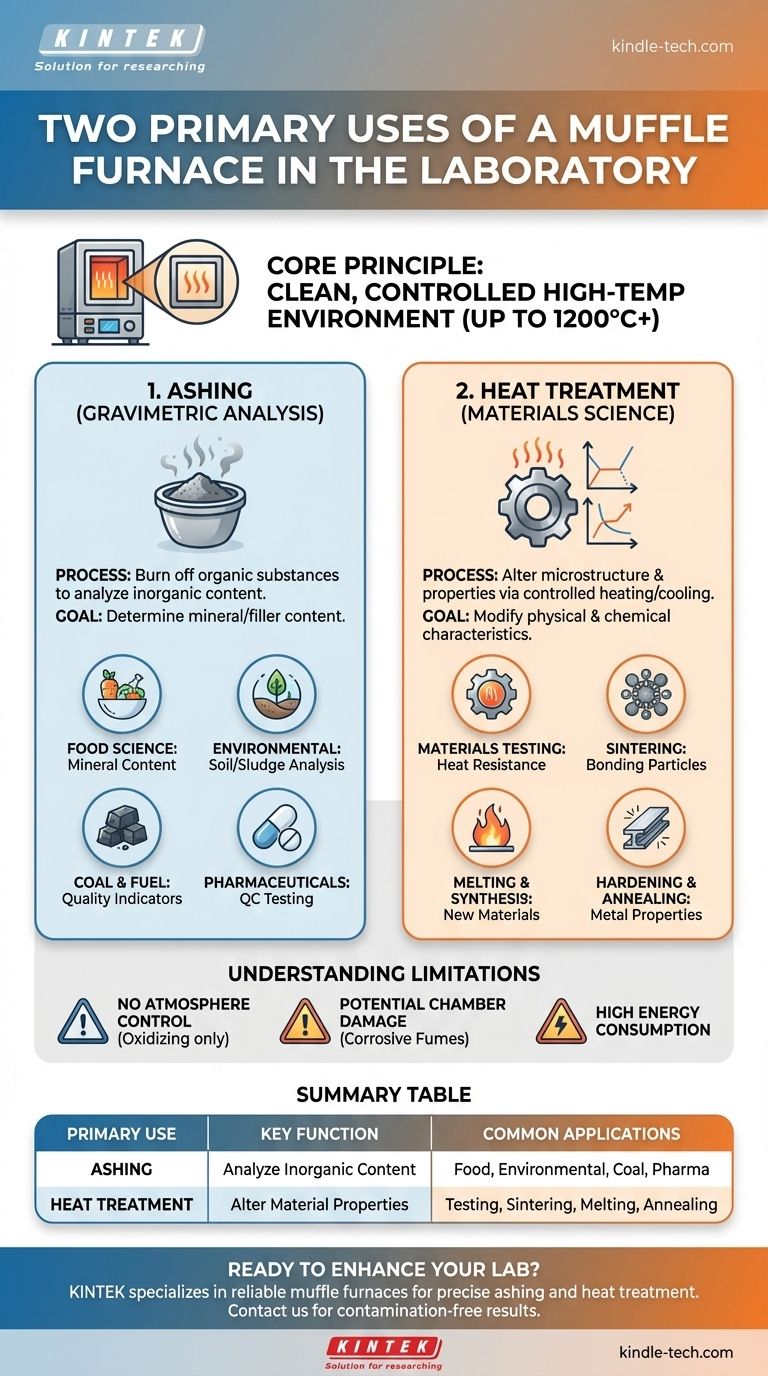
At its core, a muffle furnace is used for two primary functions in a laboratory setting: determining the inorganic, non-volatile content of a sample through a process called ashing, and heat-treating materials to study or alter their physical and chemical properties at extremely high temperatures. These processes are fundamental to quality control, materials science, and analytical chemistry.
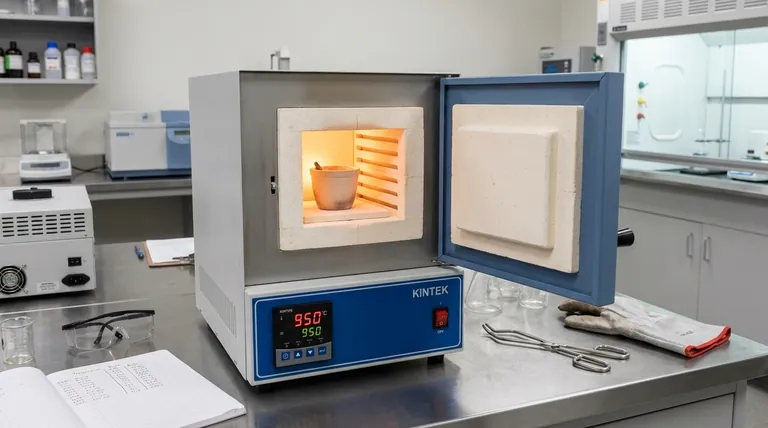
A muffle furnace's unique value comes from its ability to heat samples in a controlled, high-temperature environment that is completely isolated from the heating elements. This prevents contamination, ensuring the integrity of the analytical result or material treatment.

What a Muffle Furnace Fundamentally Does
The Principle of the "Muffle"
A muffle furnace's name comes from its core design feature: an insulated inner chamber, or "muffle," that contains the sample.
This chamber separates the material being heated from the actual heating elements and any byproducts of combustion. This design ensures the sample is heated cleanly and uniformly, primarily through radiant and convection heat.
Controlled, High-Temperature Environment
Modern muffle furnaces provide precise temperature control, often up to 1200°C (2200°F) or higher.
They allow for programmed heating cycles, enabling users to control the rate of temperature increase (ramp), how long the temperature is held (dwell), and the cooling rate. This control is critical for repeatable experiments and standardized testing protocols.
The Primary Applications in Detail
While there are many specific uses, they almost all fall into one of two major categories: analytical decomposition or materials modification.
Application 1: Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing is the process of using high heat to burn away all the organic substances in a sample, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible material (ash).
This is a form of gravimetric analysis, where the mass of the remaining ash is measured to determine the mineral or filler content of the original sample. This is essential in many fields.
- Food Science: To determine the total mineral content of a food product.
- Environmental Analysis: To process samples like wastewater sludge or soil to isolate inorganic contaminants.
- Coal and Fuel Analysis: To measure moisture, ash, and volatile matter, which are key indicators of fuel quality.
- Pharmaceuticals: For quality control testing of raw materials and finished drugs.
Application 2: Heat Treatment and Materials Science
The second major use is altering a material's microstructure and properties through carefully controlled heating and cooling.
This application is less about what is removed and more about how the material itself changes.
- Materials Testing: Engineers use muffle furnaces to test the heat resistance and structural integrity of materials like concrete or metal alloys.
- Sintering: In ceramics and powder metallurgy, fine particles are heated below their melting point until they bond together, forming a solid, cohesive object.
- Melting and Synthesis: Used on a small scale to melt glass, create metal alloys, or synthesize new crystalline materials that only form at high temperatures.
- Hardening and Annealing: To change the hardness, ductility, and strength of metals for research or component creation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly useful, muffle furnaces are not a universal solution for all high-temperature needs. Understanding their limitations is key to proper use.
Lack of Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in an ambient air (oxidizing) atmosphere. It cannot be used for processes that require an inert (e.g., argon) or reactive (e.g., hydrogen) atmosphere. For those applications, a specialized tube furnace is necessary.
Potential for Chamber Damage
While the muffle protects the sample from contamination, it does not protect the furnace from the sample. Heating highly corrosive or volatile materials can release fumes that attack and degrade the furnace's internal insulation and thermocouples over time.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures over 1000°C requires a significant amount of electrical energy. This makes them one of the more power-intensive pieces of equipment in a typical lab.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific use case dictates which furnace features are most important.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (ashing): Prioritize a furnace with exceptional temperature uniformity and accuracy to ensure all organic matter is consistently burned off.
- If your primary focus is materials science (heat treatment): Look for advanced programming capabilities that allow you to precisely control ramp rates and dwell times.
- If your primary focus is elemental analysis prep: Ensure the furnace chamber materials will not leach contaminants into your sample at high temperatures.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is an indispensable tool for any laboratory process that demands clean, controlled, and precise high-temperature heating.
Summary Table:
| Primary Use | Key Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Burning off organic matter to analyze inorganic content | Food science, environmental analysis, coal testing, pharmaceuticals |
| Heat Treatment | Altering material properties through controlled heating | Materials testing, sintering, melting, annealing, hardening |
Ready to enhance your lab's high-temperature capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable muffle furnaces and lab equipment tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require precise ashing for analytical chemistry or controlled heat treatment for materials science, our solutions ensure accurate, contamination-free results.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can support your laboratory's goals and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the operating temperature of the muffle furnace? Find Your Ideal Range for Lab Success
- Can calcination be done in a muffle furnace? Yes, for precise air-atmosphere heating.
- What does a muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing



















