Induction melting furnaces are primarily categorized by their core design and operating environment. The two most fundamental types are coreless and channel furnaces. Beyond this, they can be further classified by their operating atmosphere, such as standard air-melting or specialized vacuum induction melting furnaces, which have their own sub-types.
The choice between induction furnace types is not about which is "better," but which is the correct tool for the job. Coreless furnaces provide flexibility for various alloys and batch sizes, while channel furnaces deliver high efficiency for continuous, large-scale melting of a single metal.
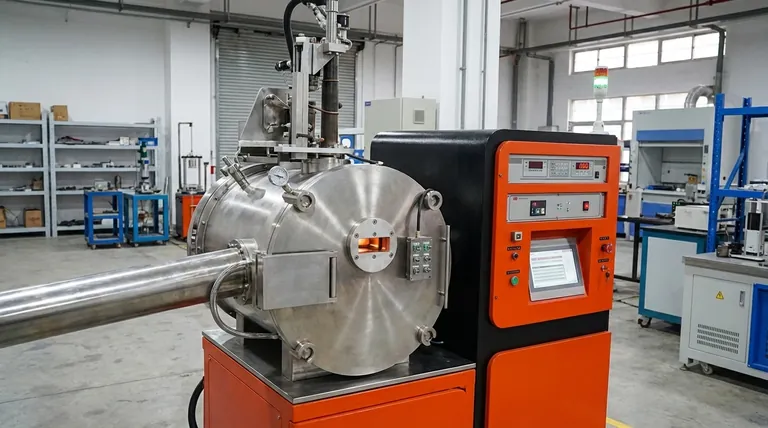

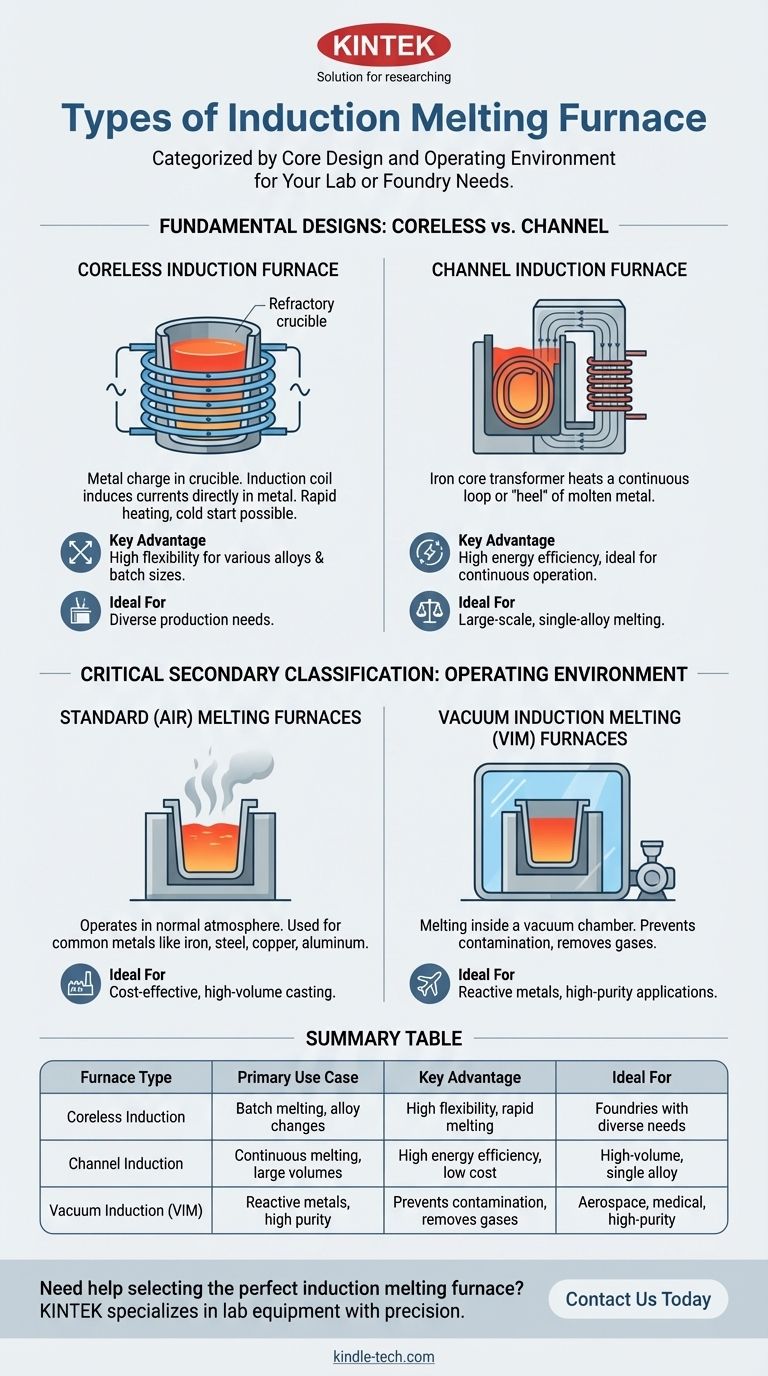
The Two Fundamental Designs: Coreless vs. Channel
The most significant distinction between induction furnaces lies in their physical construction and heating principle. This core difference dictates their ideal applications.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
In a coreless furnace, the metal to be melted is placed directly into a refractory crucible. This crucible is surrounded by a water-cooled coil carrying a powerful alternating current.
The alternating magnetic field induces intense electrical currents directly within the metal charge, causing it to heat and melt rapidly. This design is highly versatile as it can be started from cold with solid metal.
The Channel Induction Furnace
A channel furnace operates more like a transformer. An iron core directs the magnetic field through a closed loop or "channel" of molten metal.
This loop of liquid metal acts as a single-turn secondary winding, which is heated by the induced current. This design is extremely energy-efficient but requires a continuous "heel" of molten metal to operate, making it ideal for holding or continuous melting operations.
A Critical Secondary Classification: Operating Environment
After the core design, the next major classification is the environment in which the metal is melted. This choice is dictated entirely by the type of metal being processed and the required final purity.
Standard (Air) Melting Furnaces
These are the most common types of coreless and channel furnaces, operating in a normal atmosphere.
They are used extensively for melting metals like iron, steel, copper, and aluminum, where some interaction with the atmosphere is acceptable or can be managed with fluxes.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) Furnaces
For materials where atmospheric contamination is unacceptable, melting is performed inside a vacuum chamber. These furnaces are essential for producing high-purity or reactive alloys.
VIM furnaces are critical for preventing chemical reactions with oxygen and nitrogen, removing harmful dissolved gases, and producing the clean metals required for demanding industries like aerospace and medical. They can be further categorized by their process as either batch type or semi-continuous type.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each furnace type comes with a distinct set of operational advantages and limitations. Understanding these is key to making an informed decision.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
Coreless furnaces excel at flexibility. They can be completely emptied and used to melt different alloys in succession, making them perfect for foundries with diverse production needs.
Channel furnaces prioritize efficiency. Their design is optimized for maintaining a large volume of a single molten alloy 24/7. They are less flexible but offer lower energy consumption for high-volume, continuous operations.
Purity vs. Cost
Standard air-melting furnaces are less complex and more cost-effective. They are the workhorses for the vast majority of metal casting and processing.
Vacuum induction furnaces represent a significant investment in cost and complexity. However, this cost is justified when melting reactive metals like titanium or when the final product's quality requires the absolute highest levels of purity and control.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Choosing the correct furnace requires a clear understanding of your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is alloy flexibility and batch production: A coreless induction furnace is the superior choice for foundries producing varied castings.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous melting of a single alloy: A channel induction furnace offers unmatched energy efficiency for large-scale operations.
- If your primary focus is melting reactive metals or achieving maximum purity: A vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace is non-negotiable for aerospace or high-purity applications.
Ultimately, understanding these core distinctions empowers you to choose a technology that aligns precisely with your metallurgical goals and operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coreless Induction | Batch melting, alloy changes | High flexibility, rapid melting | Foundries with diverse production needs |
| Channel Induction | Continuous melting, large volumes | High energy efficiency, low operating cost | High-volume operations with a single alloy |
| Vacuum Induction (VIM) | Reactive metals, high purity | Prevents contamination, removes gases | Aerospace, medical, and high-purity applications |
Need help selecting the perfect induction melting furnace for your lab or foundry? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and expertise. Whether you require the flexibility of a coreless furnace, the efficiency of a channel furnace, or the ultra-purity of a VIM system, our team is here to guide you. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your melting operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings



















