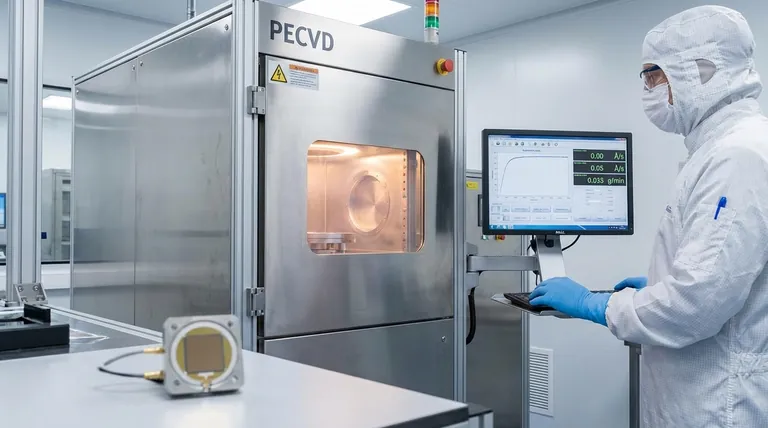
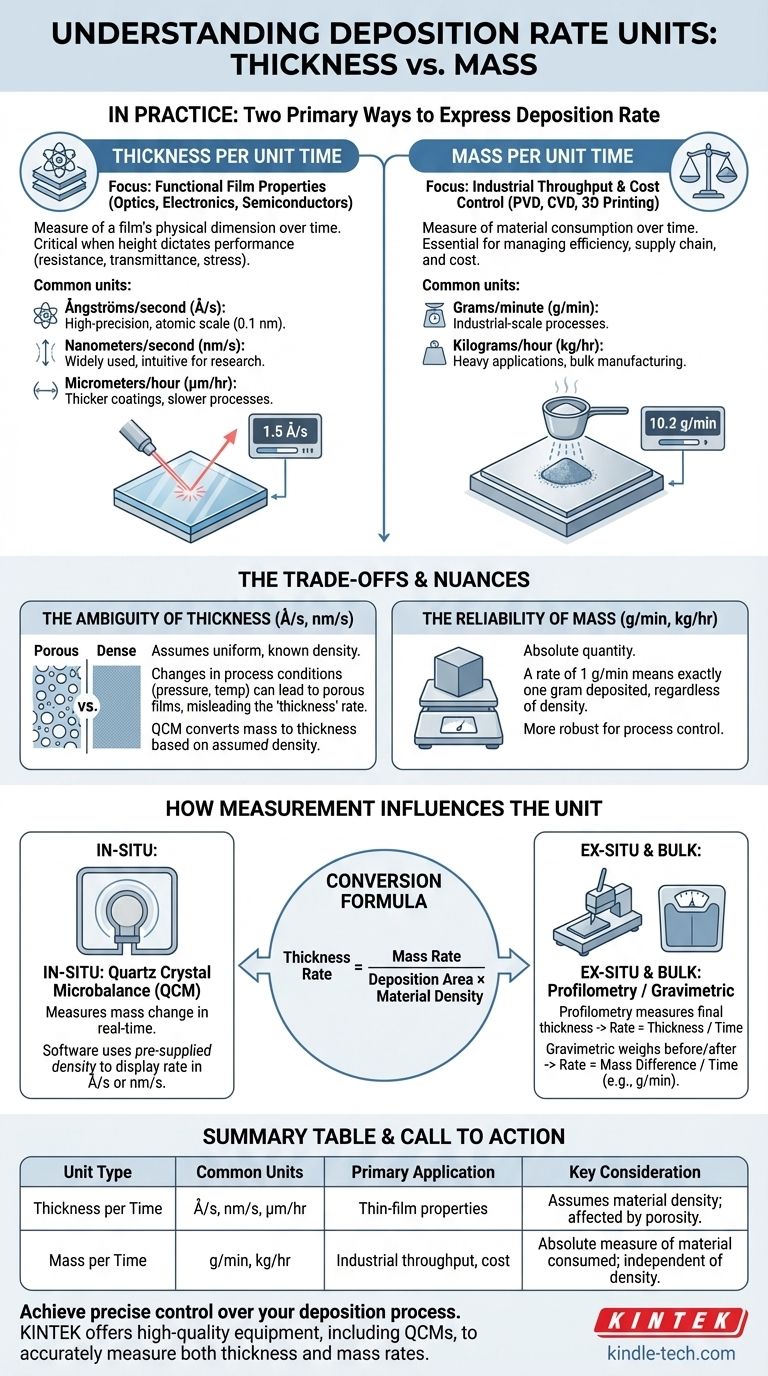
In practice, deposition rate is expressed in one of two primary ways: as a change in thickness over time or as a change in mass over time. The most common units for thin-film applications are Ångströms per second (Å/s) or nanometers per second (nm/s), while industrial or bulk processes often use units of grams per minute (g/min) or kilograms per hour (kg/hr).
The unit you choose for deposition rate is not just a matter of convention; it reflects your primary goal. Measuring thickness over time is critical for controlling a film's functional properties, while measuring mass over time is essential for managing material throughput and cost.

The Two Perspectives on Deposition Rate
At its core, deposition is the process of adding material to a substrate. How you quantify this addition depends entirely on what aspect of the process you need to control.
Thickness per Unit Time
This is the most common metric in research, semiconductor manufacturing, and optical coatings, where the physical dimensions of the film dictate its performance.
- Ångströms per second (Å/s): The standard for high-precision processes like thermal evaporation or sputtering. One Ångström (Å) is 0.1 nanometers, representing the scale of single atomic layers.
- Nanometers per second (nm/s): Widely used and slightly more intuitive than Å/s. It is common in both research and process development.
- Micrometers per hour (µm/hr): Used for thicker coatings or slower processes where measuring on a per-second basis is less practical.
Measuring thickness is essential when a film's electrical resistance, optical transmittance, or mechanical stress is directly tied to its height.
Mass per Unit Time
This metric is dominant in industrial settings where material consumption, process efficiency, and cost are the primary drivers.
- Grams per minute (g/min): A common unit for industrial-scale physical vapor deposition (PVD) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) where tracking the consumption of the source material (e.g., an evaporation boat or sputtering target) is critical.
- Kilograms per hour (kg/hr): Used in heavy industrial applications like large-area coatings, welding, or bulk additive manufacturing (3D printing) where throughput is a key performance indicator.
Measuring mass gives you a direct, unambiguous measure of how much material is being consumed and deposited, which is vital for cost analysis and supply chain management.
How Measurement Method Influences the Unit
The tool you use to measure the rate often determines the units you work with. The two types of units are directly linked through the material's density.
Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM)
A QCM is the most common in-situ tool for real-time rate monitoring. It operates by measuring a change in mass. However, the system's software almost always uses a pre-supplied density value for the material to convert this mass measurement into a thickness, which is then displayed to the user in Å/s or nm/s.
Profilometry and Ellipsometry
Stylus profilometry and optical profilometry are ex-situ methods that measure the physical height (thickness) of a film after deposition. The rate is then calculated by dividing the final thickness by the total deposition time. Ellipsometry can be used in-situ or ex-situ to measure film thickness with high precision, also yielding a thickness-based rate.
Gravimetric Measurement
For bulk processes, the simplest method is to weigh the part before and after the deposition run. Dividing the mass difference by the process time gives a direct measurement of the average deposition rate in units like g/min.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Choosing a unit is not purely academic; it has practical consequences for process control and quality.
The Ambiguity of "Thickness"
A rate measured in nm/s can sometimes be misleading. It assumes the material being deposited has a uniform, known, and fully dense structure. If process conditions change (e.g., pressure or temperature), you could deposit a less dense, more porous film.
The QCM might report the same "thickness" rate, but the film's actual properties could be drastically different because less material was deposited per unit of volume.
The Reliability of "Mass"
Mass rate is an absolute quantity. A rate of 1 g/min means exactly one gram of material is being deposited every minute, regardless of its density or porosity. This makes it a more robust metric for process control and cost modeling.
Converting Between the Two Units
You can easily convert between mass rate and thickness rate if you know the material's density and the area of deposition.
The fundamental relationship is: Thickness Rate = Mass Rate / (Deposition Area × Material Density)
This formula is precisely what a QCM controller uses to convert the mass it measures into the thickness it displays.
Choosing the Right Unit for Your Goal
Your choice of unit should be a conscious decision based on your application's specific needs.
- If your primary focus is functional film properties (optics, electronics): Use a thickness-based rate like Å/s or nm/s, but be aware of how process parameters can affect film density.
- If your primary focus is industrial throughput and cost control: Use a mass-based rate like g/min or kg/hr for a more reliable measure of material consumption.
- If your primary focus is process validation and quality assurance: Measure both. Correlating mass rate with thickness rate allows you to monitor and control the film's density, a critical but often overlooked property.
Ultimately, understanding both types of units empowers you to move beyond simple measurement and achieve true mastery over your deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Unit Type | Common Units | Primary Application | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness per Time | Å/s, nm/s, µm/hr | Thin-film properties (semiconductors, optics) | Assumes material density; can be affected by porosity. |
| Mass per Time | g/min, kg/hr | Industrial throughput, cost control | Absolute measure of material consumed; independent of density. |
Ready to achieve precise control over your deposition process?
Whether you're developing advanced thin films or scaling up for industrial production, choosing the right deposition rate unit is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including deposition systems and monitoring tools like Quartz Crystal Microbalances (QCMs), to help you accurately measure and control thickness (Å/s) or mass (g/min) rates.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss your application and optimize your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures



















