At their core, ceramics are indispensable materials that enable modern technology far beyond simple pottery and tiles. Their useful applications span from the aerospace industry, where they serve as heat shields on spacecraft, to medicine, where they are used for biocompatible dental and joint implants, and into the heart of all electronics as superior electrical insulators.
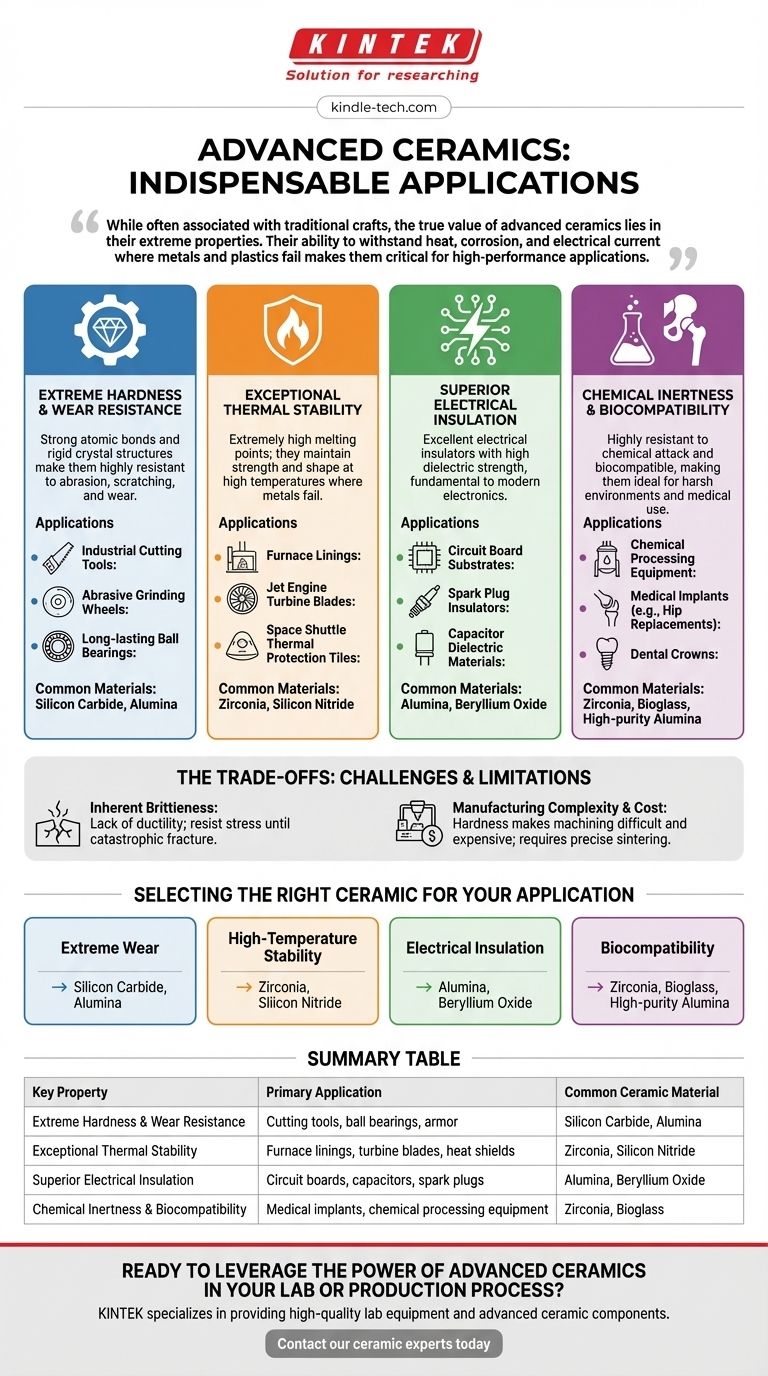
While often associated with traditional crafts, the true value of advanced ceramics lies in their extreme properties. Their ability to withstand heat, corrosion, and electrical current where metals and plastics fail makes them critical for high-performance applications, despite their inherent brittleness.

The Defining Properties of Advanced Ceramics
To understand the applications of ceramics, you must first understand the fundamental properties that make them unique. Unlike metals or polymers, ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic solids defined by their exceptionally strong ionic and covalent bonds.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Ceramics are among the hardest materials known. This property comes from their strong atomic bonds and rigid crystal structures, making them highly resistant to abrasion, scratching, and surface wear.
This makes them ideal for components that experience intense friction, such as industrial cutting tools, abrasive grinding wheels, and long-lasting ceramic ball bearings used in high-speed machinery.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Most ceramics have extremely high melting points and do not expand or contract significantly with temperature changes. They can maintain their strength and shape at temperatures that would cause metals to soften and fail.
This is why they are used for furnace linings, jet engine turbine blades, and the iconic thermal protection tiles on space shuttles, which must endure the intense heat of atmospheric reentry.
Electrical Insulation
While some ceramics can be engineered to be semiconductors or even superconductors, most are excellent electrical insulators. They have a very high dielectric strength, meaning they can withstand a strong electric field without breaking down.
This property is fundamental to all modern electronics. Ceramics like alumina are used as substrates for circuit boards, insulators for spark plugs, and as the dielectric material in capacitors.
Chemical Inertness and Biocompatibility
The strong bonding in ceramics makes them highly resistant to chemical attack from acids, bases, and other corrosive agents. They do not rust or degrade like metals.
Furthermore, many ceramics are biocompatible, meaning they do not provoke an immune response from the human body. This combination makes them perfect for chemical processing equipment and, critically, for medical implants like dental crowns and hip replacements.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brittleness and Cost
No material is perfect. The same strong atomic bonds that give ceramics their desirable properties also create their primary limitation.
The Inherent Brittleness
Unlike a metal that will bend or deform under stress, a ceramic will typically resist until it reaches its breaking point and then fracture catastrophically. This lack of ductility, known as brittleness, is the main challenge in ceramic engineering.
Modern "tough" ceramics like zirconia incorporate clever microstructures that can arrest the propagation of cracks, but the underlying brittle nature remains a key design consideration.
Manufacturing and Machining Complexity
Because they are so hard, machining ceramics into complex shapes after they are fired is extremely difficult and expensive. Most ceramic components are formed from powders that are pressed into shape and then heated to a high temperature in a process called sintering.
This manufacturing process is less forgiving than metal casting or forging, adding to the overall cost and lead time for technical ceramic parts.
Sensitivity to Flaws
The reliability of a ceramic component is highly dependent on its internal structure. Microscopic pores, grains, or tiny cracks introduced during manufacturing can become stress concentration points, leading to premature failure under load. This demands rigorous quality control.
Selecting a Ceramic for Your Application
The right material choice depends entirely on the primary stress your component will face. Different ceramic formulations are engineered to optimize for specific properties.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear and hardness: Look to materials like Silicon Carbide or Alumina for applications like cutting tools, seals, and armor.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Zirconia and Silicon Nitride are engineered for thermal shock resistance and are used in engines and furnaces.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Alumina and Beryllium Oxide are standard choices for electronic substrates and high-voltage components.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: Zirconia, Bioglass, and high-purity Alumina are the go-to materials for medical and dental implants.
By understanding their unique properties and limitations, you can leverage ceramics to solve engineering challenges that no other class of material can.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Application | Common Ceramic Material |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness & Wear Resistance | Cutting tools, ball bearings, armor | Silicon Carbide, Alumina |
| Exceptional Thermal Stability | Furnace linings, turbine blades, heat shields | Zirconia, Silicon Nitride |
| Superior Electrical Insulation | Circuit boards, capacitors, spark plugs | Alumina, Beryllium Oxide |
| Chemical Inertness & Biocompatibility | Medical implants, chemical processing equipment | Zirconia, Bioglass |
Ready to leverage the power of advanced ceramics in your lab or production process?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic components for demanding applications. Whether you need durable furnace linings, precise substrates for electronics, or biocompatible materials for research, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for superior performance and reliability.
Contact our ceramic experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve breakthrough results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What is the thermal expansion of SiC? Master Its Low CTE for Superior High-Temp Performance
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- What are the characteristics of SiC? Unlock High-Temp, Hard, and Chemically Inert Performance



















