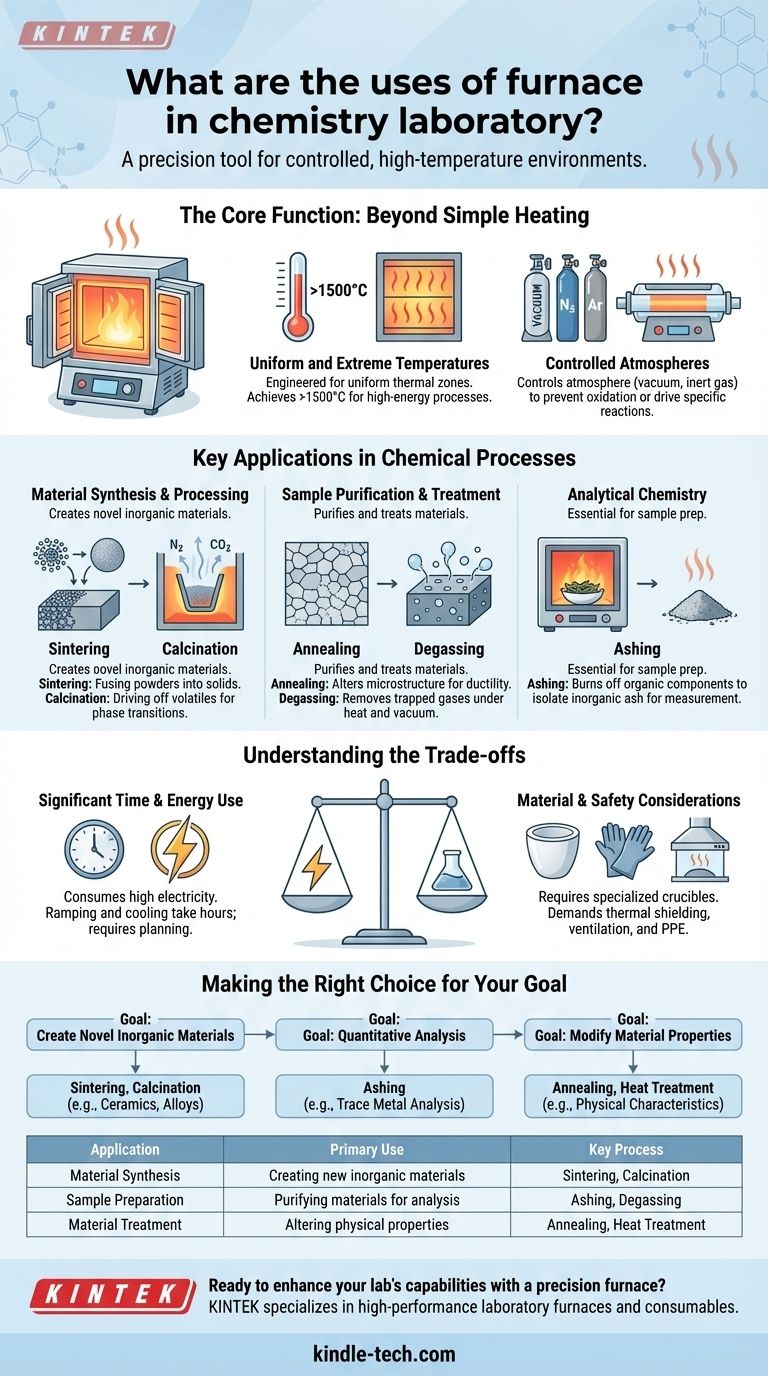
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a precision tool for subjecting materials to controlled, high-temperature environments. Unlike a simple oven, a furnace enables chemists to perform specific thermal processes like material synthesis, purification, and quantitative analysis that are impossible at lower temperatures. These processes are used to create new materials, prepare samples for analysis, or fundamentally alter a substance's chemical and physical properties.
A laboratory furnace is not just a high-powered heater; it is a controlled environment reactor. Its value lies in its ability to precisely manage extreme heat, and often atmospheric conditions, to deliberately drive chemical reactions or physical transformations.

The Core Function: Beyond Simple Heating
A furnace provides capabilities that standard laboratory heating equipment, like hot plates or ovens, cannot match. Understanding these capabilities is key to understanding its use.
Uniform and Extreme Temperatures
A laboratory furnace is engineered to create a highly uniform thermal zone, ensuring a sample is heated evenly from all sides.
Crucially, it can achieve temperatures ranging from several hundred to well over 1500°C, unlocking a range of high-energy chemical processes.
Controlled Atmospheres
Many advanced furnaces, particularly tube furnaces, allow the operator to control the atmosphere surrounding the sample. This can mean heating in a vacuum to prevent oxidation, or introducing specific gases (like nitrogen or argon) to create an inert environment.
Key Applications in Chemical Processes
The combination of high heat and atmospheric control enables several foundational techniques used across many branches of chemistry.
Material Synthesis and Processing
Many modern materials, especially inorganics, cannot be created without a furnace. The high heat provides the necessary activation energy to form robust chemical bonds.
Sintering is a primary application, where fine powders are heated below their melting point until their particles fuse together, forming a solid, dense ceramic or metallic object.
Calcination involves heating a solid material to drive off volatile substances, such as water or carbon dioxide, inducing a phase transition or decomposition. This is a common step in creating catalysts and pigments.
Sample Purification and Treatment
Furnaces are critical for preparing and purifying materials for further use or analysis.
Annealing is a heat treatment that alters a material's microstructure to increase ductility and reduce internal stresses. This process involves heating the material to a specific temperature and then allowing it to cool slowly.
Degassing uses heat, often under a vacuum, to remove dissolved or trapped gases from a solid material, which is critical for high-purity metals and materials used in vacuum systems.
Analytical Chemistry
In analytical chemistry, furnaces are essential for preparing samples in a way that allows for accurate measurement.
The most common use is ashing. A sample is heated in the furnace to a temperature that completely burns off all organic components, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-volatile ash.
This ash can then be dissolved and analyzed to determine its elemental composition, a standard technique for measuring the mineral content of food or the metal content in environmental samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a laboratory furnace is a specialized piece of equipment with inherent limitations that must be considered.
Significant Time and Energy Use
Furnaces consume a large amount of electricity to reach and maintain high temperatures.
They are also not "on-demand" instruments. The process of ramping up to the target temperature and cooling back down can take several hours, requiring careful planning.
Material and Safety Considerations
The extreme temperatures require specialized sample containers, such as high-purity ceramic crucibles, that will not melt or react with the sample.
Proper safety protocols are paramount. This includes thermal shielding, proper ventilation to handle any off-gassing, and personal protective equipment to prevent severe burns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a furnace is driven entirely by the thermal requirements of your chemical process.
- If your primary focus is creating novel inorganic materials: You will use a furnace for high-temperature synthesis, calcination, and sintering to form ceramics, alloys, or advanced composites.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: A muffle furnace is the standard tool for ashing samples to prepare them for trace metal analysis or gravimetric determination.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties: A furnace allows you to perform controlled heat treatments like annealing or tempering to improve a material's physical characteristics.
Ultimately, a furnace empowers a chemist to harness thermal energy as a deliberate and precise tool for manipulating matter.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Creating new inorganic materials | Sintering, Calcination |
| Sample Preparation | Purifying materials for analysis | Ashing, Degassing |
| Material Treatment | Altering physical properties | Annealing, Heat Treatment |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a precision furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces and consumables designed for demanding chemical processes like material synthesis, ashing, and heat treatment. Our experts will help you select the ideal equipment to achieve precise temperature control and reliable results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis
- What is the function of muffle furnace in food industry? Ensure Accurate Ash Determination for Quality Control
- What is the critical point of heat treatment? Master the Key to Steel Transformation
- What apparatus is used for heating in a lab? A Guide to Choosing the Right Tool
- What is the function of an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temp Processing



















