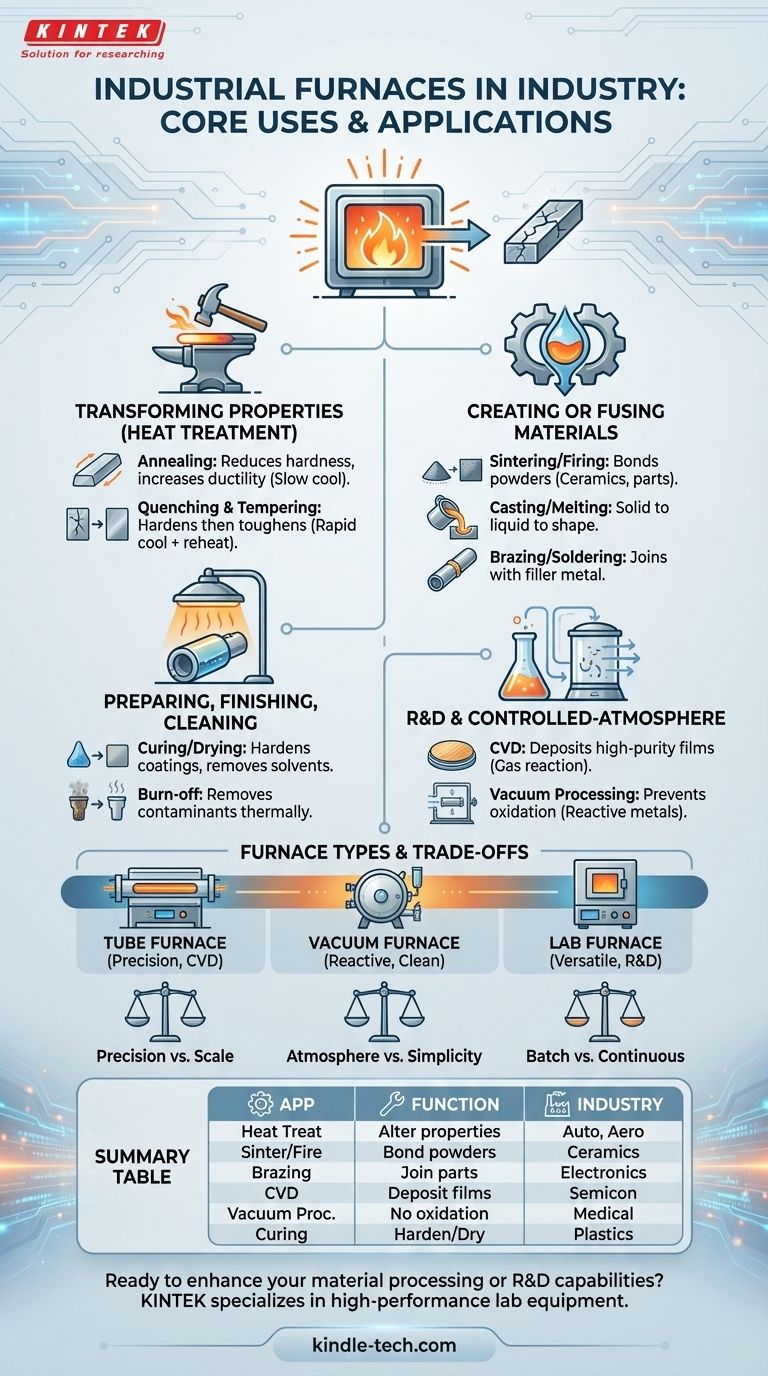
At its core, an industrial furnace is a tool for precisely controlling heat to fundamentally change a material's properties or state. Common applications range from metallurgical processes like annealing and quenching to the synthesis of advanced materials, firing ceramics, curing coatings, and performing controlled laboratory experiments.
The true purpose of a furnace isn't just to generate heat; it's to apply a specific thermal profile in a controlled environment. This precision is what allows us to transform raw or semi-finished materials into components with the exact mechanical, chemical, and physical properties required for their final use.

The Fundamental Roles of Industrial Furnaces
Industrial furnaces are best understood by the goal of the thermal process they enable. Applications fall into several key categories, from altering the internal structure of a metal to creating a new material from powder.
Transforming Material Properties (Heat Treatment)
This is one of the most common uses, focused on modifying a material's internal crystalline structure to improve its performance.
Annealing is a process that heats a material and then cools it slowly. This reduces hardness, removes internal stresses, and increases ductility, making the material easier to work with.
Quenching and tempering are often used together. Quenching involves rapid cooling to harden a metal, while tempering applies a lower-temperature heat treatment to reduce the resulting brittleness and achieve a desired balance of hardness and toughness.
Creating or Fusing Materials
These processes use heat to either form a solid object or join multiple components together permanently.
Firing and sintering involve heating powdered materials below their melting point. This causes the particles to bond together, forming a solid, dense mass. This is fundamental to creating ceramics and parts from powdered metal.
Casting and melting are used to turn solid materials into a liquid state. The molten material can then be poured into a mold to create a specific shape upon cooling.
Brazing and soldering are joining processes that use a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base materials. The furnace heats the assembly to melt the filler, which then flows between the parts and solidifies to create a strong joint.
Preparing, Finishing, and Cleaning
Many processes use furnaces to prepare materials for subsequent steps or for their final application.
Curing and drying use low to moderate heat to remove solvents, moisture, or to trigger a chemical reaction that hardens a coating, like a polymer or paint.
Burn-off processes use higher temperatures to thermally decompose and remove unwanted contaminants, coatings, or residues from a part.
Research and Controlled-Atmosphere Processing
For advanced materials and sensitive processes, controlling the atmosphere inside the furnace is as critical as controlling the temperature.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process where a tube furnace is used to heat a substrate in the presence of precursor gases. The gases react and decompose on the hot surface, depositing a high-purity solid film. This is vital in the semiconductor and coatings industries.
Vacuum processing is performed in a vacuum furnace to prevent oxidation or contamination. This is essential for heat-treating reactive metals and for high-purity applications like vacuum brazing or vacuum annealing.
Matching the Furnace to the Task
The type of furnace used is dictated by the process requirements, such as temperature range, scale, and the need for a specific atmosphere.
Tube Furnaces
These furnaces feature a cylindrical heating chamber and are prized for their temperature uniformity and ability to control the processing atmosphere. They are workhorses in laboratory research, materials testing, and specialized production processes like CVD and pyrolysis. Vertical tube furnaces are ideal for samples that benefit from gravity-assisted flow or vertical alignment.
Vacuum Furnaces
As the name implies, these systems can operate at extremely low pressures. They are indispensable for processes where any atmospheric reaction would be detrimental, such as the heat treatment of titanium alloys or the brazing of complex aerospace components.
Laboratory Furnaces
These are typically smaller, versatile furnaces used for a wide range of R&D tasks. Their applications include annealing small samples, sterilizing equipment, determining the ash content of a material, and conducting general thermal tests.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" furnace, only the one that is right for a specific application.
Precision vs. Scale
A small laboratory tube furnace can offer exceptionally precise temperature control over a small area. In contrast, a large-capacity industrial furnace used for heat-treating thousands of parts may have slightly wider temperature variations across its much larger volume.
Atmosphere Control vs. Simplicity
A simple air furnace is robust, easy to operate, and cost-effective for processes like drying or basic tempering. However, protecting a part from oxidation requires a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere, which adds significant complexity and cost to the furnace design and operation.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Many furnaces, especially in labs, are designed for batch processing, where a set amount of material is loaded, processed, and then unloaded. For high-volume manufacturing, continuous furnaces (such as belt or roller hearth furnaces) are used to move a constant stream of products through the heating and cooling zones.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right thermal process, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is improving existing parts: You will likely need heat treatment processes like annealing for formability or quenching and tempering for strength.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials or objects: Look toward processes like sintering for ceramics, CVD for advanced coatings, or casting for metal parts.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A versatile laboratory furnace or a highly controllable tube furnace is your most critical tool for experimentation.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive or high-purity materials: A vacuum furnace or a sealed tube furnace with atmosphere control is non-negotiable.
Ultimately, industrial furnaces are the essential engines that drive material innovation and enable modern manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Application | Primary Function | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment (Annealing, Quenching) | Alter material properties (hardness, ductility) | Metallurgy, Automotive, Aerospace |
| Sintering & Firing | Bond powdered materials into solid parts | Ceramics, Powder Metallurgy |
| Brazing & Soldering | Join components using filler metals | Electronics, HVAC, Aerospace |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Deposit high-purity coatings or films | Semiconductors, Advanced Coatings |
| Vacuum Processing | Heat-treat without oxidation or contamination | Medical, Aerospace, R&D |
| Curing & Drying | Harden coatings or remove moisture | Automotive, Plastics, Composites |
Ready to enhance your material processing or R&D capabilities? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including tube furnaces, vacuum furnaces, and laboratory furnaces tailored for precise thermal applications. Whether you're in materials science, manufacturing, or research, our solutions ensure controlled heating for optimal results. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















