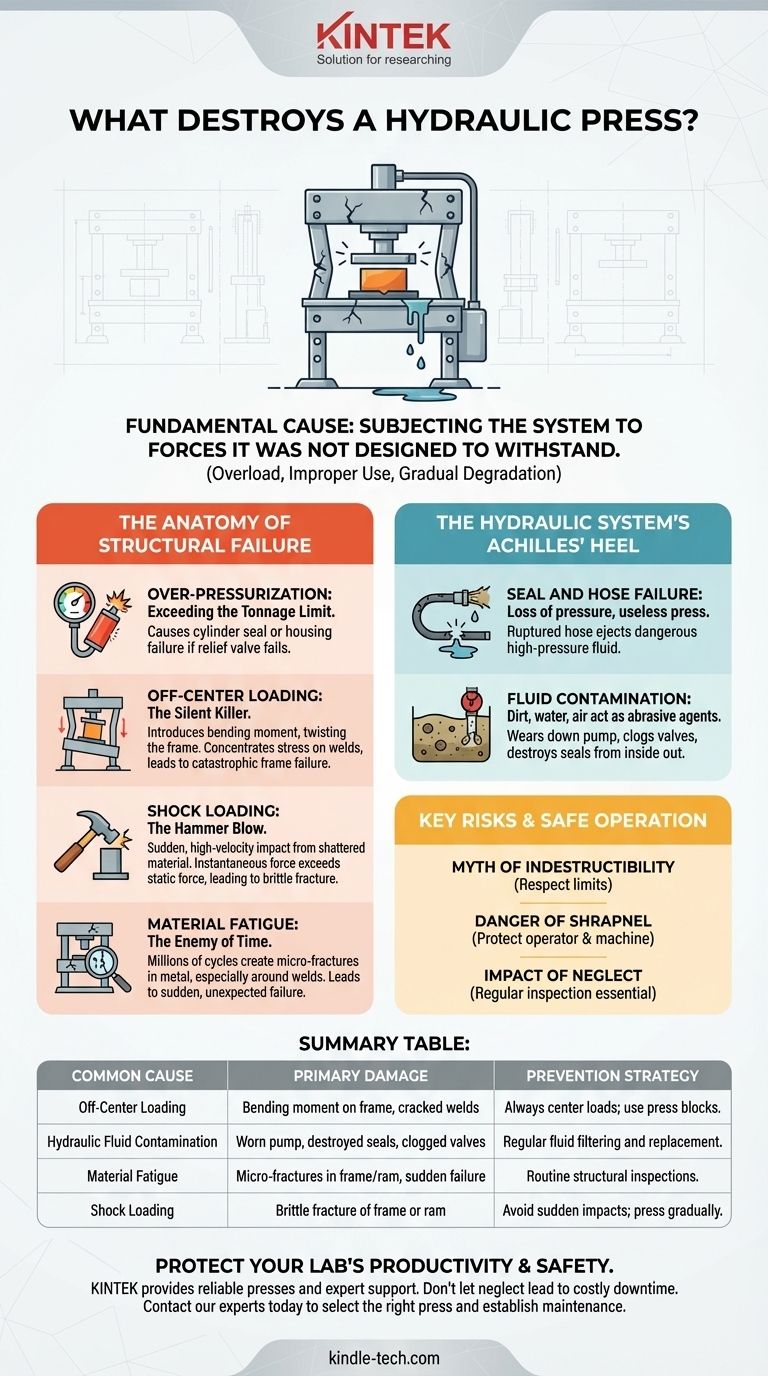
Fundamentally, a hydraulic press is destroyed by subjecting its structure or components to forces they were not designed to withstand. This can happen through a catastrophic overload, but more often it's the result of improper use, such as applying force unevenly, or through the gradual degradation of its core components from fatigue and neglect.
A hydraulic press is a system, and its failure is almost always a system failure. While spectacular over-pressurization is possible, the more common destructive forces are operational errors like off-center loading and the slow, silent decay caused by material fatigue and hydraulic contamination.

The Anatomy of Failure: Beyond Sheer Force
To understand how a press fails, you must look beyond its tonnage rating. That number represents an ideal condition: a perfectly centered, static load. The real world introduces complexities that can destroy a machine well below its stated limits.
Over-Pressurization: Exceeding the Tonnage Limit
A press is rated for a maximum force, which corresponds to a maximum hydraulic fluid pressure. Exceeding this is the most obvious failure mode.
Most industrial presses have a pressure relief valve as a safety measure, designed to open and vent fluid if the pressure exceeds a set limit. However, if this valve fails, is tampered with, or is not present on a simpler press, the pressure can build until a component gives way—typically a cylinder seal, a hydraulic hose, or, in a catastrophic event, the cylinder housing itself.
Off-Center Loading: The Silent Killer
Placing an object off-center is one of the most common and dangerous ways to damage a press. The force is no longer purely compressive.
This introduces a bending moment on the ram and, more critically, the entire frame. The press frame, designed to handle immense compression, is suddenly asked to resist being twisted or bent apart. This concentrates stress on welds and corners, potentially leading to cracks or catastrophic frame failure at a fraction of the machine's rated capacity.
Shock Loading: The Hammer Blow
A hydraulic press is designed to apply force gradually. A sudden, high-velocity impact, known as a shock load, can be devastating.
This occurs when something being pressed suddenly shatters or yields, causing the ram to accelerate and slam into the remaining material. The instantaneous force of this impact can be many times greater than the static force the press was generating, leading to brittle fracture in the frame or ram.
Material Fatigue: The Enemy of Time
Like any machine, a press's components are subject to fatigue. Every cycle of pressurizing and de-pressurizing creates tiny stresses in the metal.
Over millions of cycles, these stresses can cause micro-fractures to form and grow, particularly around welds or sharp corners. Eventually, a crack can reach a critical size, leading to a sudden, unexpected failure under a load that the press had handled countless times before.
The Hydraulic System: The Press's Achilles' Heel
Often, the destruction of a press isn't a dramatic structural collapse but a fatal failure of its hydraulic heart. The power of the press is entirely dependent on the integrity of this system.
Seal and Hose Failure
The most common points of failure are the hydraulic seals inside the cylinder and the external hoses. A blown seal will cause a loss of pressure and render the press useless. A ruptured high-pressure hose is extremely dangerous, capable of ejecting hydraulic fluid with enough force to cause severe injection injuries.
Fluid Contamination
Dirt, water, or air in the hydraulic fluid acts as an abrasive and corrosive agent. Contaminants will rapidly wear down the pump, clog valves, and destroy seals from the inside out. This slow, internal destruction guarantees eventual failure.
Understanding the Key Risks
Recognizing the potential for failure is critical for safe and effective operation. The greatest dangers often come from misunderstanding the machine's limits.
The Myth of Indestructibility
The immense force of a hydraulic press can create a false sense of invincibility. It is crucial to remember that it is a precisely engineered tool operating under extreme stress, not an unstoppable force. Respecting its design limits is paramount.
The Danger of Shrapnel
When an object being pressed fails catastrophically, it can explode, sending shrapnel in all directions. This shrapnel can easily damage the press's ram, gauges, or hoses, and poses a lethal threat to the operator. The failure of the workpiece is often a primary cause of damage to the machine itself.
The Impact of Neglect
A press that is not maintained is a press that is actively being destroyed. Leaking seals, contaminated fluid, and uninspected welds are all failures waiting to happen. Regular inspection and maintenance are not optional; they are essential for preventing destruction.
Making the Right Choice for Safe Operation
Your approach to using a hydraulic press should be dictated by your goal, whether it's production, repair, or experimentation.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Always ensure loads are perfectly centered, use press blocks to distribute force, and never stand directly in line with the press axis.
- If your primary focus is machine longevity: Prioritize hydraulic fluid health with regular filtering and replacement, and conduct routine inspections of all seals, hoses, and structural welds.
- If your primary focus is material testing or experimentation: Assume the object being pressed will fail violently and use polycarbonate safety shields, remote operation, and instruments to monitor pressure and deflection.
Ultimately, a hydraulic press is destroyed not by its power, but by a lack of respect for the engineering principles that govern it.
Summary Table:
| Common Cause of Failure | Primary Damage | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Off-Center Loading | Bending moment on frame, cracked welds | Always center loads; use press blocks. |
| Hydraulic Fluid Contamination | Worn pump, destroyed seals, clogged valves | Regular fluid filtering and replacement. |
| Material Fatigue | Micro-fractures in frame/ram, sudden failure | Routine structural inspections. |
| Shock Loading | Brittle fracture of frame or ram | Avoid sudden impacts; press gradually. |
Protect your lab's productivity and safety. The destruction of a hydraulic press often stems from operational errors and preventable maintenance issues. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable hydraulic presses and the expert support needed to maximize their lifespan and ensure safe operation.
Don't let neglect or misuse lead to costly downtime. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs, from selecting the right press to establishing a proactive maintenance schedule.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System



















