At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is remarkably versatile. It can be applied to a wide range of materials, including most metals, ceramics, and even certain plastics. The process is not limited to just inorganic substrates; both the item being coated and the coating material itself can be either inorganic or organic.
The question isn't just what materials can receive a PVD coating, but which materials are truly suitable for the high-vacuum, high-temperature environment of the process. A material's compatibility with vacuum and its ability to withstand heat are the primary factors determining a successful outcome.
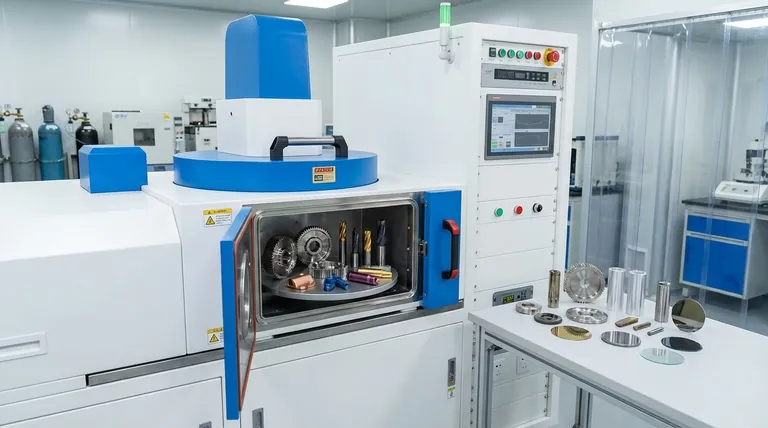

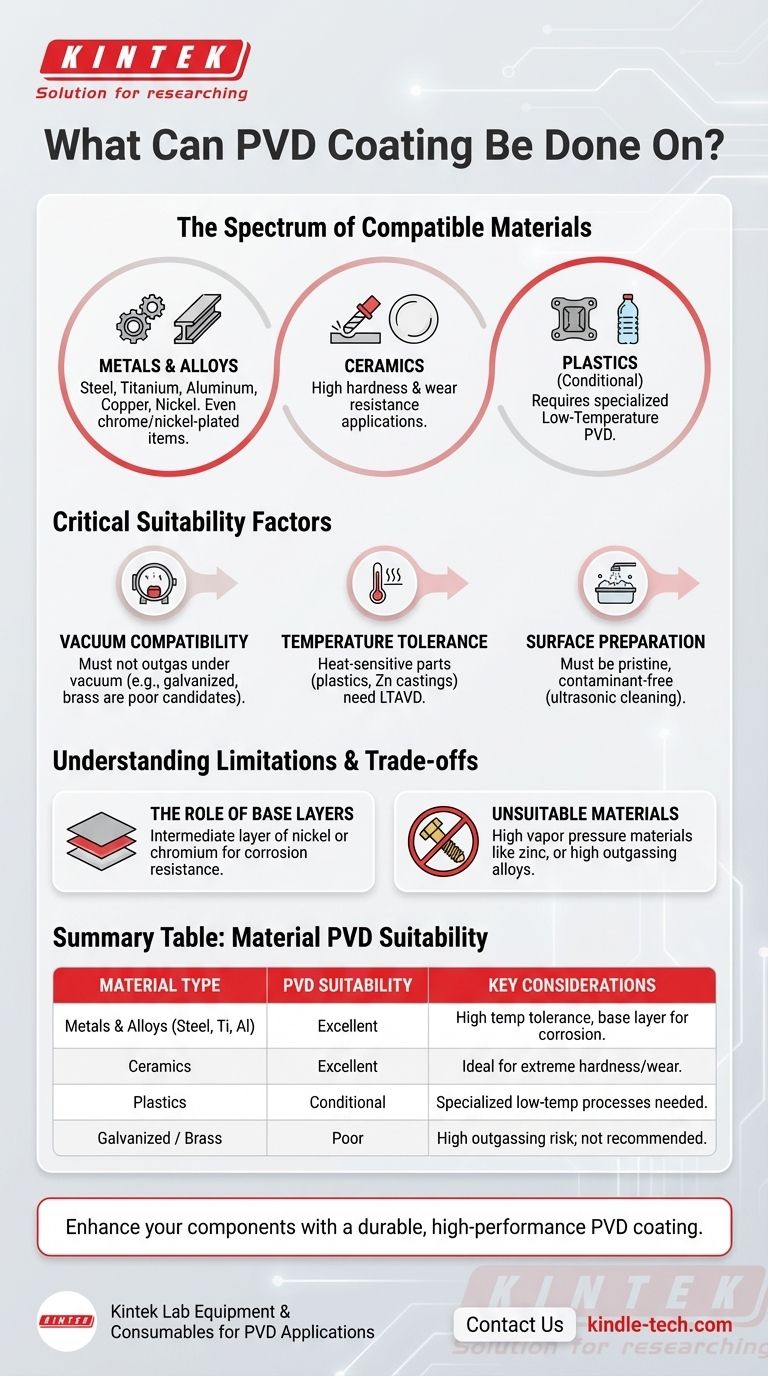
The Spectrum of Compatible Materials
PVD's adaptability makes it a valuable finishing process across numerous industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical devices and consumer hardware. The list of compatible materials is extensive, though some require special considerations.
Common Metals and Alloys
Most metals are excellent candidates for PVD coating. This includes all families of steel, particularly high-alloy variants like stainless and high-speed steels.
Non-ferrous metals such as titanium, aluminum, copper, and nickel alloys are also routinely coated. Even items that are already chrome or nickel-plated can receive an additional PVD layer.
Ceramics and Plastics
Beyond metals, PVD can be successfully applied to ceramics. This is common in applications requiring extreme hardness and wear resistance, such as cutting tools.
Certain plastics can also be coated, but this requires a specialized, low-temperature PVD process to prevent the substrate from deforming or melting.
Critical Suitability Factors
Simply being on the compatible list isn't enough. For a PVD coating to adhere properly and perform as expected, the substrate material must meet several critical requirements.
Vacuum Compatibility
The PVD process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. Materials that release gases under vacuum (a process known as outgassing) can disrupt the coating process and lead to poor quality.
This is the primary reason some materials, like brass without pre-treatment or galvanized materials, are considered unsuitable. The zinc in these materials can vaporize in the vacuum, contaminating the chamber.
Temperature Tolerance
Traditional PVD processes can involve high temperatures. The substrate must be able to withstand this heat without degrading, warping, or compromising its structural integrity.
For heat-sensitive materials like plastics, aluminum, and zinc castings, a specialized technique called Low-Temperature Arc Vapor Deposition (LTAVD) is used to achieve the desired coating without damaging the part.
Surface Preparation
A pristine surface is non-negotiable for successful PVD coating. Every item must undergo a rigorous, multi-stage cleaning process before entering the vacuum chamber.
This typically involves ultrasonic cleaning tanks with specialized detergents, followed by rinsing and drying systems to ensure the surface is completely free of oils, contaminants, and residues.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While powerful, the PVD process has specific limitations that must be respected. Understanding these will prevent costly errors and ensure the final product meets its design goals.
The Role of Base Layers
Some substrate materials may not offer sufficient corrosion resistance on their own. In these cases, a base layer is required before the PVD coating is applied.
A preparatory layer of nickel or chromium is often plated onto the part first. This underlayer provides environmental protection, and the final PVD coating is then applied on top for its aesthetic and wear-resistant properties.
Unsuitable Materials
Certain materials are fundamentally incompatible with the PVD process.
As mentioned, galvanized materials are problematic due to the high vapor pressure of zinc. Similarly, many common brass alloys outgas significantly, making them poor candidates unless they are first sealed with a suitable electroplated layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material and preparation process is key to leveraging the benefits of PVD coating.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on a metal part: High-alloy steels, stainless steels, and titanium are ideal candidates that readily accept PVD coatings.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive item: Materials like plastics or zinc castings are viable, but you must ensure the process used is a low-temperature variant like LTAVD.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance on a base metal: Plan for an intermediate electroplated layer of nickel or chrome before the final PVD finish is applied.
Ultimately, a successful PVD outcome depends on a clear understanding of your substrate material's properties and how they interact with the vacuum deposition environment.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | PVD Suitability | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Metals & Alloys (Steel, Titanium, Aluminum) | Excellent | Must withstand high temperatures; some may require a base layer for corrosion resistance. |
| Ceramics | Excellent | Ideal for extreme hardness and wear resistance applications. |
| Plastics | Conditional | Requires specialized low-temperature PVD processes to avoid deformation. |
| Galvanized Materials / Brass | Poor | High outgassing risk; not recommended without pre-treatment. |
Ready to enhance your components with a durable, high-performance PVD coating? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD applications. Whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or heat-sensitive plastics, our solutions ensure optimal substrate compatibility and coating quality. Contact us today to discuss your project needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















