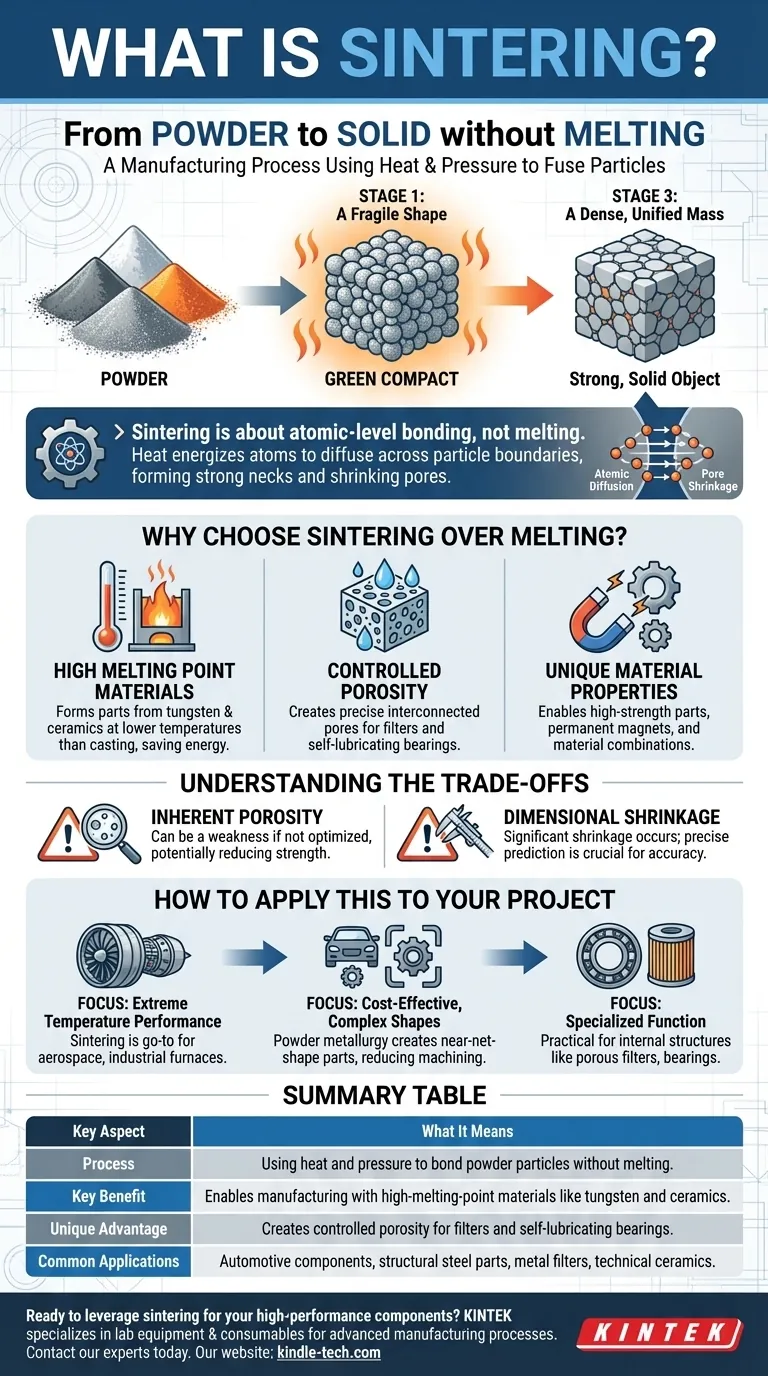
In short, sintering is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to fuse particles together into a solid object without melting them into a liquid. Imagine compressing a pile of metallic or ceramic powder and heating it just enough for the individual particles to weld themselves together at their contact points. The result is a single, solid mass created directly from powder.
Sintering is fundamentally about atomic-level bonding, not melting. It leverages heat to give atoms the energy to diffuse across particle boundaries, effectively fusing a powder compact into a dense, solid component with unique properties.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
To understand sintering, it's best to think of it as a three-stage process that transforms loose powder into a solid object.
The Starting Point: A 'Green' Compact
The process begins with a powder of a specific material, such as a metal, ceramic, or plastic. This powder is typically pressed into a desired shape, often called a "green compact." At this stage, the object has shape but is fragile, with particles only held together by mechanical friction.
The Role of Heat: Atomic Diffusion
The green compact is then heated in a controlled furnace to a temperature below the material's melting point. This heat is the critical ingredient. It provides the thermal energy needed to make the atoms at the surface of each particle highly active.
These energized atoms begin to move and diffuse across the boundaries where particles touch. This atomic transport effectively closes the gaps and pores between particles, forming strong metallurgical bonds or "necks" between them.
The Result: A Dense, Unified Mass
As this diffusion process continues, the individual particles merge, the pores shrink, and the overall part becomes denser and stronger. The final result is a single, solid piece that has been fundamentally transformed from a collection of discrete particles into a unified material.
Why Choose Sintering Over Melting?
Sintering is not just an alternative to casting (melting and pouring); it enables the creation of materials and shapes that are otherwise difficult or impossible to produce.
Working with High Melting Point Materials
Many advanced materials, like tungsten and certain technical ceramics, have extremely high melting points. Melting and casting them is energy-intensive, expensive, and technically challenging. Sintering allows them to be formed into solid parts at much lower temperatures.
Creating Controlled Porosity
Sintering is unique in its ability to create parts with a precisely controlled level of porosity. This is essential for products like metal filters or self-lubricating bearings, where a network of interconnected pores is a required feature. Casting cannot achieve this.
Achieving Unique Material Properties
The process allows for the creation of structural steel parts, high-strength components, and specialized products like permanent magnets. Because it operates in the solid state, it can also be used to combine materials that would not normally mix in a liquid state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not a universal solution. It comes with specific considerations that must be managed.
Inherent Porosity Can Be a Weakness
Unless the process is perfectly optimized, some residual porosity often remains in the final part. These microscopic voids can act as stress concentration points, potentially reducing the material's ultimate strength compared to a fully dense, wrought equivalent.
Dimensional Shrinkage Must Be Controlled
As the particles fuse and the pores close, the entire component shrinks. This shrinkage is significant and must be precisely predicted and controlled to achieve accurate final dimensions, which adds a layer of complexity to the process design.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice to use sintering depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature performance: Sintering is the go-to method for creating parts from high-melting-point materials like tungsten or advanced ceramics for aerospace or industrial furnace applications.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, complex shapes: For components like automotive gears and structural brackets, powder metallurgy (which uses sintering) can produce near-net-shape parts with minimal machining, saving significant cost.
- If your primary focus is a specialized function: Sintering is the only practical way to produce components defined by their internal structure, such as porous metal filters or oil-impregnated bearings.
Ultimately, sintering empowers engineers to build materials from the particle level upwards, unlocking properties and applications that traditional melt-based processes cannot access.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Process | Using heat and pressure to bond powder particles without melting. |
| Key Benefit | Enables manufacturing with high-melting-point materials like tungsten and ceramics. |
| Unique Advantage | Creates controlled porosity for filters and self-lubricating bearings. |
| Common Applications | Automotive components, structural steel parts, metal filters, and technical ceramics. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your high-performance components?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that power advanced manufacturing processes like sintering. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing production, we provide the reliable tools you need for R&D and quality control.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in materials science and powder metallurgy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- How much psi can a hydraulic press make? From 2,000 PSI to over 50,000 PSI Explained
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature hydraulic press? Optimize MEA Fabrication for HCl Electrolysis
- Why are hydraulic presses dangerous to operate? Uncover the Silent, Deceptive Risks



















