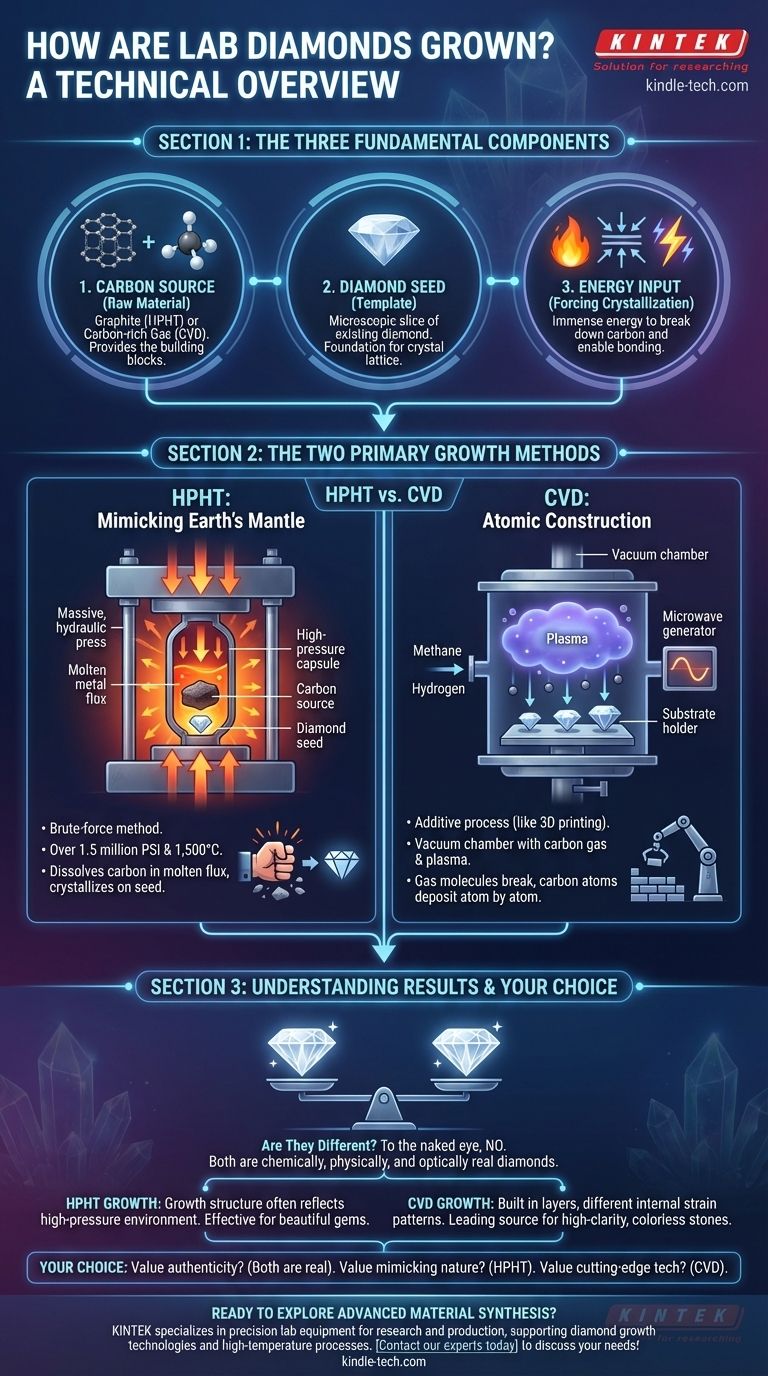
To grow a lab diamond, you need three fundamental components: a source of carbon, a tiny diamond "seed" to act as a template, and an immense amount of energy. This process uses advanced technology to replicate the extreme conditions under which diamonds form deep within the Earth, resulting in a gemstone that is chemically and physically identical to its mined counterpart.
The core challenge in creating a diamond is not about "growing" it like a plant, but about forcing carbon atoms to arrange themselves into a specific, incredibly stable crystal structure. The two dominant methods, HPHT and CVD, are simply different technological solutions to achieve this same fundamental goal.

The Three Core Ingredients for Diamond Creation
Regardless of the specific method used, the creation of any gem-quality lab diamond relies on the same three essential elements coming together under highly controlled conditions.
The Carbon Source
This is the raw material from which the diamond is built. The form of carbon used depends on the growth method. For one method, it's simple graphite (the same material in a pencil lead); for another, it is a specialized, carbon-rich gas like methane.
The Diamond "Seed"
A new diamond cannot form from scratch in a chaotic environment. It requires a template. A "seed"—a microscopic slice of a pre-existing diamond (either natural or lab-grown)—is used to provide the foundational crystal structure for the carbon atoms to bond to.
The Energy Input
Carbon atoms do not willingly form into a diamond lattice; it is a high-energy state. An enormous and sustained input of energy is required to break down the original carbon source and give the atoms the mobility to attach themselves to the seed crystal, layer by layer.
The Two Primary Growth Methods
While the ingredients are the same, the industry has standardized on two distinct methods for applying the necessary energy and forcing crystallization.
HPHT (High Pressure/High Temperature)
The HPHT method directly mimics the conditions of the Earth's mantle. A diamond seed and a refined carbon source (like graphite) are placed inside a sophisticated press capable of exerting immense force.
This press generates pressures of over 1.5 million pounds per square inch and temperatures exceeding 1,500°C (2,700°F). This extreme environment dissolves the carbon source in a molten metal flux, allowing the carbon atoms to crystallize onto the diamond seed, growing a new, larger diamond over time.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
The CVD method is less about brute force and more about atomic construction. It is sometimes compared to 3D printing on an atomic scale.
A diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber, which is then filled with a carbon-rich gas (like methane). This gas is heated to an extreme temperature using technology like microwaves, creating a plasma. This process breaks the gas molecules apart, allowing pure carbon atoms to rain down and deposit onto the diamond seed, building up the crystal one layer at a time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Results
Both HPHT and CVD are capable of producing flawless, high-quality diamonds. Neither method is definitively "better," but they represent different approaches to solving the same physics problem, which can lead to subtle differences in the final product.
The Nature of HPHT Growth
Because it simulates the conditions of natural formation, the HPHT process is a "brute-force" method. It creates a diamond with a growth structure that often reflects the high-pressure environment. It is an extremely effective and established way to create beautiful gems.
The Nature of CVD Growth
CVD is a more additive and controlled process. Because the diamond is built up in successive layers, it can sometimes result in a different type of internal strain pattern. This method has seen rapid advancements and is now a leading source of high-clarity lab diamonds, particularly colorless stones.
Is the Final Product Different?
To the naked eye, no. Both methods produce real diamonds. However, the different growth conditions can leave behind microscopic identifiers related to their formation. Gemological laboratories can use advanced equipment to identify these markers and certify a diamond's origin as lab-grown, and often as HPHT or CVD.
How This Applies to Your Choice
Understanding the process helps clarify that you are choosing between two legitimate methods of diamond creation, not between a "real" and "fake" product.
- If your primary focus is authenticity: Both HPHT and CVD produce real diamonds that are physically, chemically, and optically identical to mined diamonds.
- If you value a process that mimics nature: The HPHT method, with its use of extreme pressure and heat, is a direct technological replication of the forces in the Earth's mantle.
- If you value cutting-edge technology: The CVD method represents a more modern, "additive manufacturing" approach to building a diamond atom by atom.
Ultimately, knowing how lab diamonds are created confirms they are not imitations, but true diamonds engineered through remarkable human innovation.
Summary Table:
| Ingredient | Role in Diamond Growth | Common Forms |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Source | Raw material for diamond structure | Graphite (HPHT) or Methane gas (CVD) |
| Diamond Seed | Template for crystal growth | Thin slice of existing diamond |
| Energy Input | Forces carbon atoms into diamond lattice | High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
Ready to explore lab equipment for advanced material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for research and production needs. Whether you're developing diamond growth technologies or other high-temperature processes, our reliable solutions support innovation and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can meet your laboratory requirements!
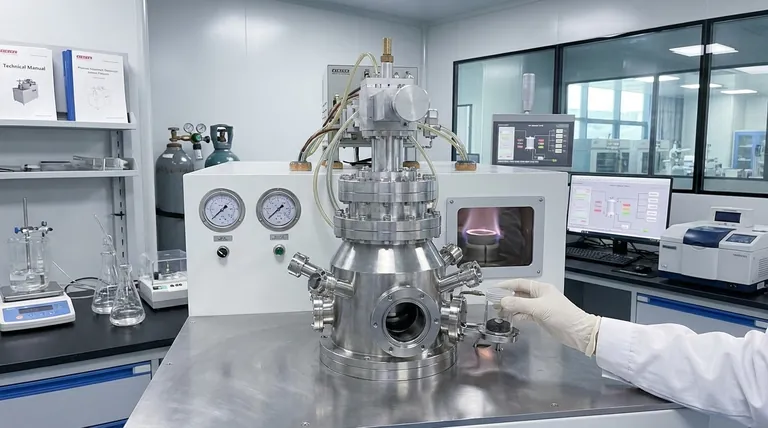
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What pressure is needed for chemical vapor deposition of diamonds? Master the Low-Pressure 'Sweet Spot'
- Is there certification for lab-grown diamonds? Get Independent Verification for Your Purchase
- What is MP CVD? Unlock the Power of Microwave Plasma for High-Purity Diamond Synthesis
- What is the hardness of a lab grown diamond? It's as Hard as a Natural Diamond
- How do microwave plasma-generated radicals facilitate the direct growth of graphene? Enhance Non-Catalytic Substrates
- What is the process of MPCVD? Grow High-Purity Diamond & Advanced Films
- What is the demand of CVD diamonds? Driven by Ethics, Purity, and Affordability
- Are CVD diamonds worth it? Unlock Brilliant Value & Ethical Clarity



















