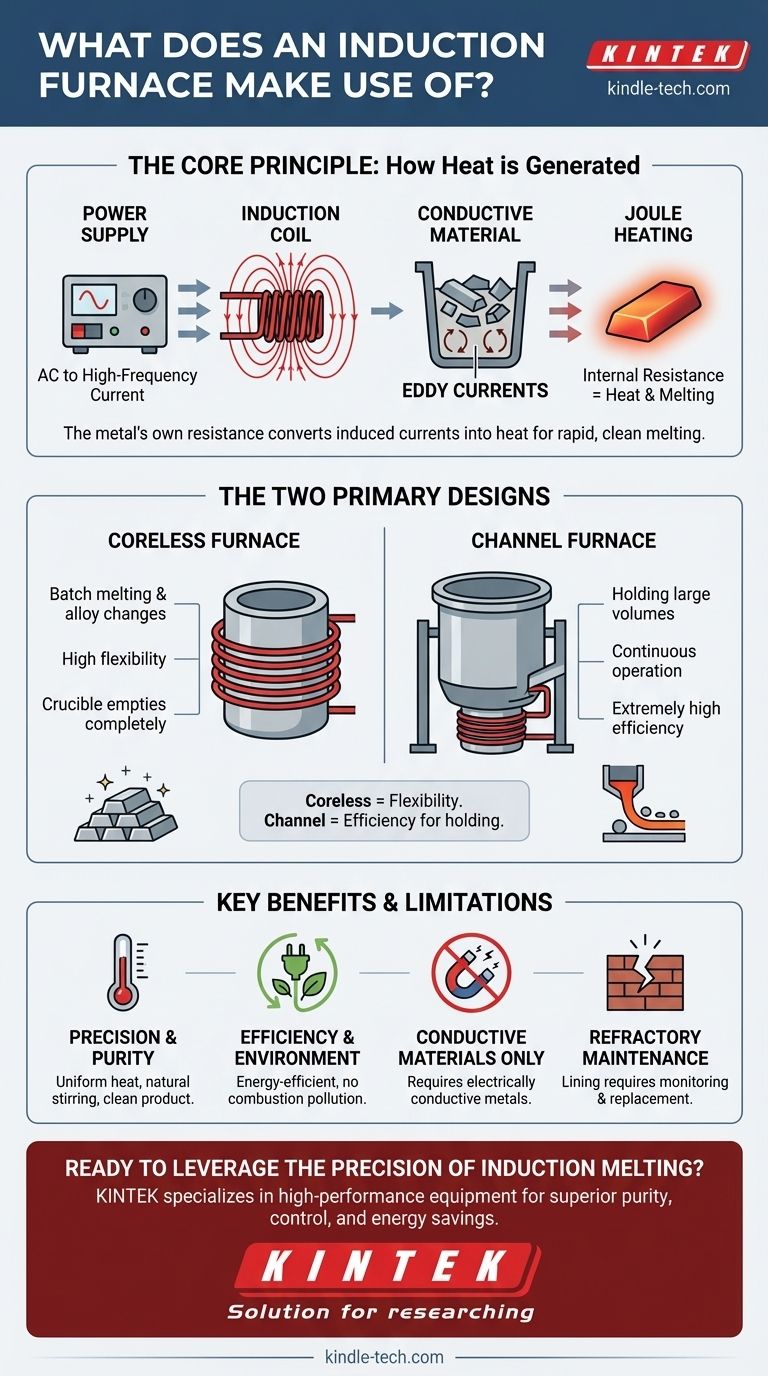
At its core, an induction furnace makes use of electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the material being melted. It accomplishes this with several key components: a high-frequency power supply, a water-cooled induction coil (the inductor), a refractory-lined vessel to contain the metal, and a control system to manage the process. The system works without any external flame or heating element touching the metal.
An induction furnace functions like a specialized transformer where the metal charge itself becomes the secondary coil. By inducing powerful electrical currents directly inside the metal, it achieves rapid, clean, and highly controlled melting through the metal's own internal resistance.
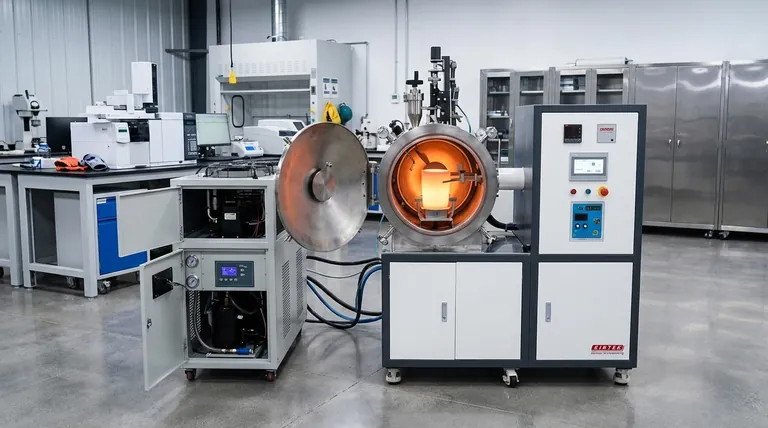

The Core Principle: How Induction Generates Heat
To understand what an induction furnace uses, you must first understand its unique heating method. It is a process of converting electrical energy into thermal energy without direct contact.
From Electricity to a Magnetic Field
The process begins with the power supply, which converts standard line-frequency AC power into a high-frequency current. This current is then fed into the induction coil, which is typically made of copper tubing and wraps around the furnace body. As the high-frequency current flows through this coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly alternating magnetic field in the space within the coil.
The Role of Eddy Currents
When a conductive material, such as scrap metal, is placed inside this alternating magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the metal itself. These circulating currents are known as eddy currents. This is the same principle of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday.
Internal Resistance Creates Heat
The metal has a natural electrical resistance. As the powerful eddy currents flow through the metal, they are opposed by this resistance, which generates immense heat. This phenomenon, known as Joule heating, is what causes the metal to heat up and eventually melt, all without any external flame or heating element.
The Two Primary Designs: Coreless vs. Channel
While the principle is the same, induction furnaces are built in two primary configurations, each suited for different applications.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
This is the most common design. It consists of a crucible-shaped refractory vessel that holds the metal charge. The induction coil is wrapped directly around this crucible.
This design is highly flexible and is ideal for melting a wide variety of metals and alloys in batches. Because the crucible can be completely emptied, it allows for frequent changes in the alloy being produced.
The Channel Induction Furnace
A channel furnace operates more like a true transformer. It consists of a large refractory-lined vessel to hold a reservoir of molten metal. Attached to the bottom of this vessel is an "induction unit" with an iron core and a primary coil.
A small loop or "channel" of molten metal from the main bath passes through this induction unit, acting as the secondary coil of the transformer. Heat is generated only in this channel, which then circulates through the main bath to keep the entire volume molten. These furnaces are extremely efficient for holding large quantities of a single alloy at temperature for long periods, often feeding continuous casting operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Benefits
Choosing induction technology involves recognizing its distinct advantages and inherent limitations.
Advantage: Precision, Purity, and Stirring
Because heat is generated within the metal, the temperature is very uniform and can be controlled with high accuracy. The electromagnetic forces created by the eddy currents also cause a natural stirring action, ensuring the molten bath is homogenous and alloys are mixed thoroughly. The absence of combustion byproducts means the final product is purer.
Advantage: Efficiency and Environment
Induction melting is highly energy-efficient because heat is generated exactly where it's needed, with minimal thermal loss to the surrounding environment. This process produces no combustion-related pollution, significantly improving the working environment and reducing the furnace's environmental footprint.
Limitation: Conductive Materials Only
The fundamental principle of induction heating relies on inducing currents in the material. Therefore, induction furnaces can only be used to heat or melt electrically conductive materials, primarily metals and their alloys.
Limitation: Refractory Maintenance
The refractory lining that contains the molten metal is a critical wear component. It is exposed to extreme temperatures and chemical reactions with the melt. Its condition must be carefully monitored, and it requires periodic replacement, which involves downtime and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct type of induction furnace depends entirely on the operational goal.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and melting various alloys in batches: A coreless induction furnace is the superior choice due to its ability to be fully emptied and cleaned between melts.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of a single alloy at temperature for continuous operation: A channel furnace provides unmatched efficiency for this specific holding application.
- If your primary focus is process control, melt purity, and environmental performance: Both furnace types offer significant advantages over traditional fuel-fired combustion furnaces.
Understanding that an induction furnace uses the metal itself as the heating element is the key to appreciating its efficiency and control.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Coreless Furnace | Channel Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch melting, alloy changes | Holding large volumes of a single alloy |
| Flexibility | High (can be fully emptied) | Low (designed for continuous operation) |
| Efficiency | High for melting | Extremely high for holding |
| Key Limitation | Refractory lining maintenance | Limited to single alloy type |
Ready to leverage the precision and efficiency of induction melting in your lab or foundry? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions tailored to your specific metal melting and processing needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for superior purity, control, and energy savings. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision



















