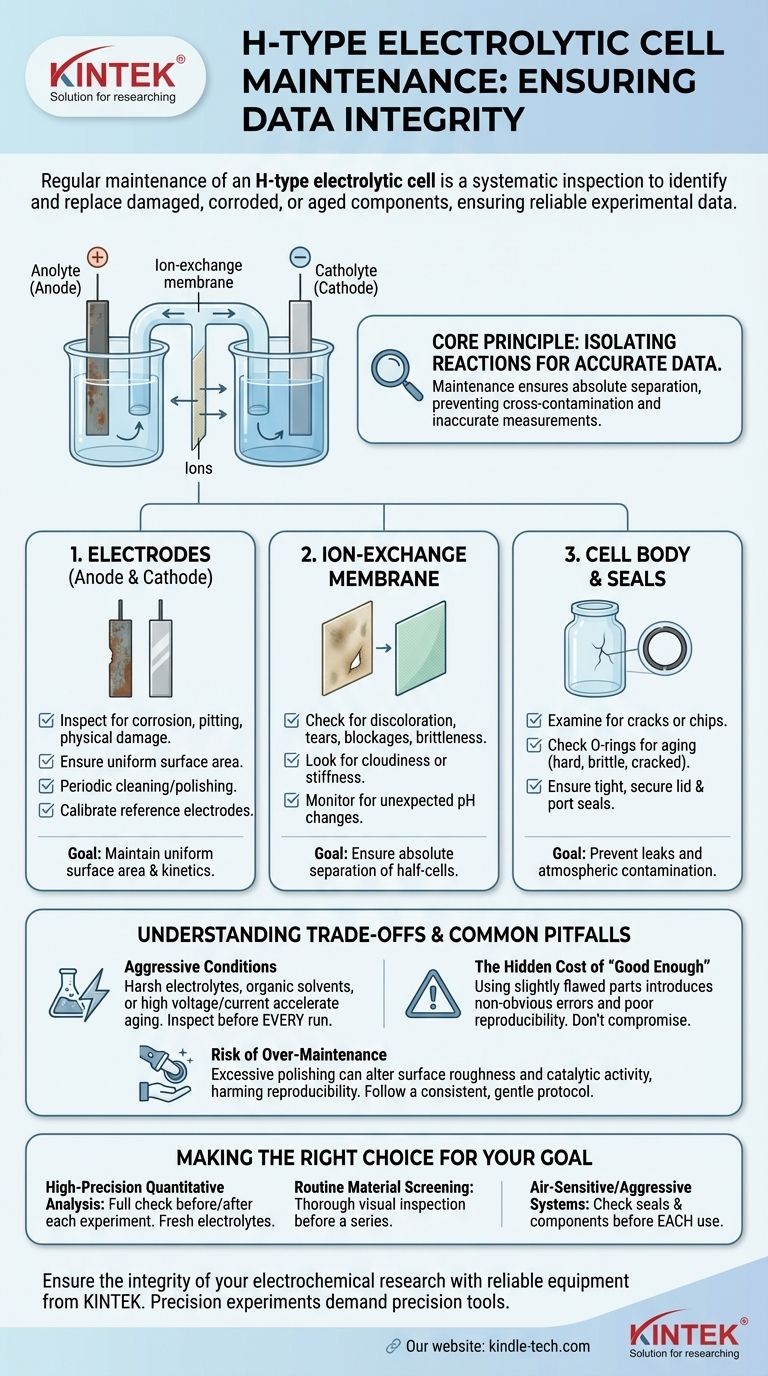
In short, regular maintenance of an H-type electrolytic cell is a systematic inspection of its core components—the electrodes, the ion-exchange membrane, the cell body, and its seals. The goal is to identify and replace any part that is damaged, corroded, or aged to ensure the cell functions correctly and produces reliable experimental data.
The central purpose of maintaining an H-type cell is not just to prevent leaks or failure. It is to protect the integrity of your electrochemical environment, as even minor degradation in a single component can compromise the separation between half-cells and invalidate your results.

The Core Principle: Isolating Reactions for Accurate Data
An H-type cell is designed for one primary reason: to physically separate the reactions occurring at the anode and the cathode. This separation is crucial for preventing the products of one half-reaction from interfering with the other.
Effective maintenance ensures this separation remains absolute. A compromised seal, a cracked cell body, or a faulty membrane breaks this isolation, leading to cross-contamination and rendering your measurements inaccurate and non-reproducible.
A Component-by-Component Maintenance Protocol
A thorough maintenance routine should be treated as a critical part of your experimental procedure. It involves a visual and sometimes functional check of each key part, ideally before and after a series of experiments.
Inspecting the Electrodes (Anode and Cathode)
The electrodes are where the chemical reactions happen, and their surface condition is paramount.
Look for signs of corrosion, pitting, or physical damage. The surface should be uniform. Any change in surface area or morphology will alter the current density and affect reaction kinetics.
Based on usage, electrodes may require periodic cleaning or polishing to remove deposits or oxidation. Calibrating reference electrodes is also a key step to ensure accurate potential measurements.
Evaluating the Ion-Exchange Membrane
The membrane is the heart of the H-type cell, selectively allowing ions to pass while separating the bulk electrolytes (the anolyte and catholyte).
Inspect the membrane for discoloration, tears, blockages, or brittleness due to aging. A compromised membrane is the most common cause of failed experiments, as it allows uncontrolled mixing of the half-cells.
If the membrane appears clouded or stiff, or if you observe unexpected pH changes in your half-cells, it has likely degraded and must be replaced immediately.
Checking the Cell Body and Seals
The physical container must be inert and perfectly sealed.
Examine the glass or PTFE cell body for any cracks or chips, which can compromise safety and lead to leaks.
Check all sealing rings or O-rings for signs of aging, such as becoming hard, brittle, or cracked. A faulty seal can allow electrolyte leakage or, equally problematic, permit atmospheric oxygen or carbon dioxide to enter the cell and cause side reactions.
Finally, ensure the lid and any ports for electrodes or gas lines form a tight, secure seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Proactive maintenance requires balancing component lifespan with experimental rigor. Simply because a part is not broken does not mean it is suitable for a high-precision experiment.
The Impact of Aggressive Conditions
Be aware that harsh electrolytes (strong acids or bases), organic solvents, or operating at high voltages or currents will dramatically accelerate the aging of membranes, electrodes, and seals. In these conditions, inspections should be performed before every single run.
The Hidden Cost of "Good Enough"
It is often tempting to reuse a slightly discolored membrane or a minimally corroded electrode to save time or cost. This is a false economy.
Such "minor" flaws introduce subtle, non-obvious errors into your data, leading to poor reproducibility and hours of wasted effort trying to diagnose a problem that originates with the equipment itself.
The Risk of Over-Maintenance
While cleaning is crucial, aggressive or excessive polishing of electrodes can alter their surface roughness and microscopic area. This can affect the catalytic activity and change your results from one experiment to the next, harming reproducibility. Follow a consistent, gentle cleaning protocol.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance schedule should adapt to your experimental needs. Not all applications require the same level of scrutiny.
- If your primary focus is high-precision quantitative analysis: You must perform a full component check before and after each experiment and use fresh electrolytes for every run.
- If your primary focus is routine material screening or educational demos: A thorough visual inspection for major damage before starting a series of experiments is often sufficient.
- If you are working with air-sensitive systems or aggressive chemicals: You must treat the cell's integrity as paramount, checking seals and component conditions before each use without exception.
Disciplined, consistent maintenance is the foundation of trustworthy and publishable electrochemical research.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Maintenance Action | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Electrodes | Inspect for corrosion/damage; clean/polish | Maintain uniform surface area & kinetics |
| Ion-Exchange Membrane | Check for discoloration, tears, brittleness | Ensure absolute separation of half-cells |
| Cell Body & Seals | Examine for cracks; check O-rings for hardness | Prevent leaks and atmospheric contamination |
Ensure the integrity of your electrochemical research with reliable equipment from KINTEK.
Precision experiments demand precision tools. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including H-type electrolytic cells and their critical components like durable membranes and electrodes. Proper maintenance starts with superior products designed for accuracy and longevity.
Let our experts help you maintain flawless experimental conditions. Contact KINTEK today to find the right solutions for your laboratory's needs and achieve reproducible, publishable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- What experimental conditions need to be controlled when using an H-type electrolytic cell? Ensure Reliable and Repeatable Results
- What preparation steps are needed before starting an experiment with an H-type electrolytic cell? A Guide to Safe and Accurate Results
- What are the standard opening specifications for an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Asymmetrical Ports for Precise Electrochemistry
- How should failures or malfunctions of an H-type electrolytic cell be handled? A Guide to Safe and Effective Troubleshooting
- What should be observed during an experiment with the H-type electrolytic cell? Key Monitoring for Precise Results