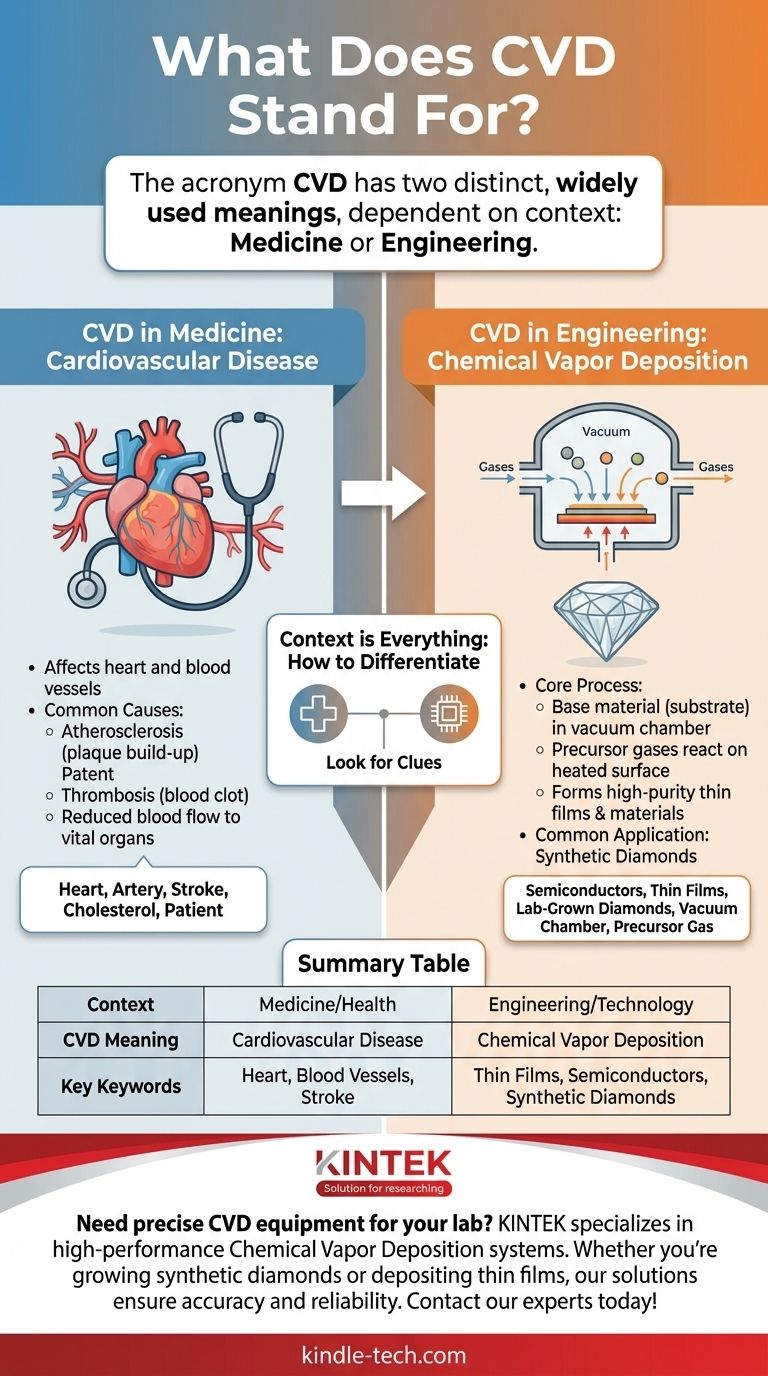
The acronym CVD has two distinct, widely used meanings. Depending on the context, it stands for either Cardiovascular Disease, a major category of medical conditions, or Chemical Vapor Deposition, a sophisticated manufacturing and materials science process. The field of discussion is the only way to determine the correct meaning.
The meaning of "CVD" is entirely dependent on its context. In medicine, it refers to diseases of the heart and blood vessels. In engineering and technology, it describes a process for creating high-purity thin films and materials like synthetic diamonds.
CVD in Medicine: Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is a general term for a class of conditions affecting the heart or blood vessels. It is one of the most common and serious health issues worldwide.
What It Affects
CVD primarily involves the circulatory system, including the heart, arteries, and veins. The core problem is often reduced blood flow to vital organs like the heart, brain, or other parts of the body.
Common Causes
Two primary mechanisms lead to the development of Cardiovascular Disease.
The first is atherosclerosis, where a build-up of fatty deposits (plaque) inside an artery causes it to harden and narrow, restricting blood flow.
The second is thrombosis, which is the formation of a blood clot that can block an artery or vein, abruptly cutting off the blood supply.
CVD in Engineering: Chemical Vapor Deposition
In materials science, physics, and engineering, CVD stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. It is a fundamental process used to produce high-quality, high-performance solid materials and thin films.
The Core Process
Chemical Vapor Deposition involves placing a base material, known as a substrate, inside a vacuum chamber.
One or more volatile gases, called precursors, are then introduced into the chamber. These gases contain the chemical elements that will make up the final material.
The gases react or decompose on the heated substrate's surface, leaving behind a thin, solid film of the desired material.
A Common Application: Synthetic Diamonds
A well-known use of CVD is creating lab-grown diamonds. Carbon-containing gas (like methane) is introduced into a vacuum chamber with a tiny "seed" diamond.
Under specific temperatures and pressures, the gas crystallizes onto the seed, atom by atom, growing a larger, high-purity synthetic diamond over time. This same principle is used to create coatings for semiconductors, optics, and cutting tools.
Context is Everything: How to Differentiate
The meaning of "CVD" is never ambiguous if you look at the surrounding topic. The two fields are so different that they rarely overlap.
Clues for Cardiovascular Disease
If the conversation involves health, medicine, biology, or lifestyle, CVD means Cardiovascular Disease. Keywords to look for include:
- Heart, blood vessels, artery
- Blood pressure, cholesterol
- Stroke, heart attack
- Doctor, hospital, patient
Clues for Chemical Vapor Deposition
If the discussion involves technology, manufacturing, materials, or physics, CVD means Chemical Vapor Deposition. Keywords to look for include:
- Semiconductors, microchips
- Thin films, coatings
- Lab-grown diamonds, synthetic materials
- Substrate, vacuum chamber, precursor gas
How to Interpret "CVD" Correctly
- If your primary focus is health or medicine: CVD refers to Cardiovascular Disease, a condition affecting the heart and blood vessels.
- If your primary focus is technology or materials science: CVD refers to Chemical Vapor Deposition, a process for creating thin films and advanced materials.
Understanding the context is the key to decoding technical acronyms without confusion.
Summary Table:
| Context | CVD Meaning | Key Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Medicine / Health | Cardiovascular Disease | Heart, blood vessels, stroke, cholesterol, patient |
| Engineering / Technology | Chemical Vapor Deposition | Thin films, semiconductors, synthetic diamonds, vacuum chamber |
Need precise CVD equipment for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance Chemical Vapor Deposition systems and lab equipment. Whether you're growing synthetic diamonds or depositing thin films, our solutions ensure accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis



















