In short, CVD stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. It is a highly controlled manufacturing process where reactive gases are used inside a vacuum chamber to create a solid, ultra-thin film on the surface of a base material, known as a substrate. This technique is fundamental to modern technology, enabling the creation of everything from lab-grown diamonds to the intricate layers inside a microchip.
Chemical Vapor Deposition is best understood as a precise, atom-by-atom construction method. By carefully controlling gas chemistry, temperature, and pressure, it allows engineers to "grow" a solid material with specific properties directly onto a foundation, one atomic layer at a time.

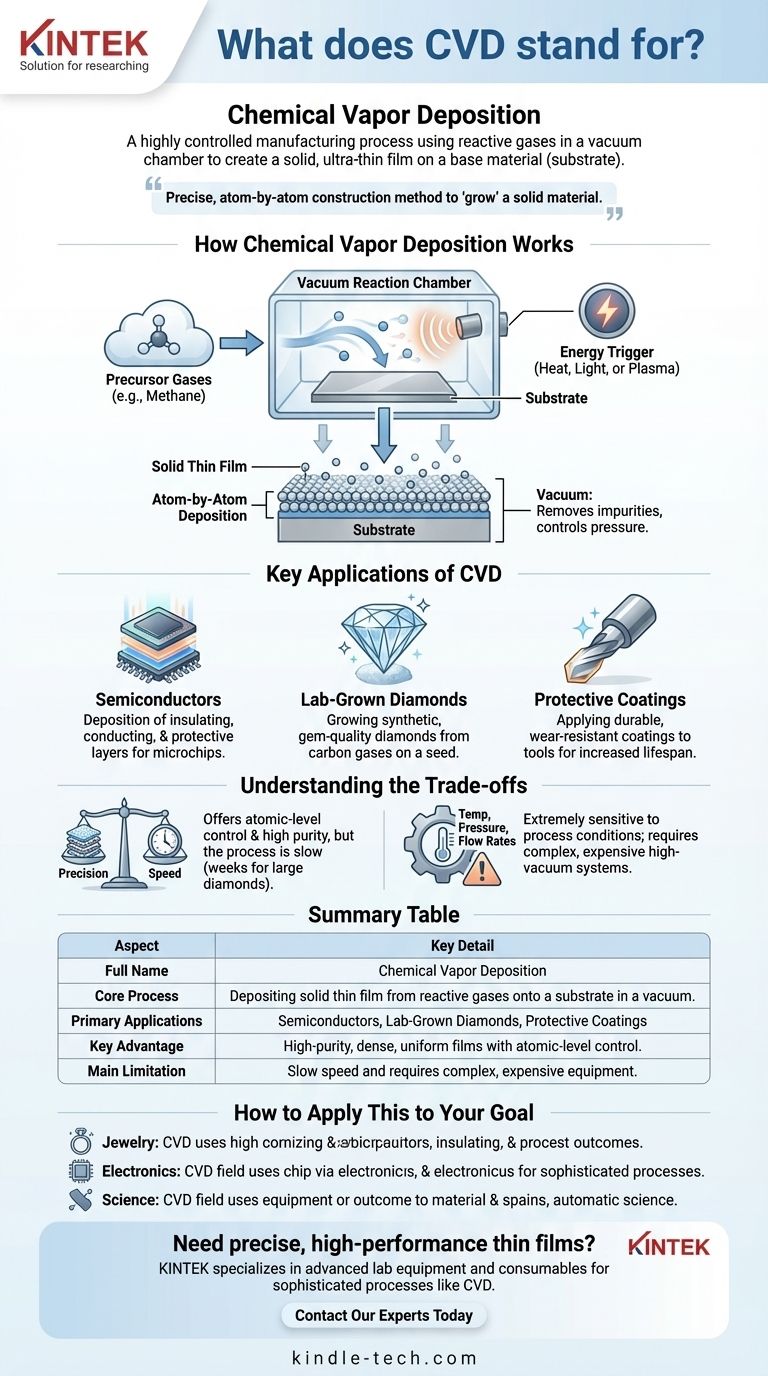
How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works
At its core, CVD is a process of transformation. It converts materials from a gaseous state into a high-purity solid film through a controlled chemical reaction. The entire process takes place inside a specialized piece of equipment.
The Core Principle: From Gas to Solid
The process begins by introducing specific precursor gases into a reaction chamber. These gases contain the chemical elements that will make up the final solid film. For example, to create a diamond, a carbon-containing gas like methane is used.
The Role of the Substrate
Inside the chamber is a substrate, which acts as the foundation for the new material. This could be a tiny, pre-existing diamond "seed," a silicon wafer for electronics, or a piece of stainless steel that needs a protective coating. The deposited film bonds directly to this substrate.
The Reaction Chamber and Vacuum
The entire process occurs within a vacuum chamber. This is critical for two reasons: it removes any air or impurities that could contaminate the film, and it allows for precise control over the pressure, which directly influences the chemical reaction.
The Energy Trigger: Heat, Light, or Plasma
The gases do not form a solid on their own. They need an energy source to trigger the chemical reaction and cause them to decompose and deposit onto the substrate. This energy is typically supplied by high heat (often 700°C to 1300°C), but can also come from plasma or light. Using plasma allows the process to run at much lower temperatures, which is essential for delicate electronic components.
Key Applications of CVD
The ability to create highly pure, dense, and uniform thin films makes CVD an indispensable technology in several leading industries.
Manufacturing Semiconductors
CVD is a cornerstone of the electronics industry. It is used to deposit the various insulating, conducting, and protective layers onto silicon wafers. The microscopic wiring and components that make up a computer processor are built using successive CVD steps.
Creating Lab-Grown Diamonds
One of the most well-known applications is growing synthetic diamonds. A small diamond seed is placed in the chamber, and carbon-rich gases are introduced. Over time, carbon atoms deposit onto the seed, crystallizing and growing it into a larger, gem-quality diamond that is chemically identical to a mined one.
Applying Protective Coatings
CVD is also used to apply extremely hard and durable coatings to tools and components. A thin film of a wear-resistant material can be deposited onto a substrate like steel or titanium to dramatically increase its lifespan and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is a complex process with specific limitations that dictate where it can and cannot be used effectively.
Precision vs. Speed
CVD offers atomic-level control over the film's thickness and purity, resulting in exceptionally high-quality materials. However, this precision comes at the cost of speed. The deposition process is slow, and growing a sizable structure, like a one-carat diamond, can take weeks.
The Critical Role of Parameters
The quality of the final film is extremely sensitive to the process conditions. Temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates must be meticulously controlled. A minor deviation can lead to defects in the crystal structure, impurities, or a film that does not adhere properly to the substrate.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
CVD systems are sophisticated and expensive. They require a high-vacuum chamber, a precise gas delivery system, a stable energy source, and robust control mechanisms. This complexity means the process is best suited for high-value applications where material performance is paramount.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the context of CVD is key to knowing why it matters for a specific application.
- If your primary focus is the jewelry industry: Recognize that "CVD" refers to a specific, high-tech method for creating lab-grown diamonds that are physically and chemically identical to mined diamonds.
- If your primary focus is electronics or semiconductors: View CVD as an essential manufacturing step for building the microscopic, multi-layered structures of every modern microchip.
- If your primary focus is material science or engineering: Understand CVD as a fundamental tool for depositing high-purity, high-performance thin films with precisely controlled properties.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition is a foundational technology for building the advanced materials that define our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Chemical Vapor Deposition |
| Core Process | Depositing a solid thin film from reactive gases onto a substrate in a vacuum chamber. |
| Primary Applications | Semiconductors, Lab-Grown Diamonds, Protective Coatings |
| Key Advantage | Creates high-purity, dense, and uniform thin films with atomic-level control. |
| Main Limitation | Slow process speed and requires complex, expensive equipment. |
Need precise, high-performance thin films for your lab or production process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for sophisticated processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition. Whether you are developing new semiconductor components, creating lab-grown materials, or applying durable coatings, our expertise can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can meet your specific laboratory needs and enhance your research and development capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the two techniques used for preparing nano thin films? A Guide to PVD and CVD Methods
- What is sputtering method of thin film deposition? A Guide to Precision Coating
- What is the temperature of vapor deposition? Unlock the Key Process Parameter for Your Application
- What is the vacuum deposition of film? A Guide to Ultra-Thin, High-Purity Coatings
- Why is high-precision precursor heating and temperature-controlled piping necessary in MOCVD? Ensure Film Integrity
- What is the significance of chemical Vapour deposition? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Thin Films
- How long does a sputter target last? Master the kW-h Metric for Maximum Uptime and Yield
- What are the applications of CVD method? From Microchips to Lab-Grown Diamonds



















